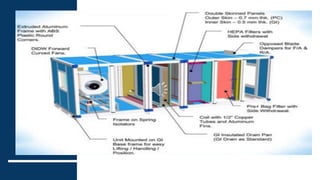
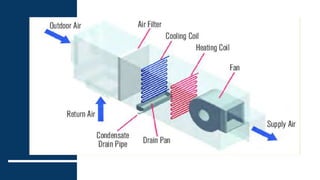
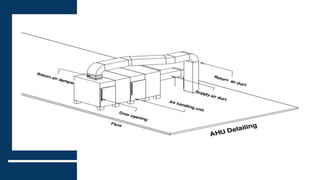
1) Air handling units (AHUs) are devices used to regulate and circulate air as part of HVAC systems. They contain components like fans, filters, coils, and dampers.
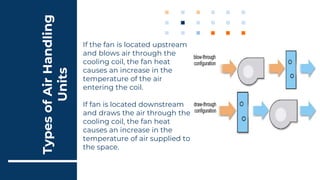
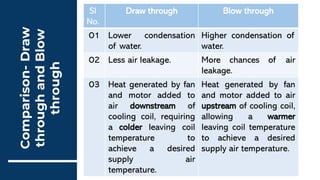
2) AHUs can be classified based on fan location as draw-through or blow-through units. Draw-through units have fans after coils while blow-through units have fans before coils.
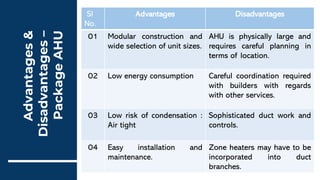
3) Other classifications include vertical, horizontal, ceiling-suspended, and packaged AHUs. Packaged AHUs have components in a single casing and are commonly used in smaller buildings.