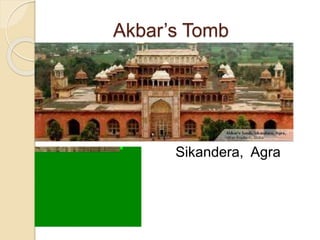
Akbar the Great was the third Mughal emperor who ruled from 1556 to 1605 CE. He consolidated the Mughal Empire and expanded its boundaries. Some key points:
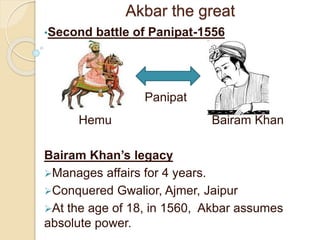
1) He defeated Hemu at the Second Battle of Panipat in 1556 and assumed direct control of the empire in 1560 at age 18 after Bairam Khan's regency.
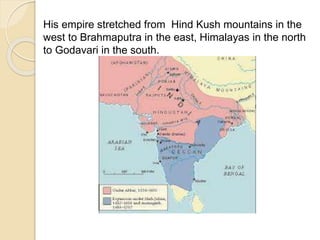
2) His conquests expanded the empire to include Malwa, Gondwana, Gujarat, Bengal, Kashmir, and parts of the Deccan.
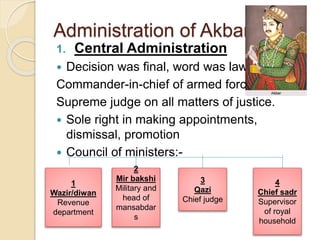
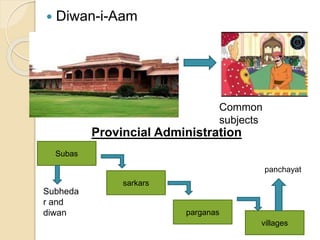
3) He established a centralized administration with the mansabdari military ranking system and Todar Mal's land revenue system.
4)