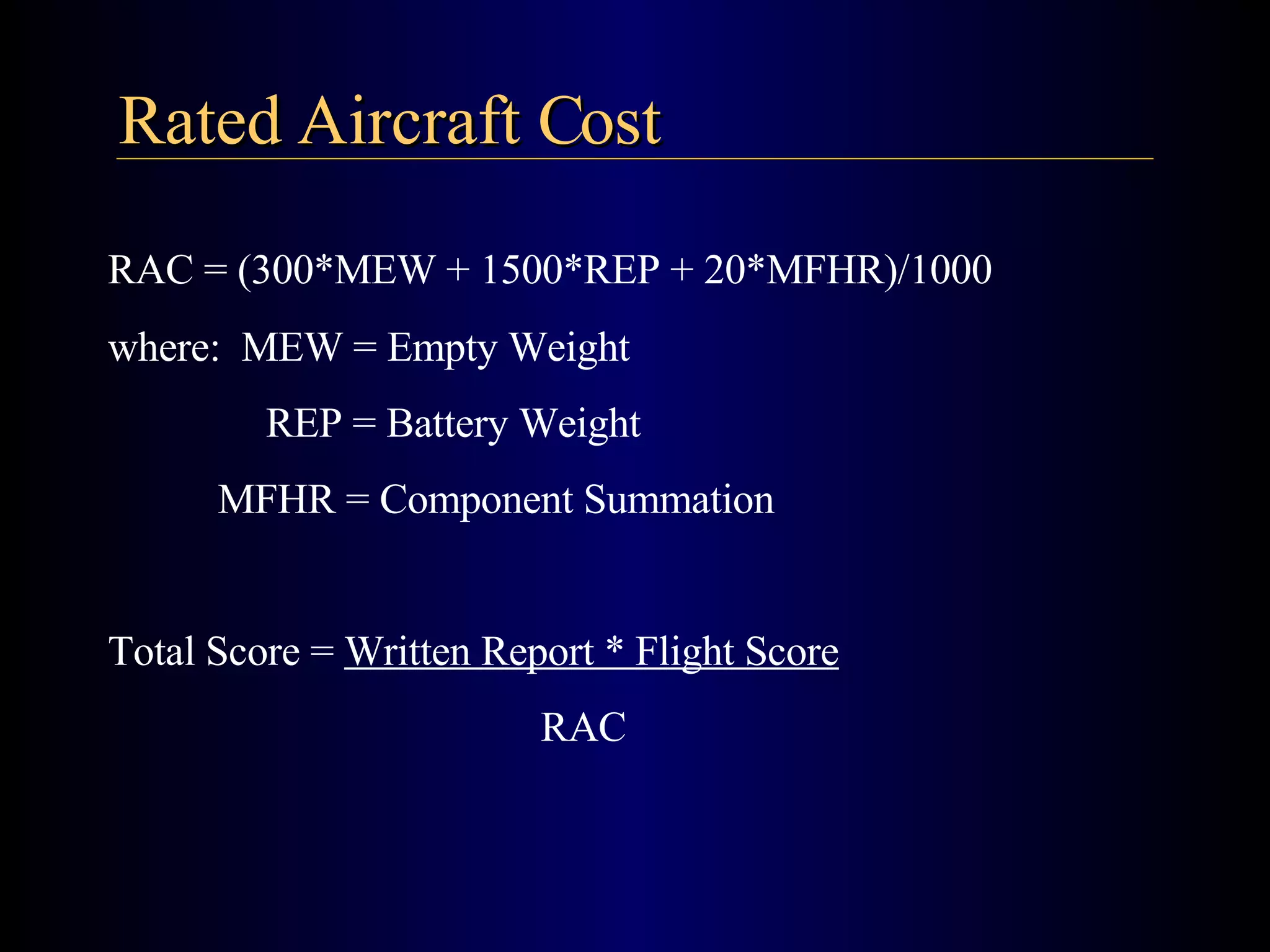
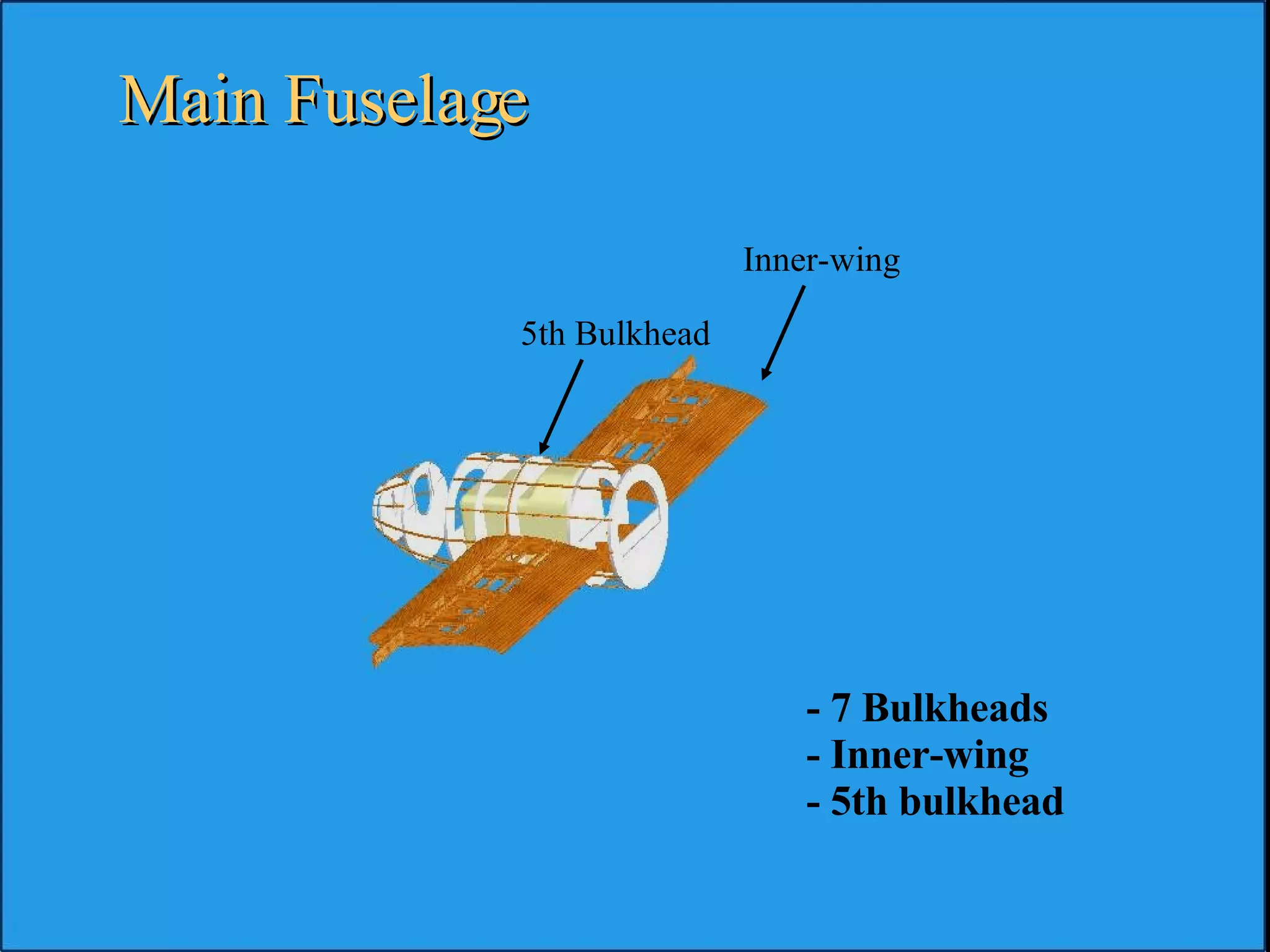
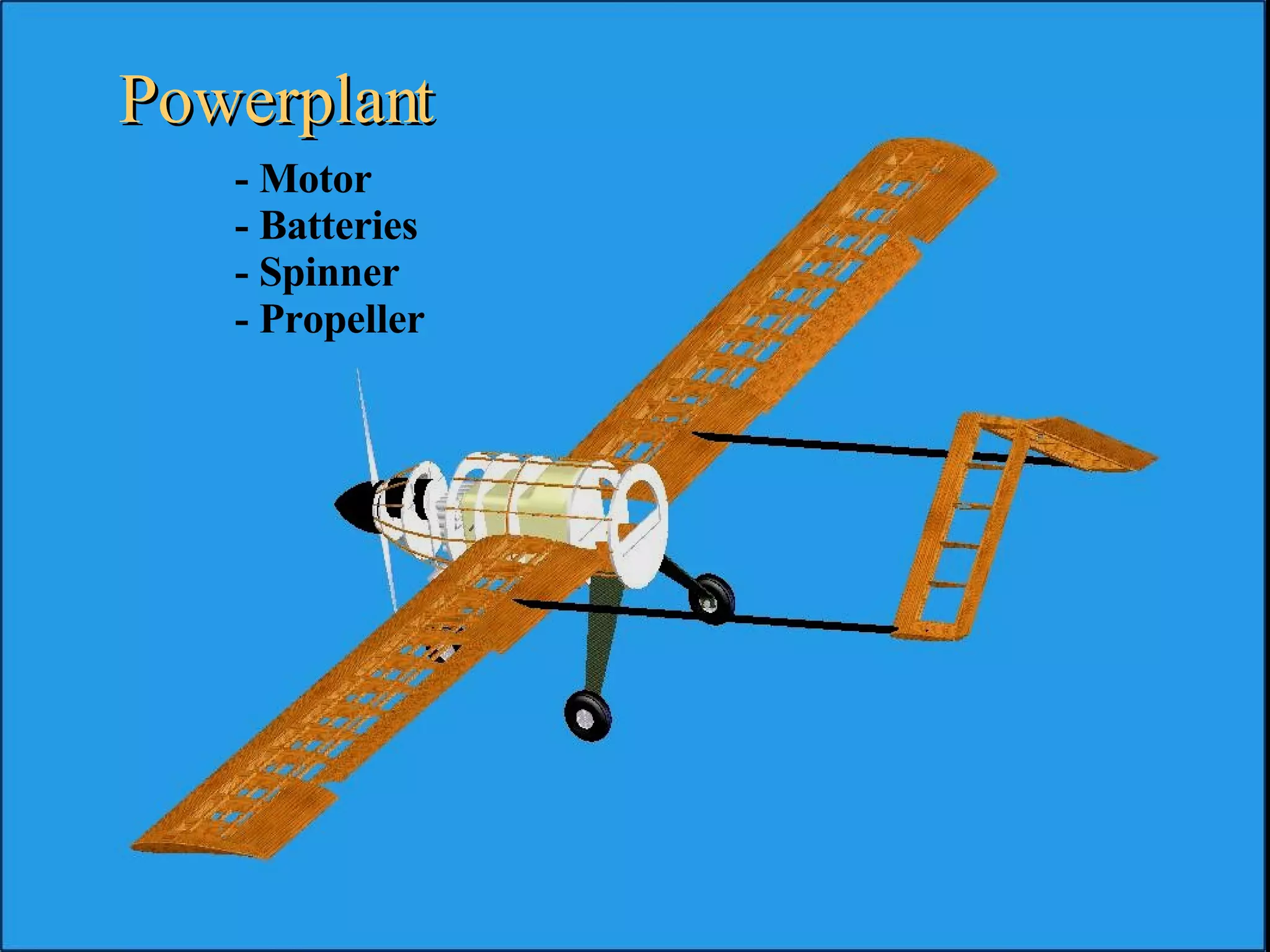
