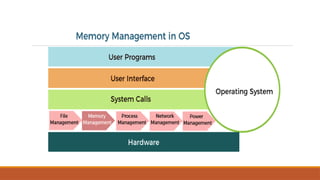
The document discusses process synchronization and scheduling in operating systems, emphasizing their role in managing multiple processes to prevent race conditions and ensure efficient resource access. It categorizes processes into independent and cooperative types and outlines various scheduling mechanisms and queues like job, ready, and device queues. Additionally, it covers memory management techniques and the allocation of memory in multiprogramming environments.