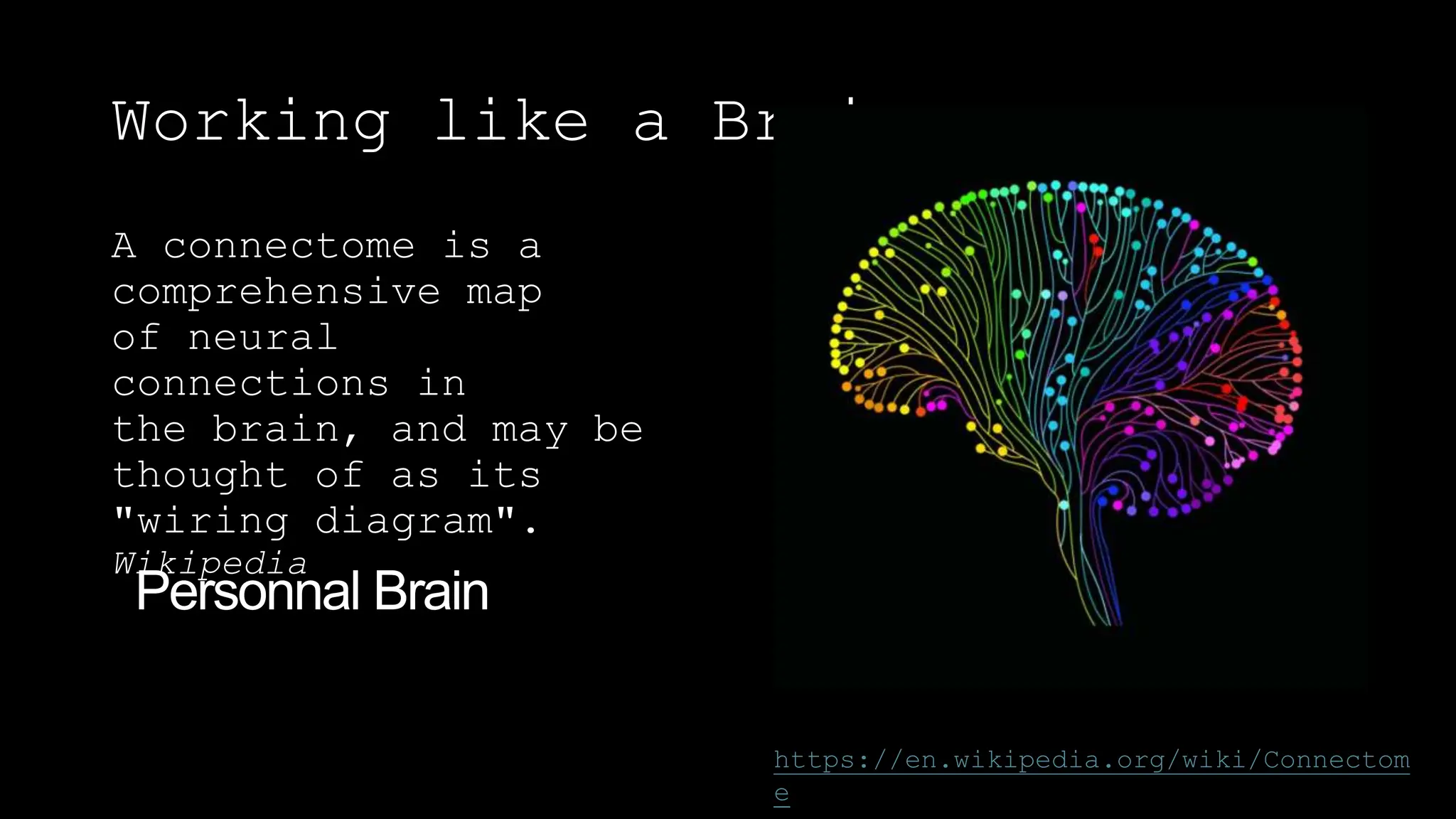
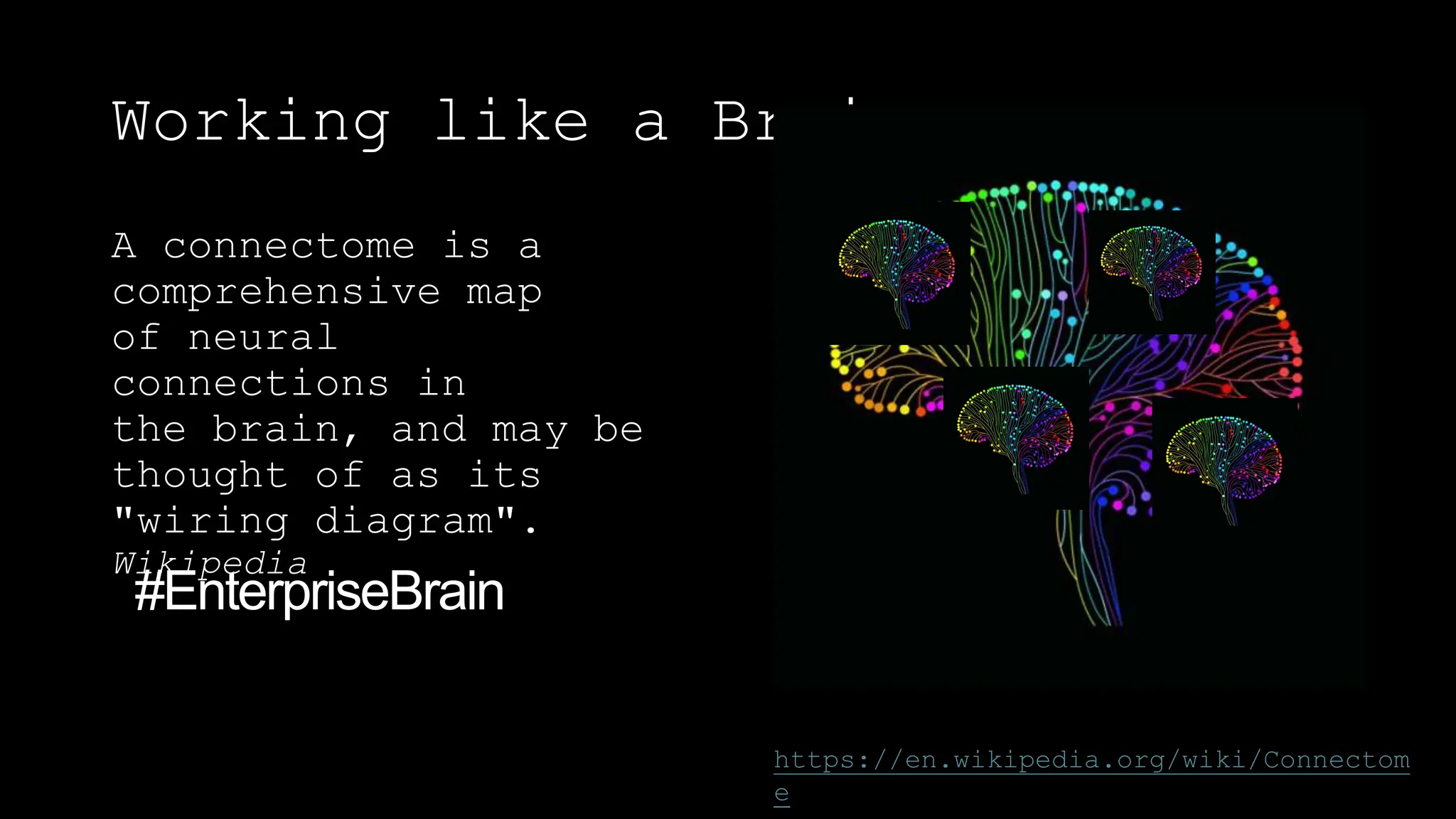
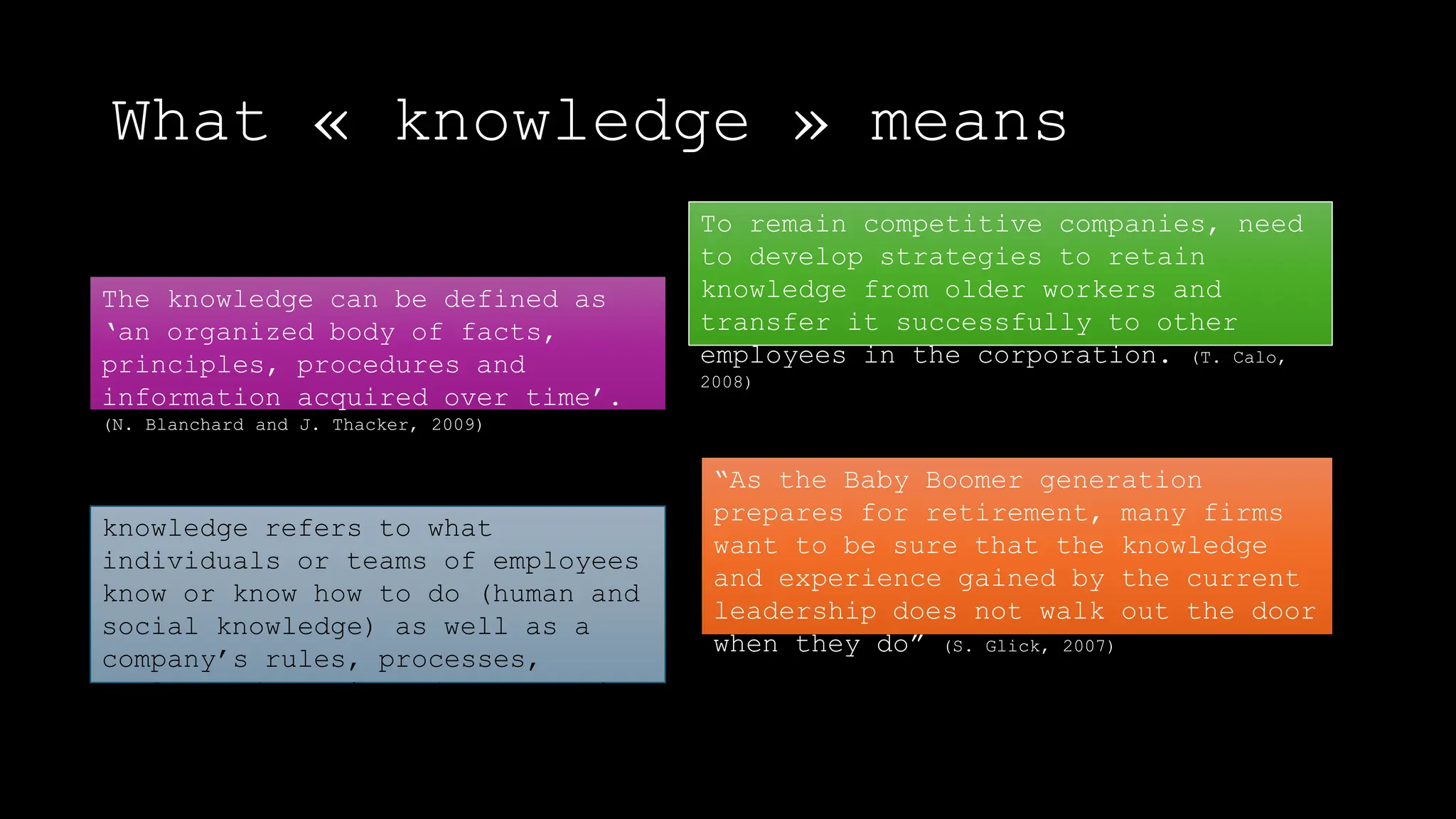