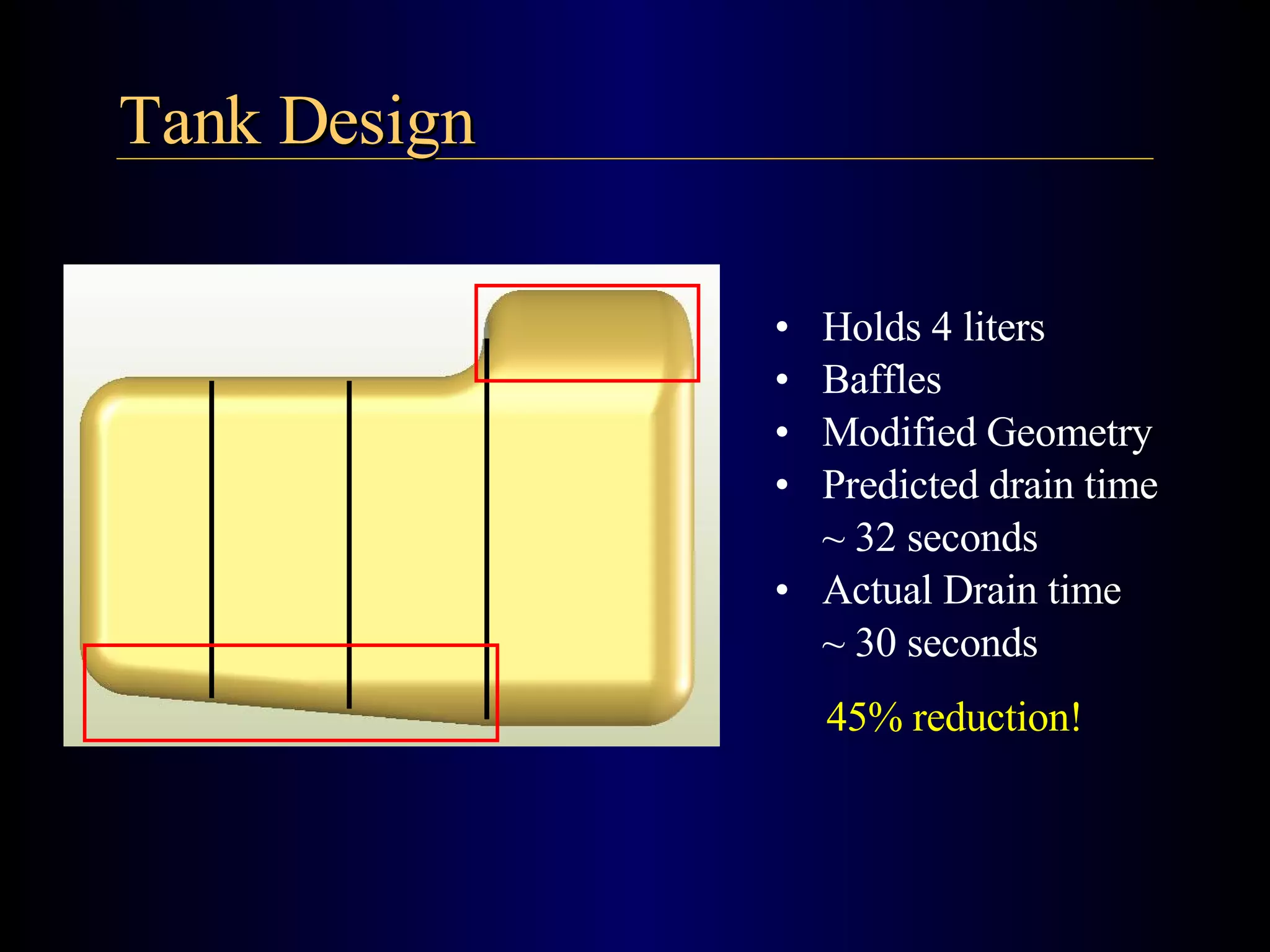
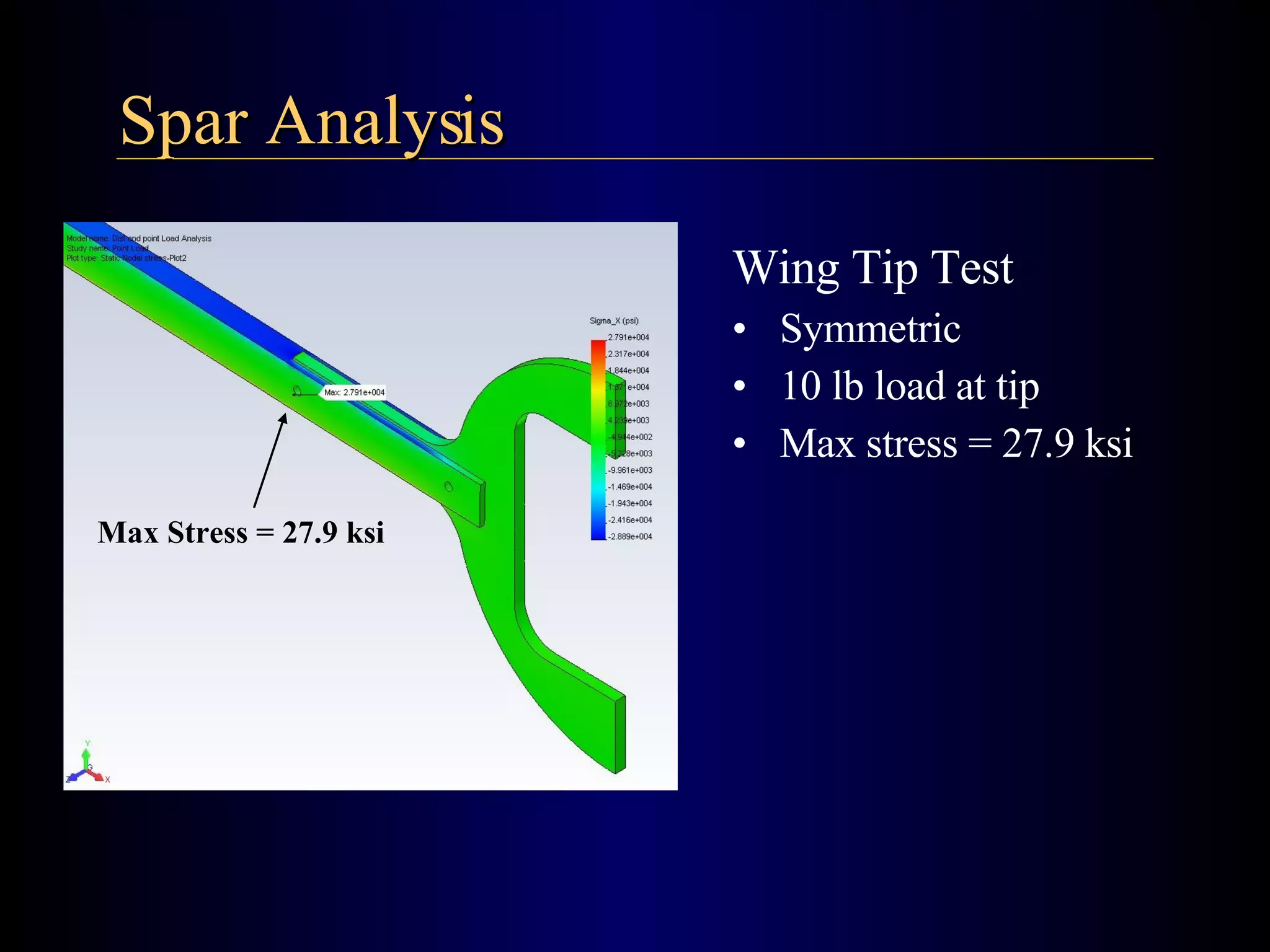
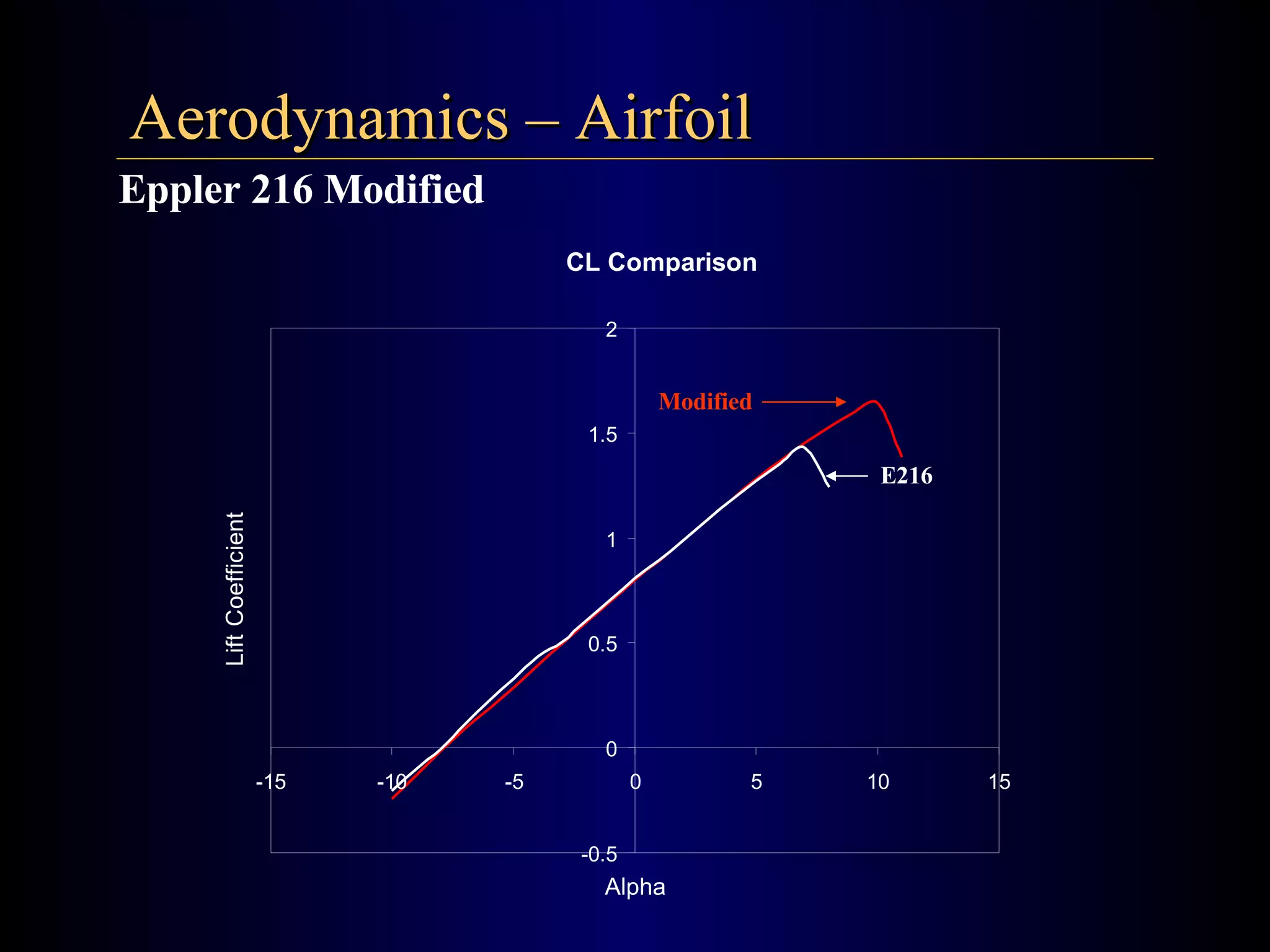
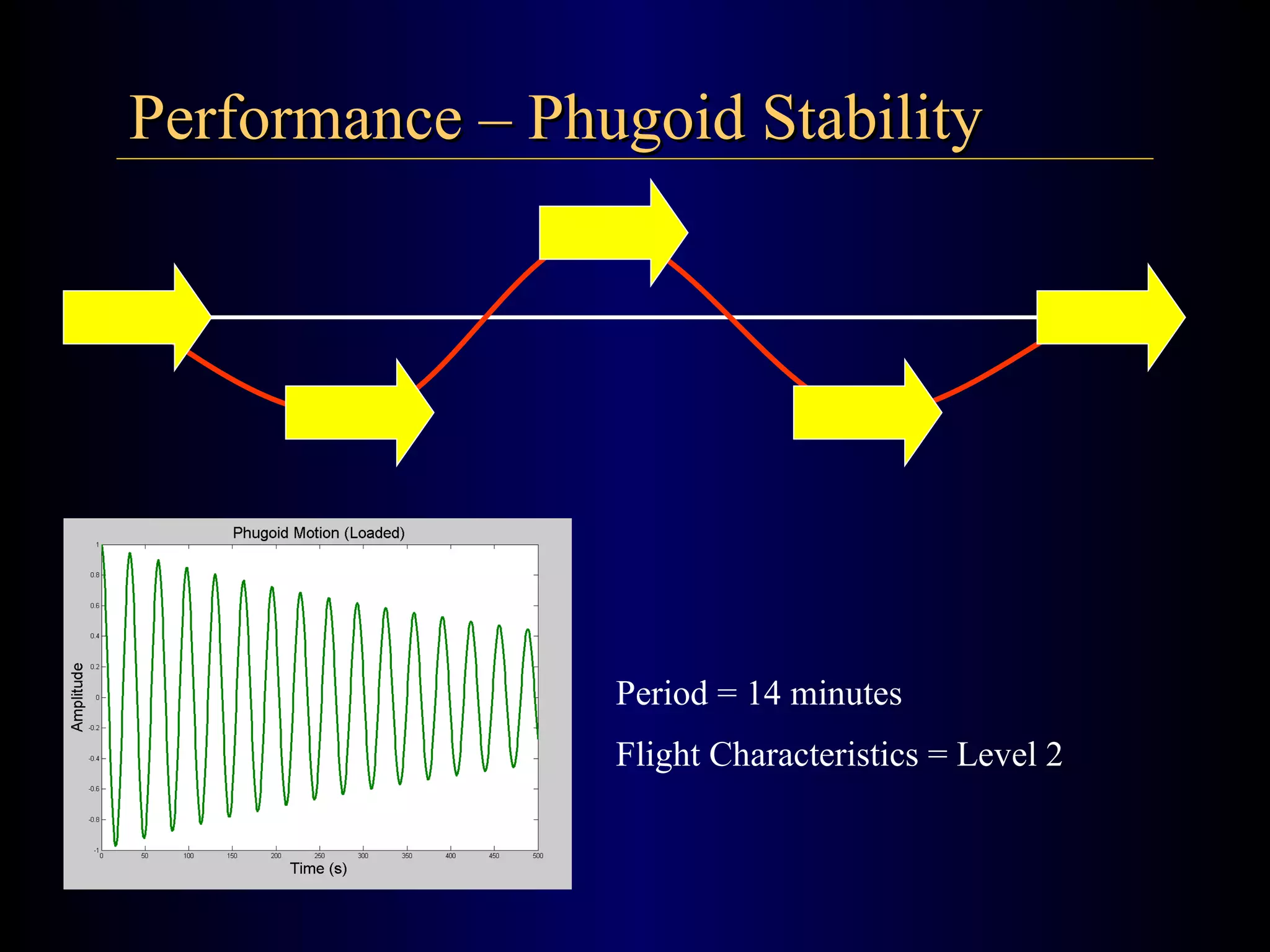
