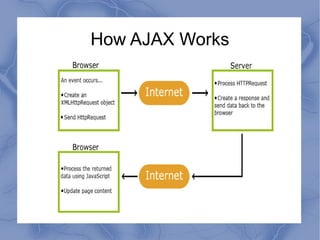
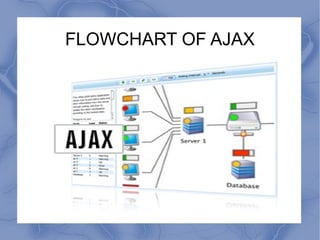
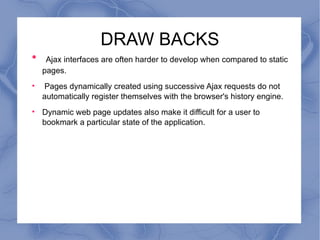
AJAX allows parts of a web page to be updated asynchronously by exchanging small amounts of data in the background without reloading the entire page. It uses a combination of XMLHttpRequest objects, JavaScript, DOM, and CSS. When an AJAX request is made, JavaScript code calls an XMLHttpRequest object to request data from the server in the background. The returned data is then used to update specific elements on the web page without reloading. While AJAX improves interactivity, it also has drawbacks like pages being harder to develop and not registering with the browser history.



![HTML: HTML defines the structure and layout of a Web document by using a variety of tags and attributes. The structure of an HTML <html><head><body></body></HTML>. XHTML: Extensible Hypertext Markup Language and which is a application of XML CSS : "Cascading Style Sheet" are used to format the layout of Web pages. They can be used to define text styles, table sizes, and other aspects of Web pages that previously could only be defined in a page's HTML. JAVASCRIPT: JavaScript is an object-oriented[4] scripting language used to enable programmatic access to objects within both the client application and other applications and it is mainly used for client-side JavaScript](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaxppt-100402064523-phpapp02/85/Ajaxppt-4-320.jpg)