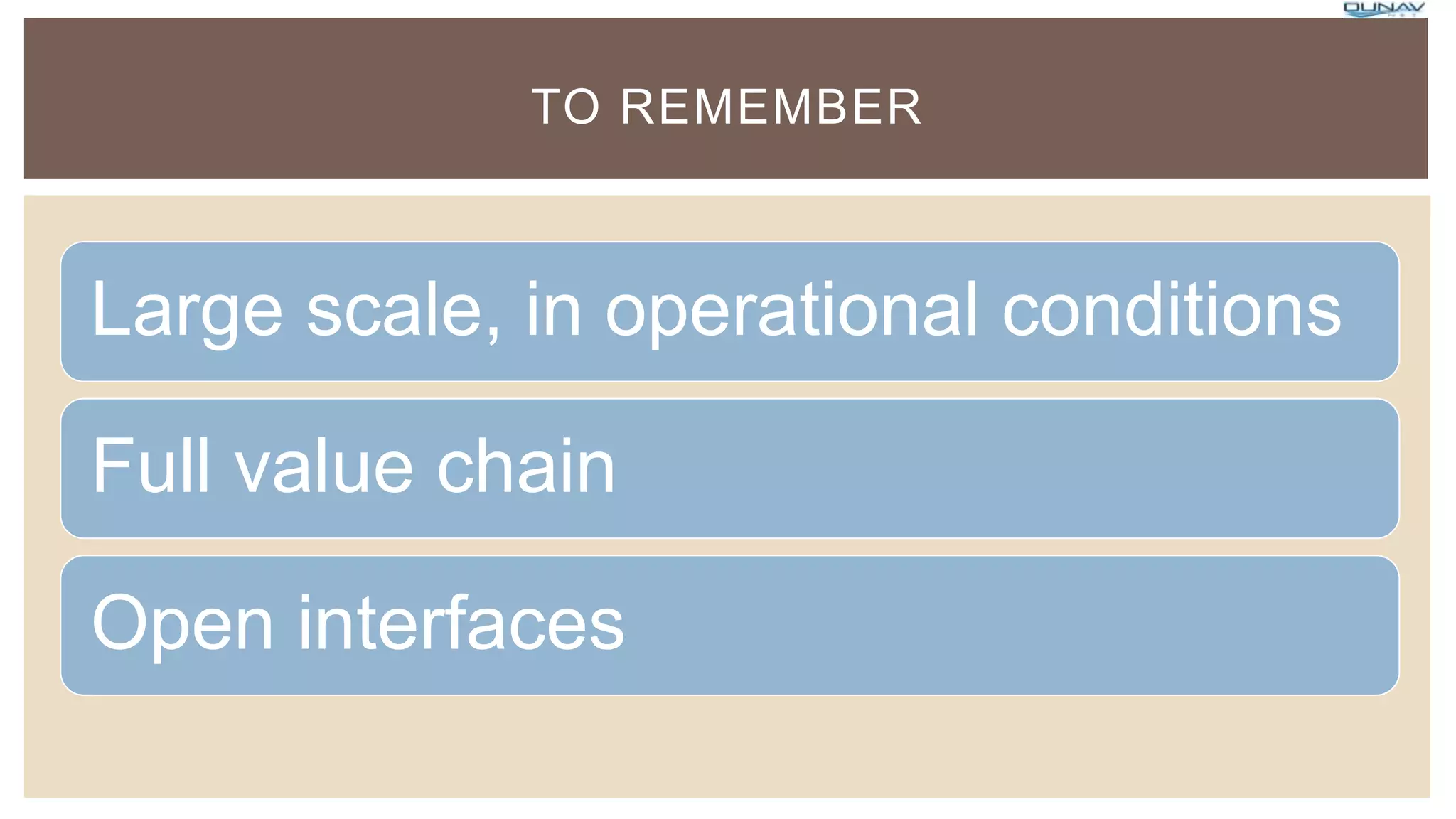
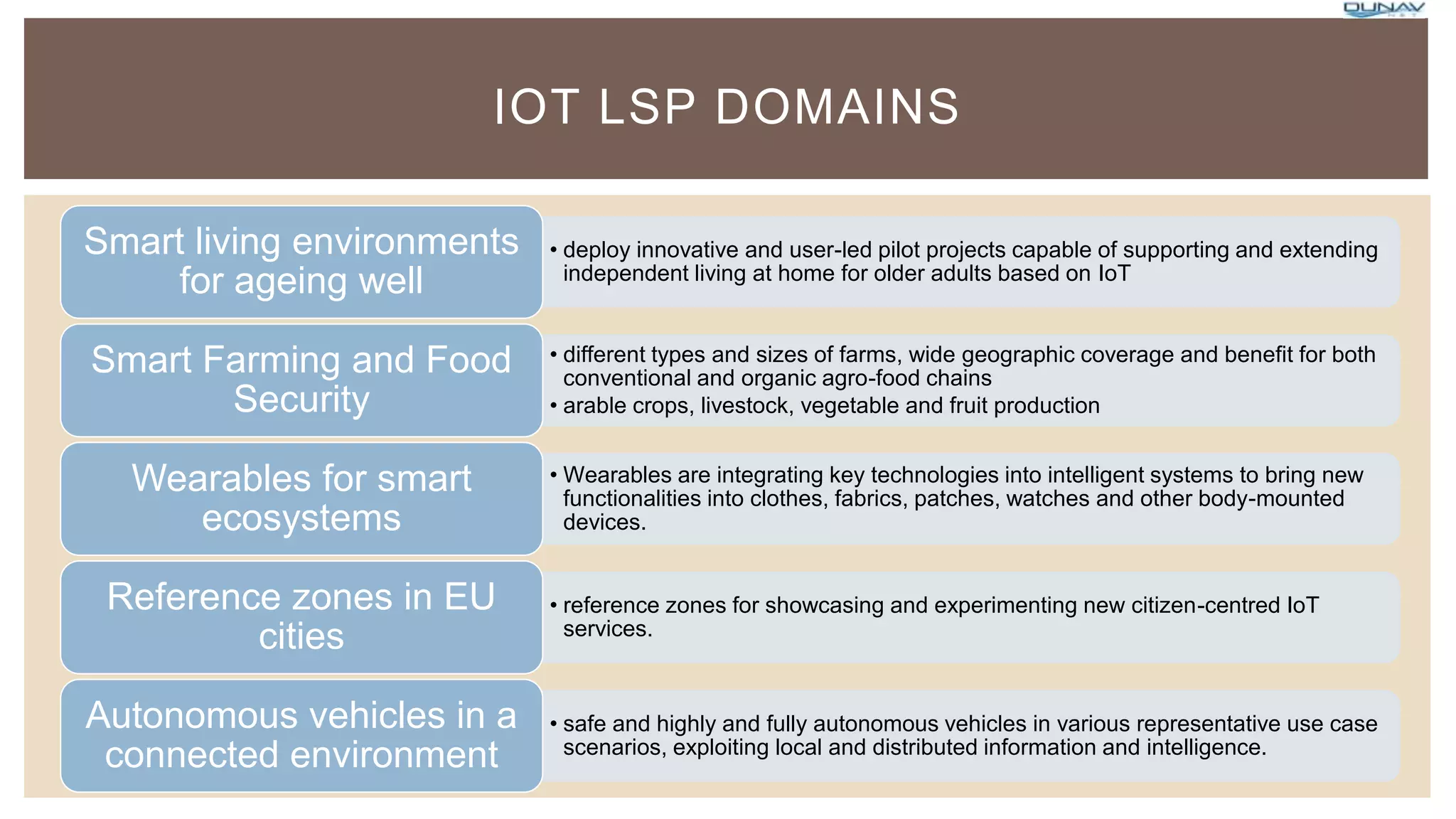
The document describes an upcoming large scale pilot program for Internet of Things projects from the European Union with a budget of 100 million euros. The pilots will involve stakeholders across industries and societies to test IoT approaches for specific challenges. They must be large in scale, test under real conditions, and demonstrate scalability. The objectives are to foster innovation, deployment of IoT solutions in Europe, and create value across the IoT sector with a focus on European SMEs. Several potential pilot domains are described including smart farming, wearables, smart cities, and autonomous vehicles.