Embed presentation
Download to read offline

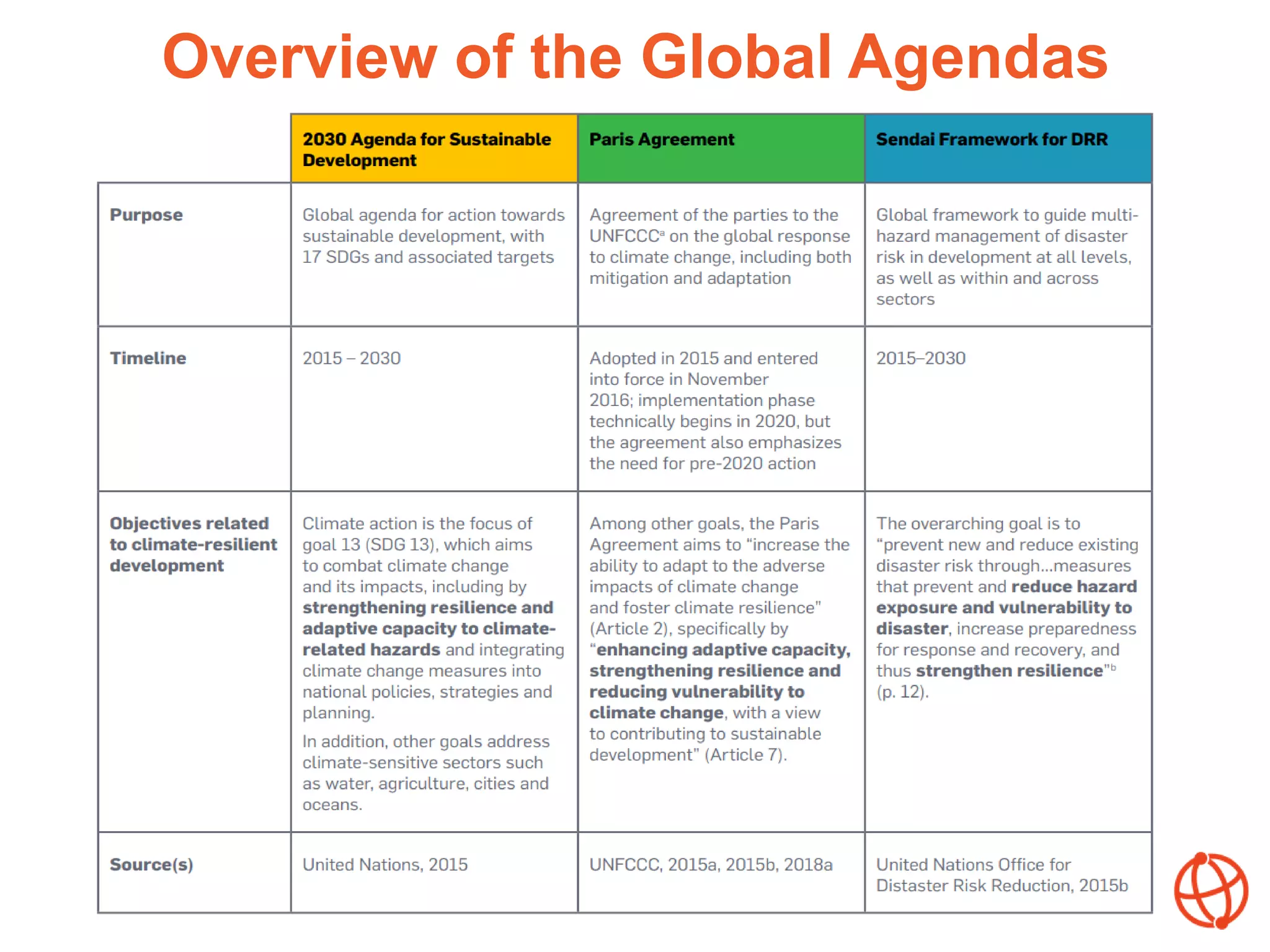
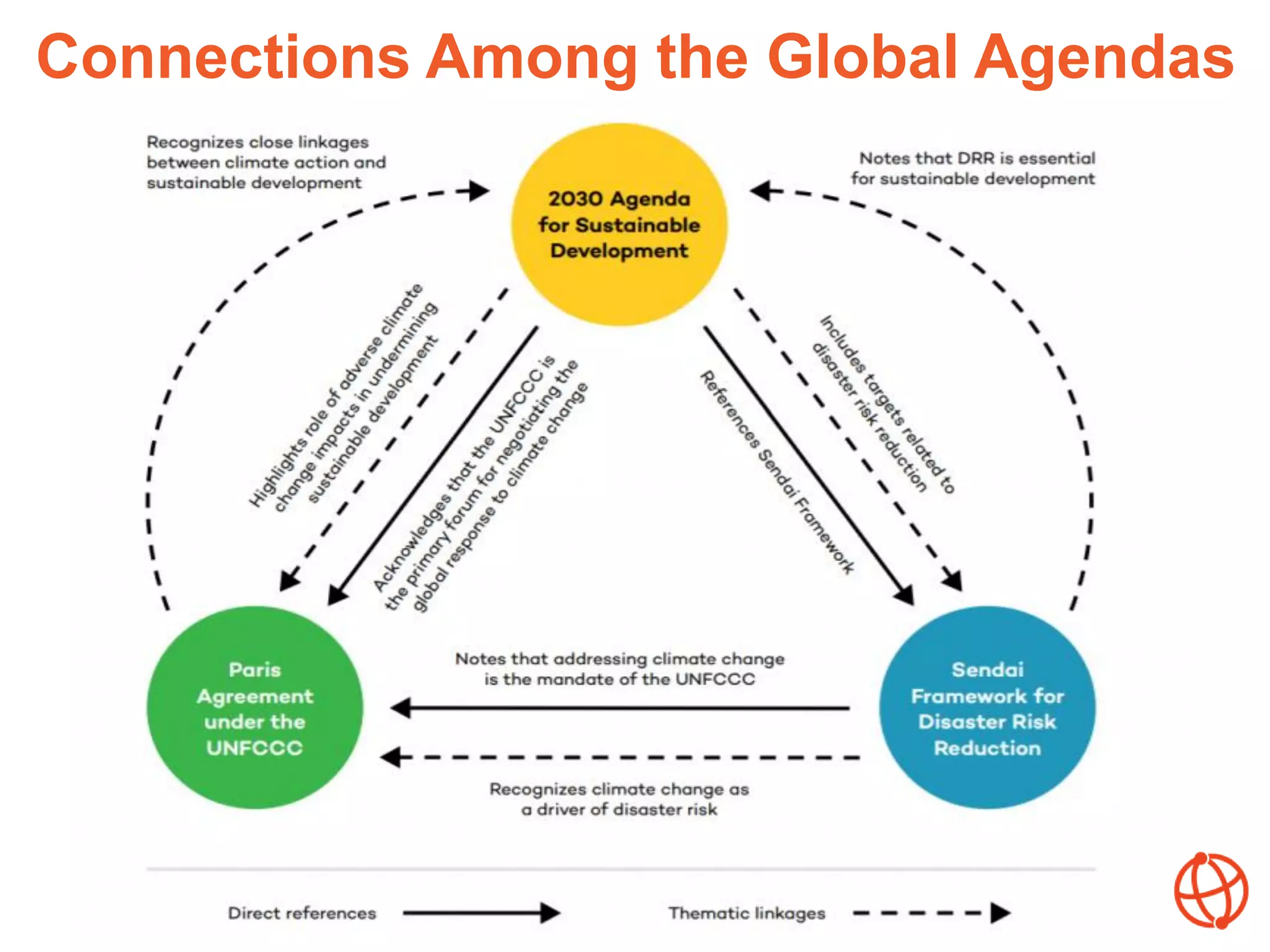


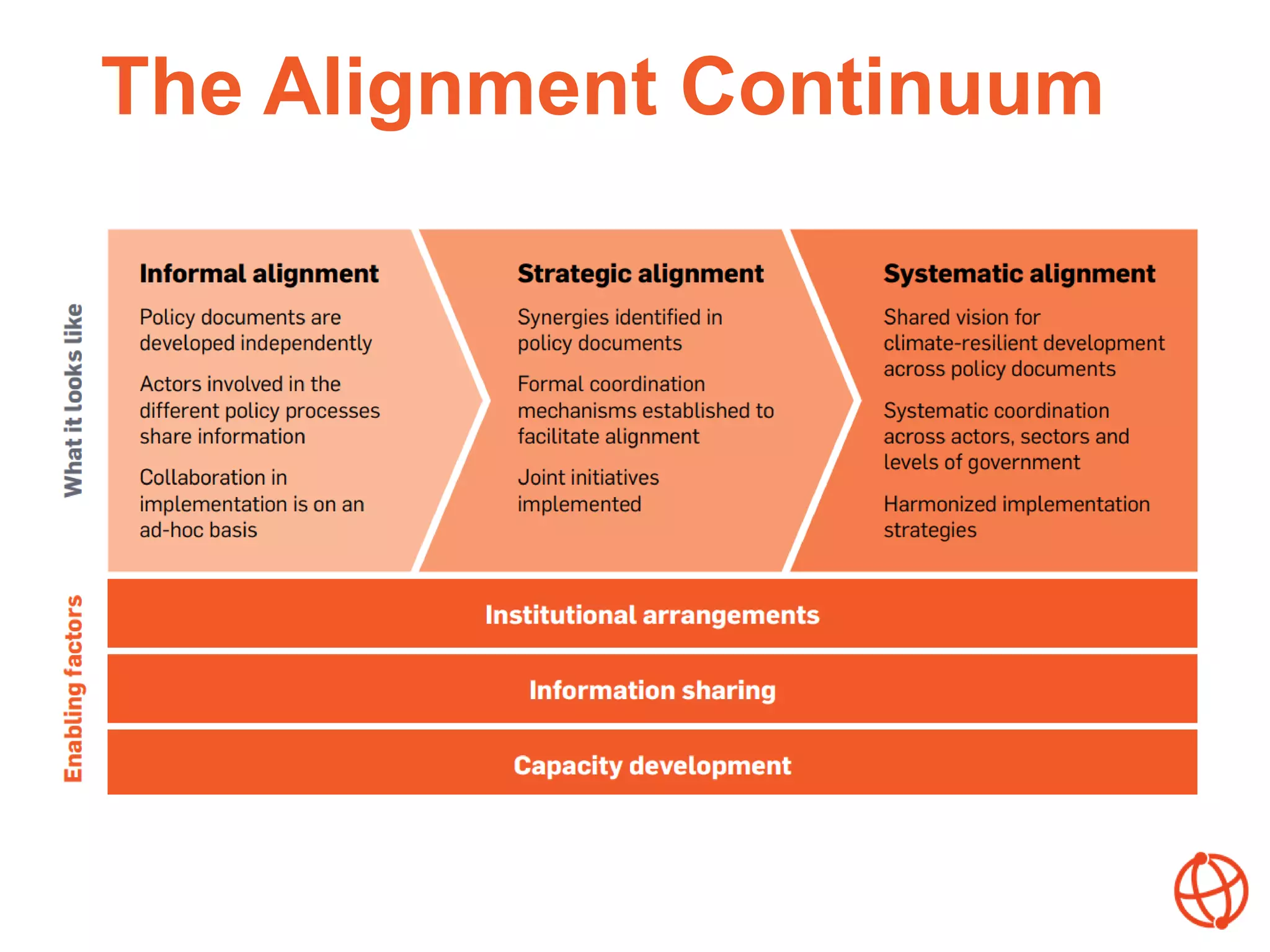



The document discusses the importance of aligning various policy processes related to climate-resilient development, emphasizing the synergies among global agendas such as the SDGs, Paris Agreement, and Sendai Framework. It highlights that alignment can enhance coherence, efficiency, and effectiveness in achieving climate resilience and outlines the factors influencing alignment at the country level. Key messages encourage collaborative efforts in aligning policies to foster improved outcomes in climate adaptation and disaster risk reduction.