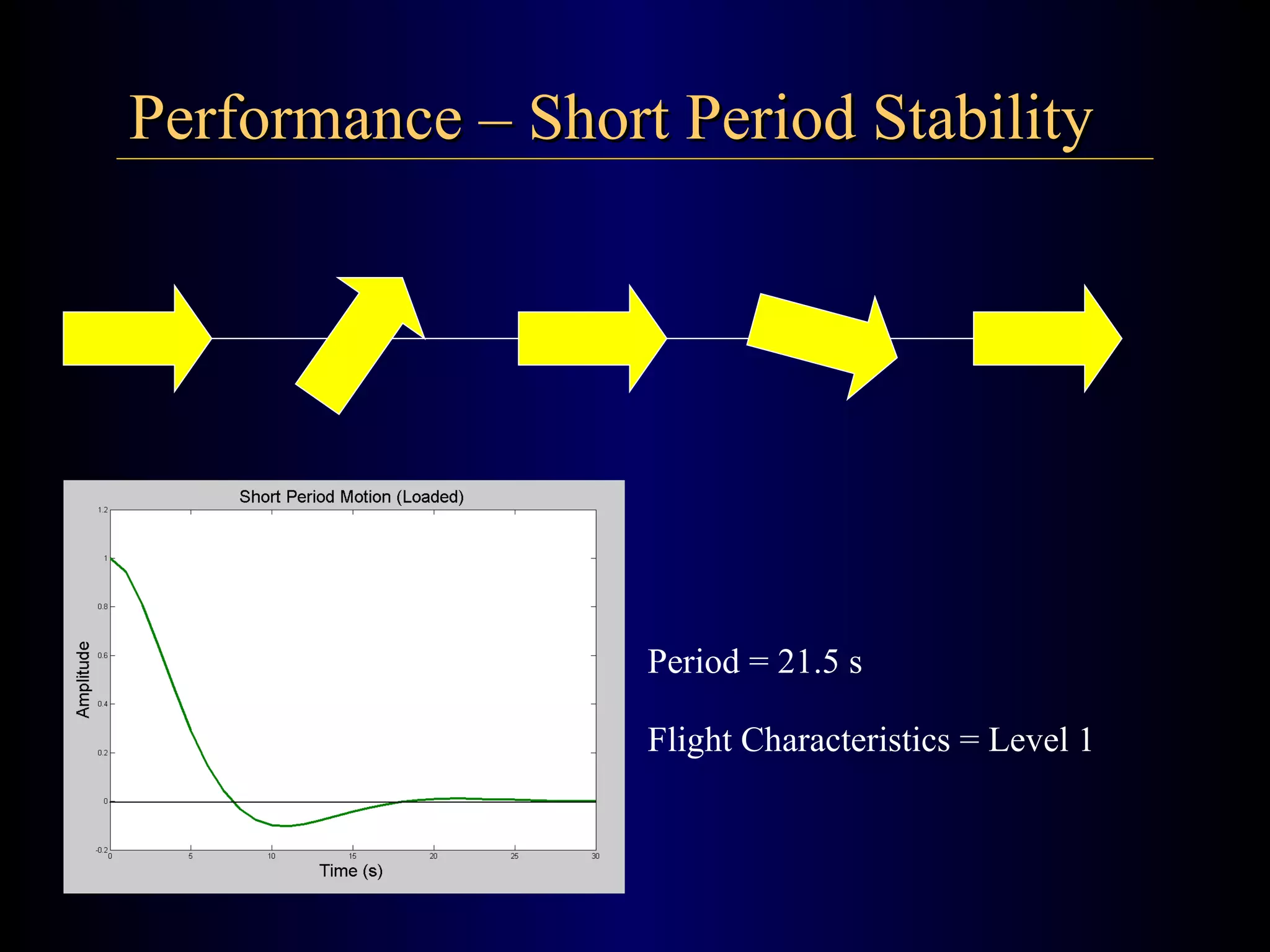
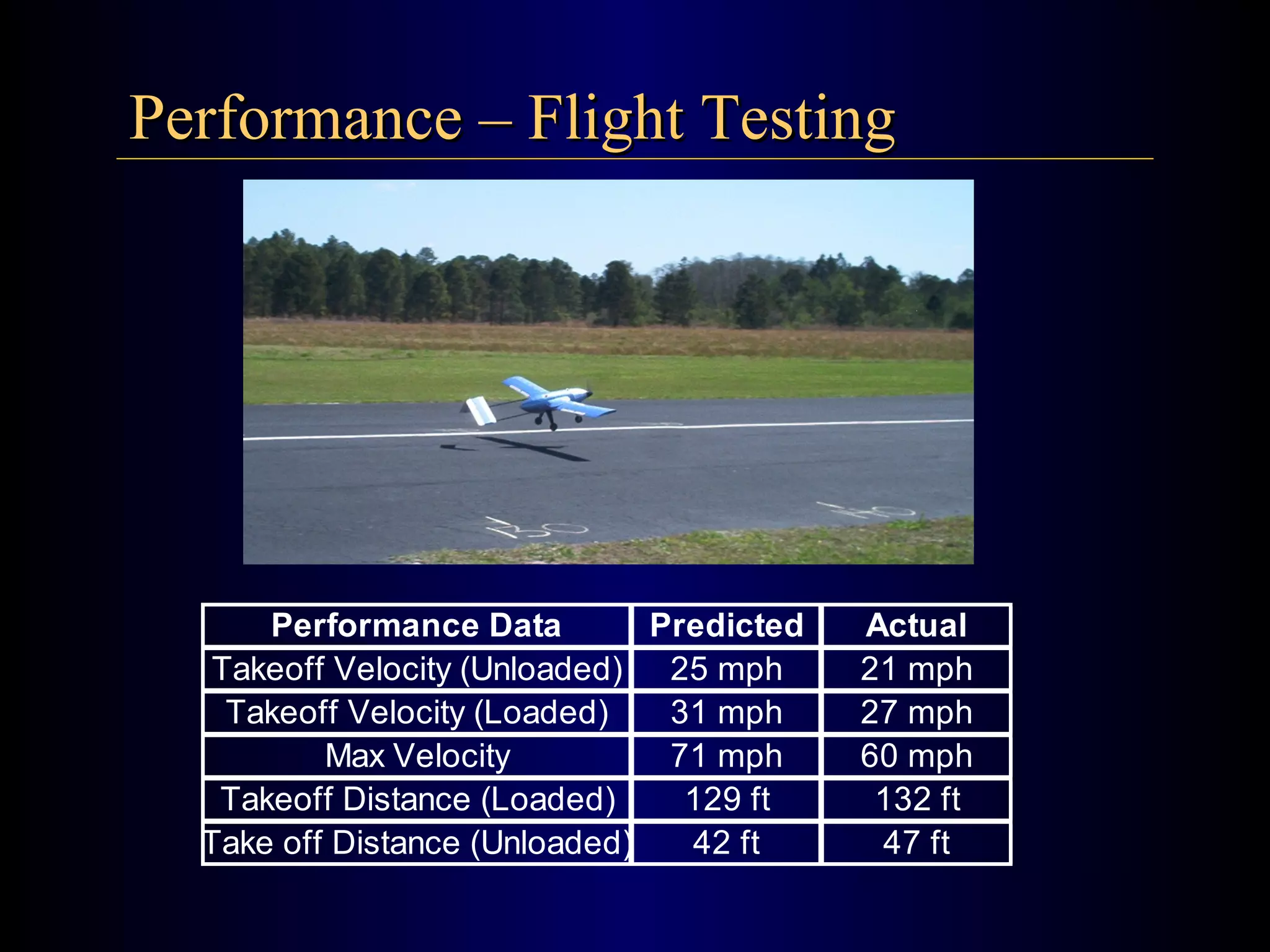
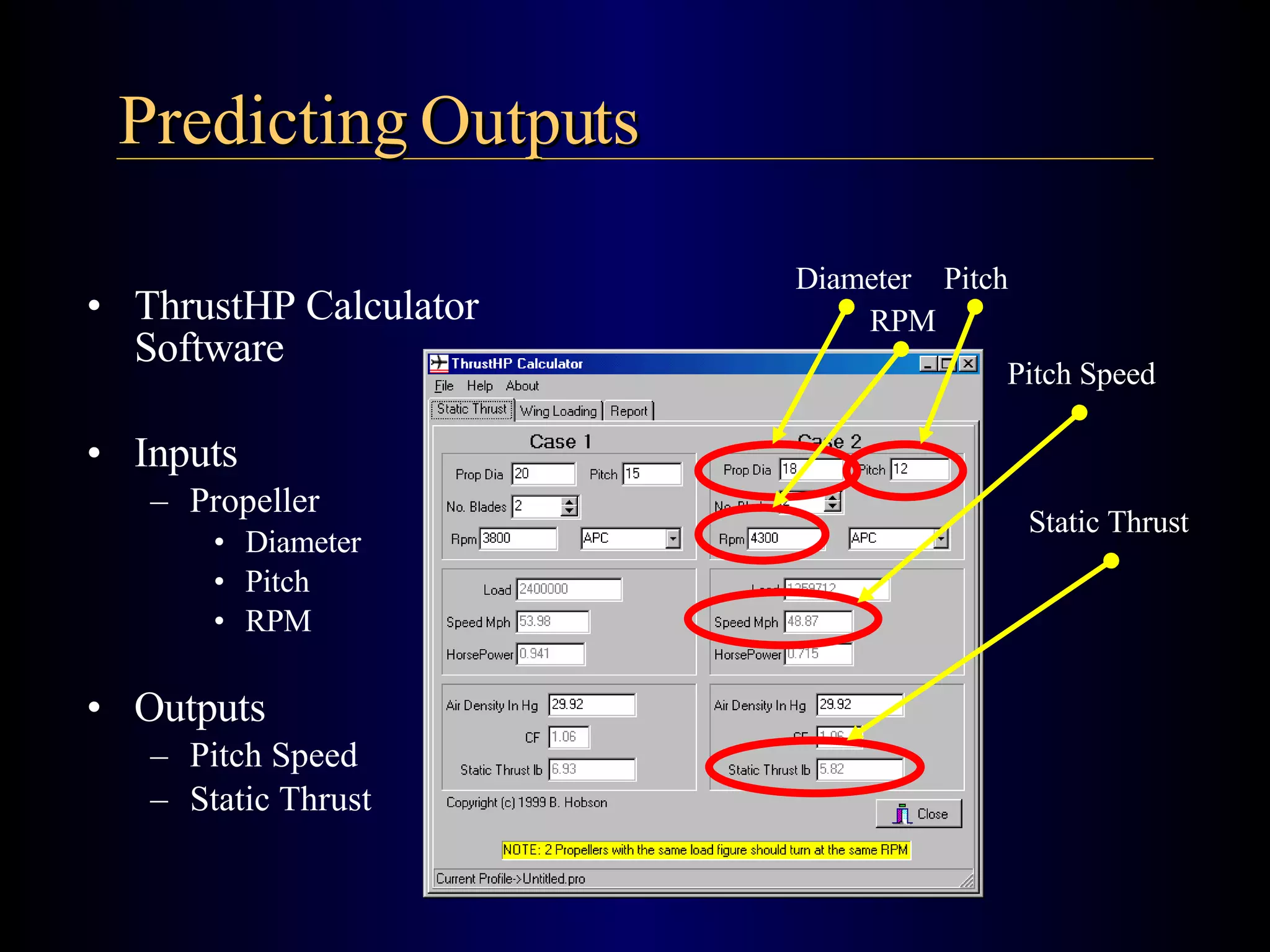
