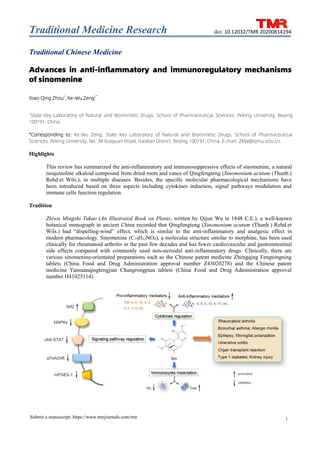
Advances in anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory mechanisms of sinomenine
- 1. Traditional Medicine Research 1 Submit a manuscript: https://www.tmrjournals.com/tmr doi: 10.12032/TMR 20200814194 Traditional Chinese Medicine Advances in anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory mechanisms of sinomenine Xiao-Qing Zhou1 , Ke-Wu Zeng1* 1 State Key Laboratory of Natural and Biomimetic Drugs, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Peking University, Beijing 100191, China *Corresponding to: Ke-Wu Zeng. State Key Laboratory of Natural and Biomimetic Drugs, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Peking University, No. 38 Xueyuan Road, Haidian District, Beijing 100191, China. E-mail: ZKW@bjmu.edu.cn. Highlights This review has summarized the anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of sinomenine, a natural isoquinoline alkaloid compound from dried roots and canes of Qingfengteng (Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd.et Wils.), in multiple diseases. Besides, the specific molecular pharmacological mechanisms have been introduced based on three aspects including cytokines induction, signal pathways modulation and immune cells function regulation. Tradition Zhiwu Mingshi Tukao (An Illustrated Book on Plants, written by Qijun Wu in 1848 C.E.), a well-known botanical monograph in ancient China recorded that Qingfengteng (Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd.et Wils.) had “dispelling-wind” effect, which is similar to the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect in modern pharmacology. Sinomenine (C19H23NO4), a molecular structure similar to morphine, has been used clinically for rheumatoid arthritis in the past few decades and has fewer cardiovascular and gastrointestinal side effects compared with commonly used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Clinically, there are various sinomenine-orientated preparations such as the Chinese patent medicine Zhengqing Fengtongning tablets (China Food and Drug Administration approval number Z43020278) and the Chinese patent medicine Yansuanqingtengjian Changrongpian tablets (China Food and Drug Administration approval number H41025114).
- 2. REVIEW 2 doi: 10.12032/TMR20200814194 Submit a manuscript: https://www.tmrjournals.com/tmr Abstract Sinomenine, a major active ingredient from traditional Chinese medicine Qingfengteng (Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd.et Wils.), has been proven to have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anti-tumor, immunomodulatory and other pharmacological effects, and is clinically used for various inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. However, due to complex molecular mechanisms and pathological characteristics in inflammatory and immune responses, the precise anti-inflammatory and immunological mechanisms of sinomenine are still unclear. This review summarizes the anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory mechanisms of sinomenine during recent years in rheumatoid arthritis, respiratory system, nervous system, digestive system and organ transplant rejection. The molecular pharmacological mechanisms of sinomenine responsible for anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects were in detail introduced based on 3 aspects including cytokines induction, signal pathways modulation and immune cells function regulation. Moreover, this review also raises some concerns and challenges in future sinomenine study, which will contribute to crucial theoretical and practical significance for in-depth development and utilization of sinomenine as medicinal resource. Keywords: Sinomenine, Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd.et Wils., Anti-inflammatory, Immunosuppression, Molecular mechanism, Immunocyte Author contributions: Ke-Wu Zeng contributed to conceive the research; Xiao-Qing Zhou and Ke-Wu Zeng contributed to write the manuscript. Competing interests: The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Acknowledgments: This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81973505) and The National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2019YFC1708902, 2019YFC1711000). Abbreviations: Sin, sinomenine; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; AR, allergic rhinitis; ICH, intracerebral hemorrhage; MAPKs, mitogen-activated protein kinases; TGF, transforming growth factor; Treg cells, regulatory T cells; Th17 cells, T helper type 17 cells; AhR, aromatic hydrocarbon receptor; CIA, collagen induced arthritis; Nrf2, nuclear factor NF-E2 related factor 2; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; α7nAChR, α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; mPGES-1, microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1; PG, prostaglandin; DCs, dendritic cells. Citation: Zhou XQ, Zeng KW. Advances in anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory mechanisms of sinomenine. Tradit Med Res. 2021; 6(1): 6. doi: 10.12032/TMR 20200814194. Executive editor: Yu-Ping Shi. Submitted: 22 June 2020, Accepted: 14 August 2020, Online: 26 August 2020. © 2021 By Authors. Published by TMR Publishing Group Limited. This is an open access article under the CC-BY license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/BY/4.0/).
