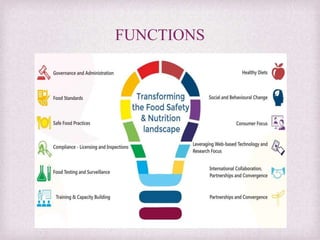
The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) was established under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006 to consolidate various acts related to food safety and set unified standards. It is responsible for regulating food manufacture, storage, distribution, sale, and import, and aims to enhance food safety through scientific standards. The FSSAI operates with a hierarchical structure, including a chairperson and 22 members, and provides several licensing categories based on food business turnover.