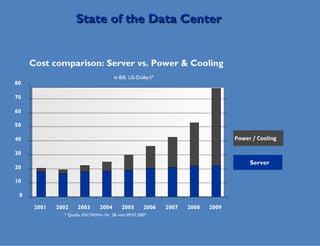
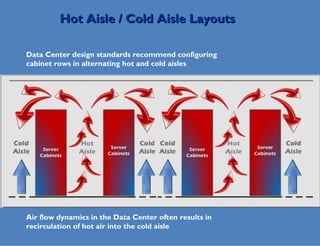
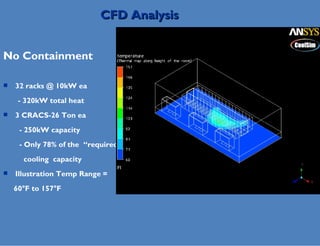
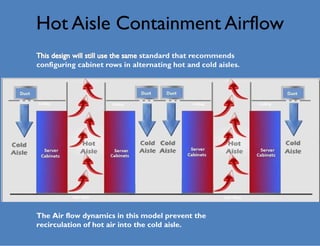
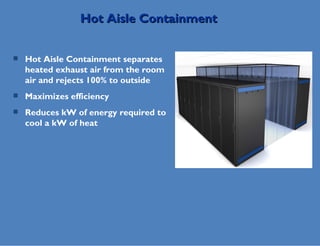
Wade Lewis discusses how traditional data center designs are inefficient due to mixing of hot and cold air, which can reduce cooling efficiency by up to 30%. Hot aisle containment is presented as an alternative that prevents this recirculation of hot air, allowing increased supply air temperatures and higher rack densities of up to 30kW per cabinet. This approach maximizes cooling capacity and efficiency through separation of hot and cold air flows.