- 3. Traditional Medicine Research 3 Submit a manuscript: https://www.tmrjournals.com/tmr doi: 10.12032/TMR 20200814194 Introduction Qingfengteng (Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd.et Wils.) is a traditional Chinese medicine with anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects (Figure 1) [1]. The earliest engraved herbal atlas in China, Bencao Tujing (Atlas of Materia Medica, written by Song Su et al. in 1061 C.E.) reported that Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd.et Wils. could be used in Chinese medicine. Zhiwu Mingshi Tukao (An Illustrated Book on Plants, written by Qijun Wu in 1848 C.E.), a well-known botanical monograph in ancient China recorded that Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd.et Wils. had “dispelling-wind” effect, which is similar to the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect in modern pharmacology. Moreover, the famous Chinese medical book, Bencao Gangmu (Compendium of Materia Medica, written by Shizhen Li in 1590 C.E.) demonstrated that Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd.et Wils. could be applied for treating rheumatic diseases. Sinomenine (Sin, C19H23NO4) is a natural isoquinoline alkaloid compound from dried roots and canes of Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd.et Wils., with a molecular structure similar to morphine [2]. Sin has been found to show wide pharmacological activities including anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anti-tumor, and immunosuppressive effects [3]. Sin has been used clinically for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in the past few decades and has fewer cardiovascular and gastrointestinal side effects compared with commonly used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [4]. Moreover, Sin also has kidney protective effect [5] and has recently been used in transplantation immunology research [6]. Clinically, there are various Sin-orientated preparations such as the Chinese patent medicine Zhengqing Fengtongning tablets (China Food and Drug Administration approval number Z43020278) and the Chinese patent medicine Yansuanqingtengjian Changrongpian tablets (China Food and Drug Administration approval number H41025114). However, meanwhile, Sin possesses a short half-life, low efficacy and large administration dose [7], thus limiting its wide application. Notably, precise pharmacological mechanism of Sin is still largely unexplored. Therefore, systematic literature summary of Sin pharmacological studies has become an urgent need to promote Sin further development. This review aims to summarize the anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory mechanisms of Sin, to provide a theoretical reference for the in-depth development and utilization of Sin. Anti-inflammatory and immunological activities of Sin Sin for RA RA is a common autoimmune disease characterized by chronic arthritis accompanied with various symptoms [8]. The pathogenesis of RA is not completely clear, but it is generally considered to be associated with disorders of autoimmune and cytokine networks, resulting in persistent immunocyte activation. Wang et al. reported that acupoint application of Sin had good therapeutic effect on RA [9]. Moreover, Feng et al. studied the inhibitory effect of Sin on angiogenesis in a collagen-induced arthritis mouse model and found that Sin (30 mg/kg) could significantly improve swelling and erythema prolongation, decrease arthritis index, and reduce cartilage damage and bone erosion. Sin also showed inhibitory effect on CD31 positive cells number on synovium [10]. In addition, Qian et al. reported that Sin (30 mg/kg) improved synovial cell hyperplasia and synovial swelling in collagen induced arthritis (CIA) rats, thus significantly improving joint pathological damage in RA [11]. Furthermore, Liu et al. evaluated Sin effect on CIA mice and RA patients, and results suggested that Sin could regulate tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, IL-12 p40, monocyte chemotactic protein-1, Eotaxin-2, M-CSF, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 and RANTES secretion to suppress RA progression [12]. Thus, these studies provide a reliable experimental basis for Sin treatment of RA. Figure 1 Sinomenium acutum whole plant, rhizome slices and its main component Sin. Sin, sinomenine.
