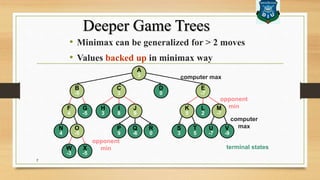
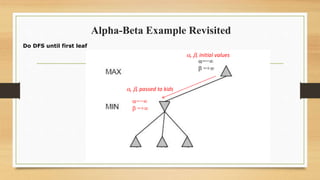
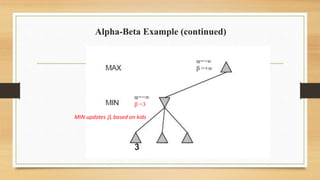
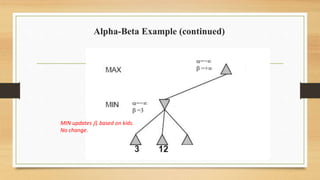
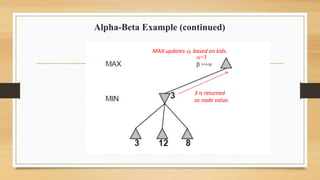
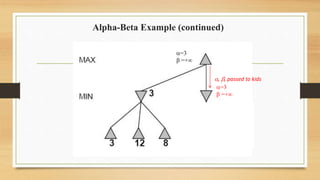
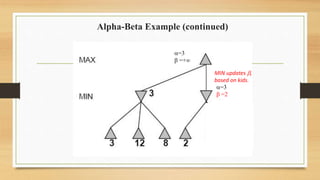
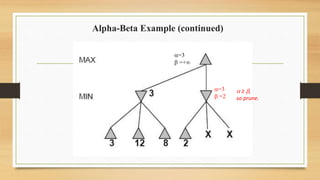
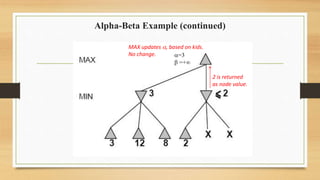
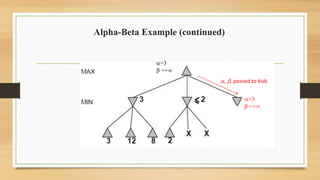
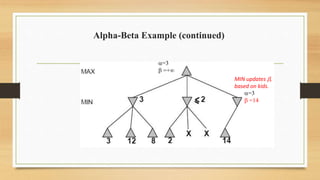
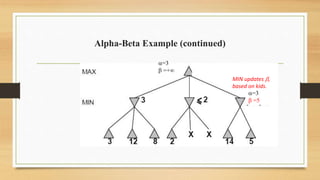
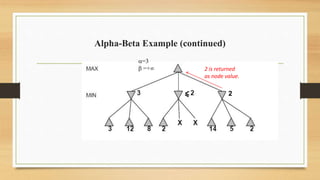
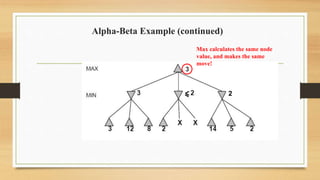
The document discusses minimax decision-making in game theory, focusing on its properties, requirements, and algorithmic implementation. It also covers alpha-beta pruning, which enhances the efficiency of minimax by eliminating unnecessary subtree evaluations, thus preserving optimality. An example is provided to illustrate the application of alpha-beta pruning in decision-making.