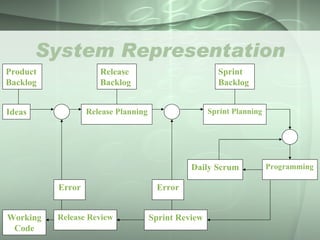
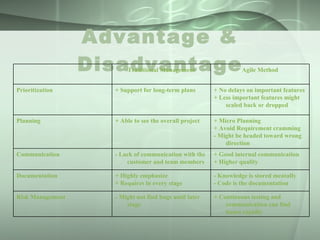
The document presents an overview of the Agile Method - Scrum. It discusses the Waterfall life cycle and introduces Agile Method. Key aspects of Scrum covered include sprints, potentially shippable product increments, the product owner, product backlog, scrum master, daily scrum meetings, sprint planning, sprint reviews, and the advantages and disadvantages of the Agile Method compared to traditional management.