- 4. REVIEW 4 doi: 10.12032/TMR20200814194 Submit a manuscript: https://www.tmrjournals.com/tmr Sin for respiratory inflammation Bronchial asthma is a hyperresponsive disease caused by a variety of immune cells responsible for chronic airway inflammation. Bao et al. showed that Sin significantly reduced asthmatic mice smooth muscle thickness, mucinous gland hypertrophy, goblet cell hyperplasia, collagen deposition and eosinophil inflammatory response in a dose-dependent manner. Sin (25 mg/kg) also significantly inhibited malondialdehyde production and myeloperoxidase activity in asthmatic mice lung tissue [13]. Moreover, allergic rhinitis (AR) is a chronic allergic airway disease in nasal mucosa. Chen et al. found that Sin (100 mg/kg) effectively improved AR symptom by decreasing eosinophils, anti-ovalbumin specific IgE and IL-4 levels in an AR mouse model [14]. Therefore, Sin exhibited a significant effect on respiratory inflammation such as bronchial asthma and AR. Sin for neuroinflammation Epilepsy is a neurological disorder that is currently not well controlled by available drugs. Neuroinflammation is considered to be a key risk factor for epilepsy. Gao et al. established a chronic epilepsy model induced by pentylenetetrazole and found Sin reduced epilepsy incidence and complete seizure, and increased rat seizuresin latency. Meanwhile, Sin could block hippocampal neurons injury and minimize spatial learning and memory loss. In addition, Sin (20 mg/kg) showed inhibitory effect on NLRP1 inflammatory complexes and inflammatory cytokines production including IL-1β, IL-18, IL-6 and TNF-α in pentylenetetrazole kindled rats [15]. Notably, microglial polarization plays an important role in neuroinflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), whose exact mechanism remains unclear. Shi et al. reported that Sin (100 mg/kg) could protect hippocampal neurons against ICH-induced microglial cytotoxicity and inhibit matrix metalloproteinase-3/9 expressions and neurological deficits in C57/BL6 mice ICH model [16]. Therefore, Sin is considered to protect brain function by inducing microglial M2 phenotype and inhibiting MMP-3/9 expressions, which is a promising therapeutic strategy for neuroinflammation. Sin for digestive system inflammation Ulcerative colitis is a major clinical digestive system disease, which is associated with autoimmune dysfunction. Zhou et al. found that Sin (100 mg/kg) significantly inhibited disease activity index and improved colon histological damage in sodium dextran sulfate-induced colitis mouse model. Moreover, Sin markedly down-regulated TNF-α, IL-6 and inducible nitric oxide synthase levels, and promoted nuclear factor NF-E2 related factor 2 (Nrf2), heme oxygenase-1 and NQO-1 expressions, suggesting that Nrf2/NQO-1 may be a key signaling pathway for colitis therapy [17]. Additionally, Xiong et al. confirmed the effect of Sin on inflammatory bowel disease. Result showed that Sin (30 mg/kg) significantly decreased TLR4, MyD88, NF-κB p65 and pro-inflammatory cytokines expression in a dose-dependent manner in mouse model of colitis employs dextran sodium sulfate, indicating Sin may regulate TLR/NF-κB signaling pathway for inflammatory bowel disease [18]. Therefore, Sin plays an important therapeutic role in digestive system inflammation. Sin for organ transplant rejection Sin has also been tested on potential therapeutic effect on organ transplant rejection. Cai et al. investigated immunosuppressive effect of Sin on the orthotropic liver transplantation rats and found that Sin (40 mg/kg) showed inhibitory effect on immune rejection and reduced transplant liver damage in rats [19]. Moreover, Xiong et al. reported that Sin (30 mg/kg) together with cyclosporine could effectively protect kidney transplant rats [20]. Similarly, Wang et al. found that Sin (15 mg/kg) could significantly prolong rat survival time of high-risk corneal graft, and combination of Sin with cyclosporine A showed a better therapeutic effect [21]. These studies suggest that Sin can exert obvious synergistic effect with cyclosporine A to alleviate adverse reactions and enhance curative effect. Thus, Sin can be used as an adjuvant agent of immunosuppressive agents for acute or chronic transplant rejection. Other therapeutic effects of Sin Wang et