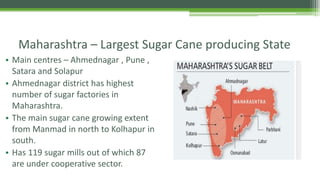
The document summarizes India's sugar industry. It discusses that sugar industry is an important agro-based industry in India that uses sugarcane as its main raw material. It produces sugar and byproducts like molasses. The document outlines the major sugarcane producing states in India like Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, and South Indian states. It notes the development of the modern sugar industry in India in the 20th century. It also discusses the distribution of sugarcane growing areas in different states and the problems faced by sugar industry like low yields and sucrose content. Recent developments in sugarcane variety by Sugarcane Breeding Institute is also mentioned.