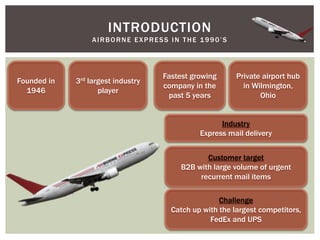
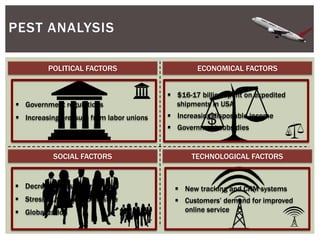
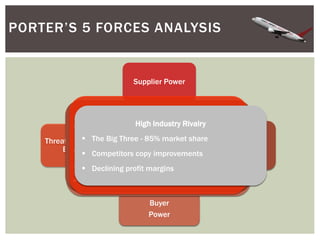
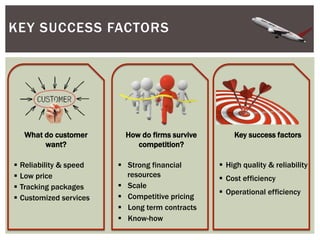
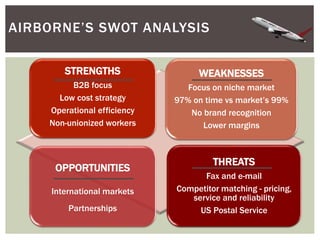
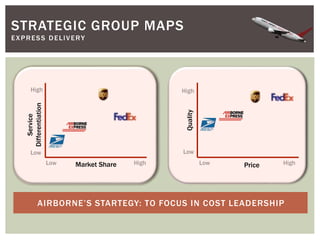
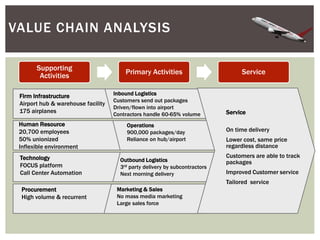
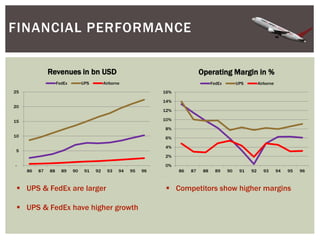
This document provides an analysis of Airborne Express and the express mail delivery industry in the 1990s. It summarizes Airborne's business model, competitors, and the key factors influencing the industry at the time. Through various frameworks like PEST, Porter's Five Forces, and SWOT, it analyzes the competitive environment, Airborne's position and strategies, and the strategic challenges it faced in catching up to larger competitors like FedEx and UPS. The document concludes with a recommendation for Airborne to merge or get acquired by a bigger competitor.