al. studied Sin effect on type 1 diabetes in non-obese diabetic mice and found that Sin (25 mg/kg) significantly reduced diabetes incidence and improved glucose tolerance. Meanwhile, Sin decreased serum IFN- γ and IL- 2 levels and down-regulated IFN-γ and IL-2 expressions in pancreas. These results suggested that Sin might have a preventive effect on diabetes development in non-obese diabetic mice [22]. Moreover, Zhao et al. reported that Sin (200 mg/kg) could attenuate serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen levels and inhibit renal tubular cell apoptosis; thereby alleviating inflammatory response in ischemia-reperfusion-induced mice kidney injury [23]. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory mechanisms of Sin Cytokines regulation Cytokines are soluble low molecular weight proteins secreted by immune cells and non-immune cells, which have various functions such as regulating innate and adaptive immunity, hematopoiesis, cell growth and tissue repair. Cytokines can be divided into pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory categories
- 5. Traditional Medicine Research 5 Submit a manuscript: https://www.tmrjournals.com/tmr doi: 10.12032/TMR 20200814194 according to their effects on inflammation. Numerous studies have shown that Sin exerts anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects by regulating the levels of different cytokines. Pro-inflammatory cytokines. Pro-inflammatory cytokines can promote inflammatory reactions, including TNF-α, serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine), and most interleukins such as IL-1β, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8. Shen et al. studied Sin effect on ankle fracture and found that Sin could effectively inhibit IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, p-p38 and p-NF-κB increases and balance antioxidants and detoxifying enzymes, indicating that Sin could treat ankle fracture by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress [24]. Moreover, Lin et al. established an in vitro model of atopic dermatitis by stimulating RAW264.7 cells with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and found that Sin remarkably inhibited TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 production against LPS in a dose-dependent manner. Besides, Sin significantly reduced inducible nitric oxide synthase and COX2 expressions [25], indicating that Sin may play an anti-inflammatory role by suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines production. Anti-inflammatory cytokines. Anti-inflammatory cytokines including IL-4, IL-10, IL-13 and transforming growth factor (TGF), are mainly produced by activated T cells and can regulate biological functions of B cells, T cells and monocytes. Chen et al. previously established AR mouse model to study Sin effect in AR treatment as well as potential mechanism. It was found that Sin significantly down-regulated serum anti-OVA specific IgE and IL-4, and increased TGF-β expression in serum and nasal mucosa of AR mice. It is suggested that the immunosuppressive effect of Sin on AR may be due to TGF-β induction [14]. Signaling pathways regulation Nrf2 pathway. Nrf2 is a key transcription factor regulating oxidation/reduction balance and inflammatory response. Qin et al. found that Sin prominently reduced Nrf2 inhibitor Keap1 through PKC-sensitive ubiquitination-proteasome degradation and was an activator of Nrf2. Thus, Sin significantly increased Nrf2 level and promoted Nrf2 nuclear translocation for anti-inflammatory effect. Moreover, Sin can regulate M1/M2 polarization of macrophages and inhibit IκBα phosphorylation and NF-κB nuclear translocation through regulating Nrf2 [5]. Furthermore, Zhang et al. investigated Sin effect on motor dysfunction and neuropathology of traumatic spinal cord injury, and discovered that Sin could promote Nrf2 translocation from cytoplasm to nucleus as well as Nrf2-mediated transactivation, thereby inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress. Notably, Sin-mediated anti-inflammatory effect was significantly reversed by siRNA knockdown of Nrf2 expression [26]. In addition, Qin et al. also found that Sin achieved inhibition of oxidative stress through the Nrf2 pathway [5]. Collectively, these results indicate that Sin inhibits inflammation and oxidative stress by activating Nrf2. Mitogen-activated protein kinases pathway. Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) are key signaling pathways mediating inflammatory reactions including ERKs, JNKs and p38 MAPKs. Liu et al. found that Sin could not only inhibit IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α expressions induced by LPS, but also promote mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 expression by down-regulating miRNA-101, thereby blocking JNK signaling pathway to exert anti-inflammatory effect in vivo [27]. Xu et al. found Sin combined with acupuncture obviously effectively reduced serum TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β and IL-8 levels, and increased superoxide dismutase production by regulating p38 MAPK expression in arthritis rats [28]. These results indicate that MAPK signaling pathway play an important role in Sin treatment of arthritis. Janus kinase-signal transduction and transcription activator pathway. Janus kinase-signal transduction and transcription activator pathway can rapidly transmit signal from membrane to nucleus and is widely involved in various physiological and pathological processes, such as cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and inflammation. Qiu et al. studied protective effect of Sin on astrocyte-mediated neuroinflammation and revealed that Sin remarkably inhibited astrocyte activation and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) phosphorylation. Further studies showed that dopamine D2 receptor or αB-crystallin (encoded by CRYAB gene) knockdown could obviously antagonize Sin-dependent suppressive effect on STAT3. Moreover, it was found that Sin induced CRYAB up-regulation and nuclear translocation in astrocytes, and enhanced CRYAB interaction with STAT3, thus exhibiting a neuroimmune regulatory characteristic [29]. α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor pathway. α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7nAChR) is a member of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and is a ligand-gated ion channel composed of homologous pentamers. α7nAChR belongs to neuronal acetylcholine receptor and plays an important role in anti-inflammatory pathway. Yue et al. found that Sin may bind directly to α7nAChR by targeting Tyr184 and Tyr191 residues to activate PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway, thereby specifically enhancing vasoactive intestinal polypeptide production [30]. Moreover, Yi et al. found that α7nAChR was involved in TNF-α-induced invasive proliferation of fibroblast-like synoviocyte, and Sin could reduce the α7nAChR expression and the fibroblast-like synoviocyte proliferation, exerting an anti-arthritic effect [31]. Furthermore, Zhu et al. reported that Sin inhibited CD14/TLR4 expression via targeting α7nAChR to decrease intracellular free calcium level [32].
- 6. REVIEW 6 doi: 10.12032/TMR20200814194 Submit a manuscript: https://www.tmrjournals.com/tmr Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 pathway. Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1) is a promising anti-inflammatory target, which plays an anti-inflammatory role without adverse effects caused by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Zhou et al. found that Sin could selectively decrease mPGES-1 expression and reduce prostaglandin (PG) E2 level without affecting PG I2 and thromboxane A2 synthesis. Meanwhile, mPGES-1 expression was effectively reduced by Sin in carrageenan-induced edema rat model and CIA mouse model. Furthermore, Sin could block NF-κB binding to DNA, thereby inhibiting mPGES-1 expression, which represents a new direction for anti-inflammatory agent discovery [4]. In addition, scholars found that Sin inhibited the production of another type of PG D2 [33], but no effect of Sin on PG F2α was reported. Immunocytes regulation Regulatory T cells and T helper type 17 cells. As a subset of T cells, regulatory T cells (Treg cells) play a valuable role in maintaining immune homeostasis mainly by secreting IL-10 and TGF-β1. T helper type 17 cells (Th17 cells) can produce IL-17 and effectively mediate the stimulating process of neutrophil mobilization, thereby mediating the pre-inflammatory response. The balance between