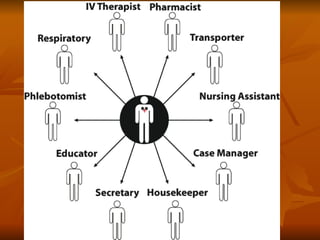
The document discusses the nursing shortage and its implications for quality of care for the elderly population. It notes that the nursing shortage is projected to worsen significantly by 2020 and beyond as the elderly population doubles. Higher nurse-to-patient ratios are linked to negative health outcomes for patients like infections, pneumonia, and medical errors. As patients age, they have more complex medical needs, so the nursing shortage diminishes quality of care through issues like inadequate pain management, medication errors, and increased falls and potential for abuse in hospitals. Some solutions discussed are state mandated nurse staffing ratios and basing staffing levels on patient acuity levels.