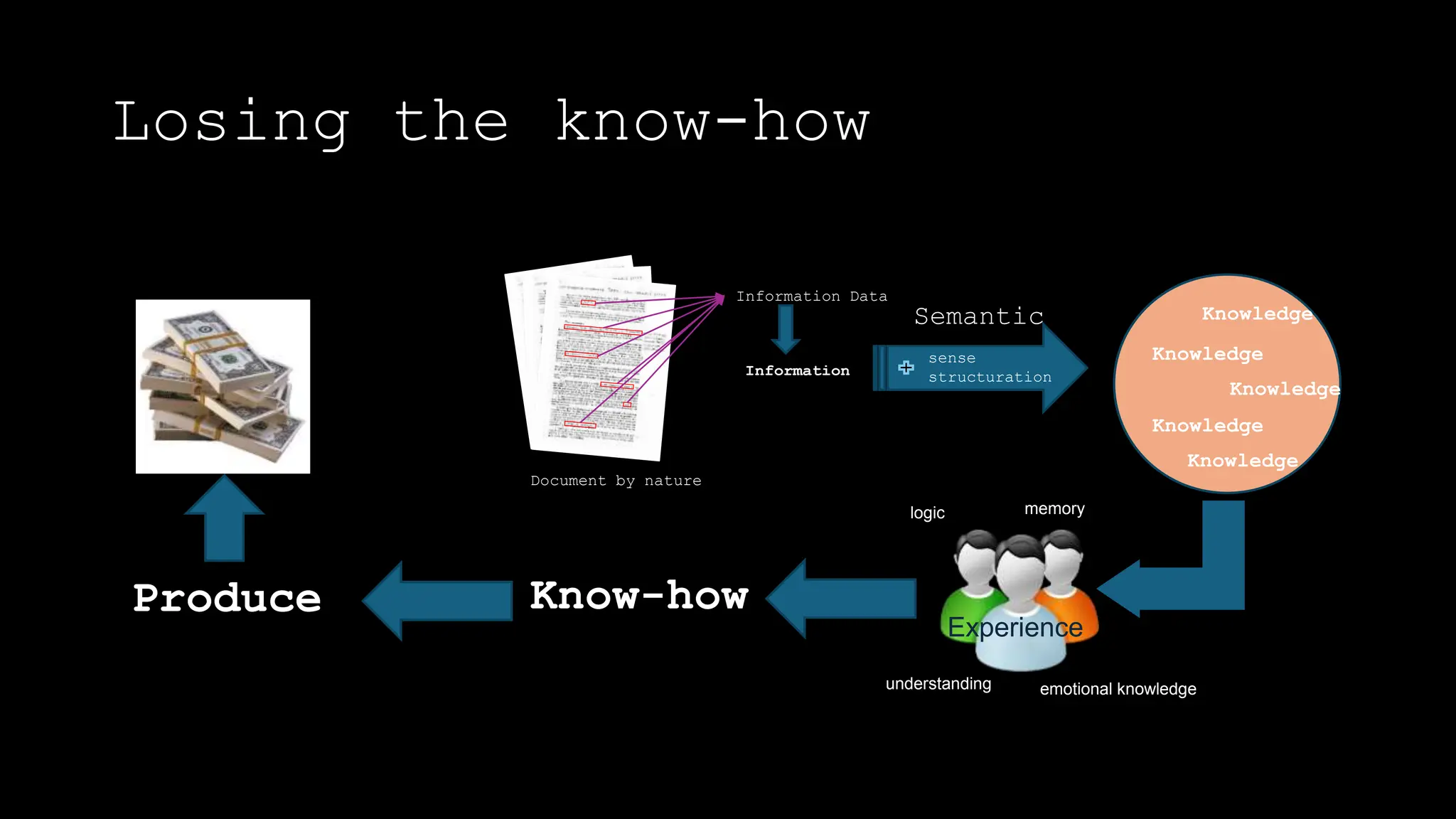
The document discusses the concept of working like a brain by creating a corporate knowledge network that mirrors the human brain's neural connections. It emphasizes the importance of retaining and transferring knowledge as the workforce transitions, particularly with older employees retiring. Strategies for effective knowledge management, including the use of AI and process mining, are also outlined.