Treg and Th17 cell numbers is highly associated with autoimmune diseases. Tong et al. used collagen-induced arthritis mouse model to evaluate Sin effect on Treg and Th17 cells in autoimmune arthritis and indicated that Sin increased Treg cells frequency while decreased Th17 cells frequency [34]. Further studies showed Sin promoted aromatic hydrocarbon receptor (AhR)/Hsp90 dissociation and nuclear translocation of AhR by inducing AhR expression, demonstrating that Sin may be a potential AhR agonist. In addition, resveratrol, an AhR antagonist, could obviously inhibit intestinal Treg cells function and attenuate anti-arthritis effect of Sin. Thus, it can be concluded that Sin can regulate Treg cells function through AhR for its anti-arthritic effect [35]. Dendritic cells. Dendritic cells (DCs) are the most important antigen-presenting cells. DCs are classified into 2 types: mature DCs and immature DCs. Mature DCs are highly responsive to allogeneic T lymphocytes and are crucial to transplant rejection. Meanwhile, immature DCs can induce allogeneic lymphocytes hyporesponse and reduce T cell-mediated cellular immune response. Wang et al. observed the effect of Sin on DC2.4 DCs stimulated by LPS and found that TNF-α, CD80, IFN-γ, IL-6 and IL-12 decreased after Sin treatment, indicating that Sin could inactivate DC2.4 cells and reduce inflammatory factors secretion of DC [36]. Moreover, Li et al. used Sin to block donor-derived DCs before kidney transplantation and found donor-derived DCs maturation could be markedly inhibited by Sin pretreatment, further leading to Treg cells increase in recipient spleen after kidney transplantation [37]. Collectively, these observations suggest that Sin can regulate DCs before allograft transplantation, thereby increasing immune tolerance to allograft. Current problems and challenges in Sin research As a major active ingredient of Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd.et Wils., Sin has been proved to be a promising immunoregulatory agent, which has been used for treatment of various inflammatory diseases. Although, during recent years, some progresses have been made in Sin research, there are still some problems that require further investigation. Notably, though some potential anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive signaling pathways have been discovered, the direct pharmacological targets identification of Sin is still lacking. Thus, it is recommended to pay more attentions to explore the potential molecular target of Sin in vivo for anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects, to reveal potential pharmacological mechanism of Sin and guide its clinical precision medication. Furthermore, although Sin has a wide range of pharmacological activities, the clinical dose is still high resulting in some side effects. Therefore, it is necessary to advance investigations on Sin toxicology and pharmacokinetic studies. Therefore, structural modification coupled with activity screening of Sin as a lead compound may discovery some high-efficiency and low-toxic Sin derivatives, which promote Sin development in the future. In fact, multiple studies on the structural modification of Sin and the anti-inflammatory activity screening of Sin derivatives have been carried out. Zhao et al. tested the anti-inflammatory activity of 6 Sin derivatives in 3 murine inflammation models and screened out an anti-inflammatory drug candidate S1a, the 1, 4 bits on the A ring of which had been changed [7]. Jin et al. synthesized various Sin derivatives and evaluated their anti-inflammatory activity in vivo and in vitro and found derivative 3g had powerful anti-inflammatory effect [38]. The structural modifications of Sin have been mostly carried out in A, B, C, and D 4 rings [39], while these 4 rings have not shown the regularity affecting the anti-inflammatory activity of Sin derivatives. Moreover, the anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities of these synthesized Sin derivatives still need to be confirmed by further studies. In addition, current Sin agents mainly include tablets, injections, capsules and patches, but low absorption demands further development of novel pharmaceutical dosage forms. Concluding remarks
