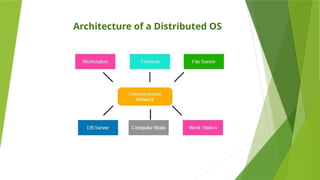
This document discusses distributed operating systems (DOS), which utilize multiple processors to manage real-time applications and data processing. It details different types of distributed systems, their architectures, and applications, including file and computer server systems, as well as design issues like scalability and security. Additionally, the document outlines approaches for detecting distributed deadlocks, including centralized, hierarchical, and distributed methods.