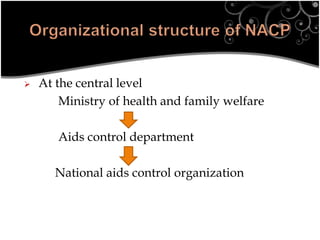
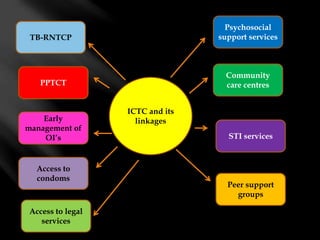
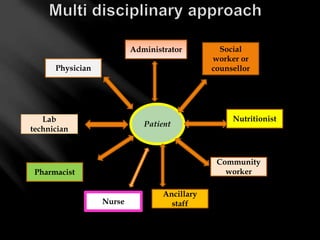
This document provides an overview of HIV/AIDS and the National AIDS Control Programme (NACP) in India. It discusses the magnitude of the HIV/AIDS problem globally and in India, the goals and activities of NACP Phase III, and the roles and responsibilities of community health nurses in supporting the program. Key points include statistics on HIV prevalence, the transmission route in India, objectives of reducing incidence rates, activities under NACP III including prevention, care, and treatment, and approaches for nurses to provide multidisciplinary care and support to people living with HIV/AIDS.