- 7. Traditional Medicine Research 7 Submit a manuscript: https://www.tmrjournals.com/tmr doi: 10.12032/TMR 20200814194 Figure 2 Anti-inflammatory and immuno- modulatory mechanisms of Sin. Sin, sinomenine. Broad biological effects of Sin, such as anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anti-oxidant, anti-tumor, et al., have been proved by a large number of experimental and clinical studies. This article reviewed anti-inflammatory and immunological pharmacological mechanisms of Sin, including pharmacological effects of Sin in RA, respiratory system, nervous system and organ transplant rejection, as well as associated molecular signaling pathways (Figure 2). These contents can lay a solid foundation for future research on pharmacological mechanisms and therapeutic targets and promote innovative drugs development of Sin for inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. References 1. Yi L, Luo JF, Xie BB, et al. α7 Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor is a novel mediator of sinomenine anti-Inflammation effect in macrophages stimulated by lipopolysaccharide. Shock 2015, 44: 188–195. 2. Sun YH, Zhu Q, Li JX. Research progress on anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor effects of sinomenine. Chin Pharm Bulletin 2015, 31: 1040–1043. 3. Liu WW, Zhu Y, Wang Y. Advance on active ingredients and pharmacological effects of caulis sinomenii alkaloid. J Liaoning Univ Tradit Chin Med 2016, 43: 1765–1769. 4. Zhou H, Liu JX, Luo JF, et al. Suppressing mPGES-1 expression by sinomenine ameliorates inflammation and arthritis. Biochem Pharmacol 2017, 142: 133–144. 5. Qin T, Du RH, Huang FJ, et al. Sinomenine activation of Nrf2 signaling prevents hyperactive inflammation and kidney injury in a mouse model of obstructive nephropathy. Free Radical Biol Med 2016, 92: 90–99. 6. Li JJ, Chen XC, Tan SB, et al. Effect of CTLA4Ig combined with sinomenine on survival time of renal xenotransplantation. J Mod Med Health 2018, 34: 2276–2278. 7. Zhao ZJ, Xiao J, Wang JC, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of novel sinomenine derivatives. Int Immunopharmacol 2015, 29: 354–360. 8. Kourilovitch M, Galarza-Maldonado C, Ortiz-Prado E. Diagnosis and classification of rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun 2014, 48–49: 26–30. 9. Wang R, Yang J, Liu YX, et al. The effect of acupoint application of sinomenine for rheumatoid arthritis measured by microdialysis and UPLC-MS/MS. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2019, 2019: 5135692. 10. Feng ZT, Yang T, Hou XQ, et al. Sinomenine mitigates collagen-induced arthritis mice by inhibiting angiogenesis. Biomed Pharmacother 2019, 113: 108759–108765. 11. Qian X, Zhao ZM, Shang W, et al. Serum proteomic analysis of the anti-arthritic effects of sinomenine on rats with collagen-induced arthritis. Mol Med Rep 2018, 18: 49–58. 12. Liu WW, Zhang YJ, Zhu WN, et al. Sinomenine inhibits the progression of rheumatoid arthritis by regulating the secretion of inflammatory cytokines and monocyte/macrophage subsets. Front Immunol 2018, 9: 2228. 13. Bao HR, Liu XJ, Li YL, et al. Sinomenine attenuates airway inflammation and remodeling in a mouse model of asthma. Mol Med Rep 2016, 13: 2415–2422. 14. Chen Z, Tao ZZ, Zhou XH, et al. Immunosuppressive effect of sinomenine in an allergic rhinitis mouse model. Exp Ther Med 2017, 13: 2405–2410. 15. Gao B, Wu Y, Yang YJ, et al. Sinomenine exerts anticonvulsant profile and neuroprotective activity in pentylenetetrazole kindled rats: involvement of inhibition of NLRP1 inflammasome. J Neuroinflammation 2018, 15: 152–163. 16. Shi H, Zheng K, Su ZL, et al. Sinomenine enhances microglia M2 polarization and attenuates inflammatory injury in intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neuroimmunol 2016, 299: 28–34. 17. Zhou Y, Liu HY, Song J, et al. Sinomenine alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis via the Nrf2/NQO-1 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep 2018, 18: 3691–3698. 18. Xiong HF, Tian L, Zhao ZH, et al. The sinomenine enteric-coated microspheres suppressed the TLR/NF-κB signaling in DSS-induced experimental colitis. Int Immunopharmacol 2017, 50: 251–262. 19. Cai ZG, Yu ZJ, Wen S, et al. An experimental