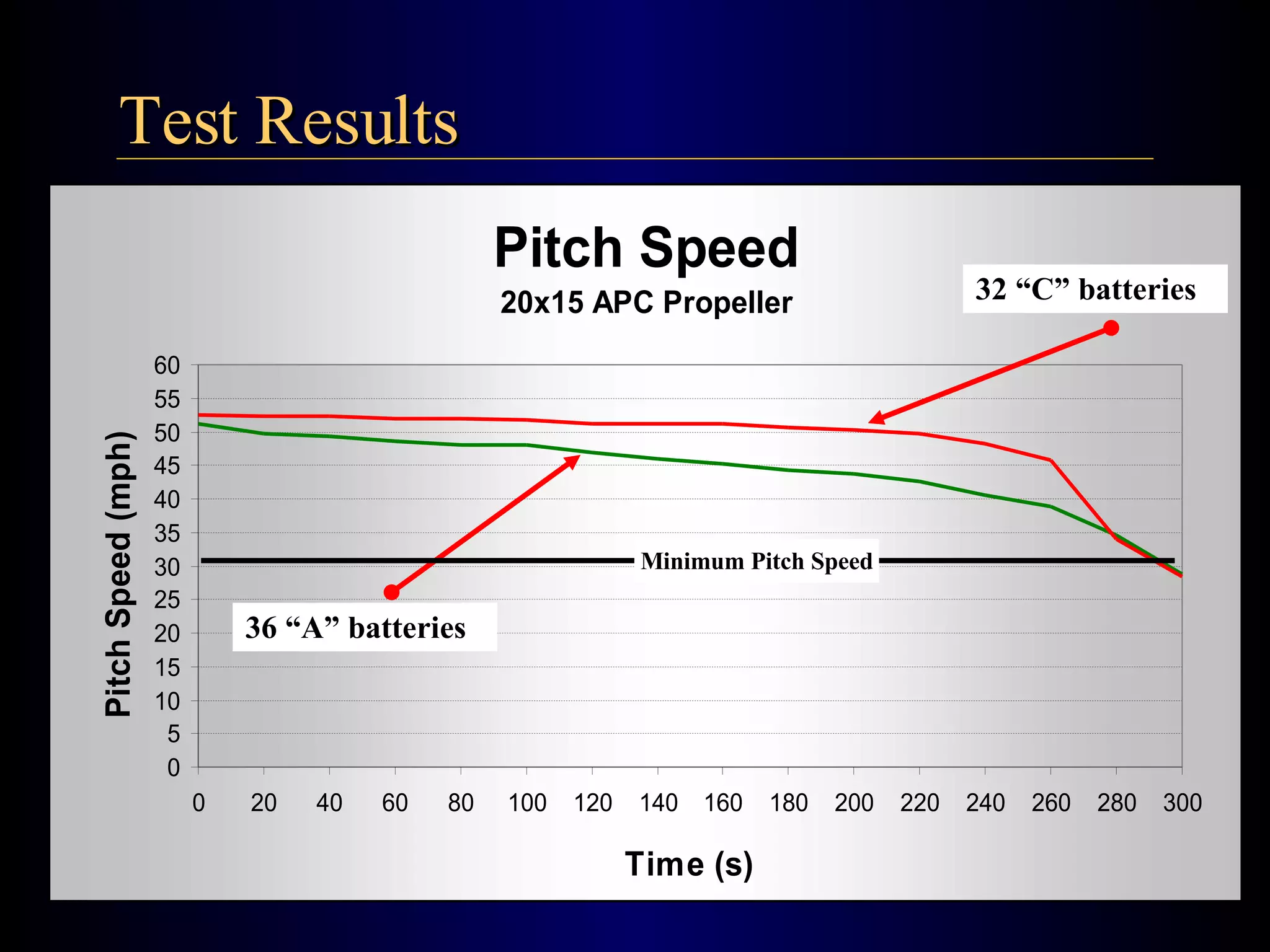
The document summarizes the design of an electric RC aircraft called Poseidon's Fury. Key features include carrying a 4 liter payload, draining within 30 seconds, lifting around 25 lbs, and having a low rated aircraft cost. The aircraft uses carbon fiber spars and booms, has a tricycle landing gear configuration, and modified Eppler 216 airfoils. Flight testing showed good longitudinal and directional stability. The propulsion system uses 32 NiCad batteries providing over 4 lbs of thrust and a pitch speed of 47 mph, meeting requirements. The aircraft design satisfies competition rules and successfully completed test missions.