- 8. REVIEW 8 doi: 10.12032/TMR20200814194 Submit a manuscript: https://www.tmrjournals.com/tmr study on the effect of sinomenine on the acute rejection after orthotropic liver transplantation in rats. J Liaoning Univ Tradit Chin Med 2010, 12: 112–114. 20. Xiong L, Yang LY. Effects of alkaloid sinomenine on levels of IFN-γ, IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6 in a rat renal allograft model. Immunotherapy 2012, 4: 785–791. 21. Wang Y, Ma DL, Jie Y, et al. Sinomenine can prolong high-risk corneal graft survival in a rat model. Immunotherapy 2012, 4: 581–586. 22. Wang Y, Yang F, Xiang Y, et al. Preventive effects of sinomenine on the development of diabetes in NOD mice. Lat Am J Pharm 2014, 33: 87–92. 23. Zhao ZQ, Guan R, Song SH, et al. Sinomenine protects mice against ischemia reperfusion induced renal injury by attenuating inflammatory response and tubular cell apoptosis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013, 6: 1702–1712. 24. Shen J, Yao R, Jing M, et al. Sinomenine regulates inflammatory response and oxidative stress via nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) and NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) signaling pathways in ankle fractures in children. Med Sci Monit 2018, 24: 6649–6655. 25. Lin SW, Wei ML, Zhu W. Molecular mechanisms of the anti-inflammatory effect of sinomenine on atopic dermatitis. Die Pharmazie 2018, 73: 474–476. 26. Zhang LL, Zhang WJ, Zheng BB, et al. Sinomenine attenuates traumatic spinal cord Injury by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation via Nrf2 pathway. Neurochem Res 2019, 44: 763–775. 27. Liu SM, Man YG, Zhao L. Sinomenine inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory injury by regulation of miR-101/MKP-1/JNK pathway in keratinocyte cells. Biomed Pharmacother 2018, 101: 422–429. 28. Xu MM, Liu SF, Wan RJ, et al. Combined treatment with sinomenine and acupuncture on collagen-induced arthritis through the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathway. Oncol Lett 2018, 15: 8770–8776. 29. Qiu J, Yan ZJ, Tao K, et al. Sinomenine activates astrocytic dopamine D2 receptors and alleviates neuroinflammatory injury via the CRYAB/STAT3 pathway after ischemic stroke in mice. J Neuroinflammation 2016, 13: 263. 30. Yue MF, Zhang XY, Dou YN, et al. Gut-sourced vasoactive intestinal polypeptide induced by the activation of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor substantially contributes to the anti-inflammatory effect of sinomenine in collagen-induced arthritis. Front Pharmacol 2018, 9: 675. 31. Yi L, Lyu YJ, Peng C, et al. Sinomenine inhibits fibroblast-like synoviocyte proliferation by regulating α7nAChR expression via ERK/Egr-1 pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 2018, 56: 65–70. 32. Zhu RL, Zhi YK, Yi L, et al. Sinomenine regulates CD14/TLR4, JAK2/STAT3 pathway and calcium signal via α7nAChR to inhibit inflammation in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Immunopharm Immunot 2019, 41: 172–177. 33. Oh YC, Kang OH, Choi JG, et al. Anti-allergic effects of sinomenine by inhibition of prostaglandin D2 and leukotriene C4 in mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells. Immunopharm Immunot 2011, 33: 266–270. 34. Tong B, Yu JT, Wang T, et al. Sinomenine suppresses collagen-induced arthritis by reciprocal modulation of regulatory T cells and Th17 cells in gut-associated lymphoid tissues. Mol Immunol 2015, 65: 94–103. 35. Tong B, Yuan XS, Dou YN, et al. Sinomenine induces the generation of intestinal Treg cells and attenuates arthritis via activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Lab Invest 2016, 96: 1076–1086. 36. Wang Z, Wang BB, Guan JM, et al. Sinomenine inhibites biological activity of DC2.4 dendritic cells and reduces secretion of inflammatory cytokines. Chin J Cell Mol Immunol 2015, 31: 660–663. 37. L. Li, Z. Luo, Z. Song, et al. Pre-transplant infusion of donor-derived dendritic cells maintained at the immature stage by sinomenine increases splenic Foxp3+ Tregs in recipient rats after renal allotransplantation. Transpl Immunol 2017, 45: 22–28. 38. Jin J, Teng P, Liu HL, et al. Microfluidics assisted synthesis and bioevaluation of sinomenine derivatives as antiinflammatory agents. Eur J Med Chem 2013, 62: 280–288. 39. Tang J, Raza A, Chen J, et al. A systematic review on the sinomenine derivatives. Mini Rev Med Chem 2018, 18: 906–917.