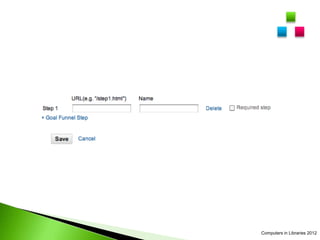
The document provides instructions for setting up filters, advanced segments, goals, and event tracking in Google Analytics. It discusses how to exclude specific IP addresses from reports using filters. It also describes how to create custom advanced segments to compare traffic from different devices. The document outlines the process for setting up conversion goals and funnels. Additionally, it explains how to use event tracking to monitor actions on pages like video plays or file downloads. Lastly, the document provides steps for tracking outbound links to other websites.















![^136.142.(1.([2-9]|[1-9][0-9]|1([0-9][0-
9])|2([0-4][0-9]|5[0-5]))|(([2-9]|[1-2][0-
9]|3[0-4]).([0-9]|[1-9][0-9]|1([0-9][0-
9])|2([0-4][0-9]|5[0-5])))|35.([0-9]|1[0-
2]))$](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gaadvanced-final1-120327073556-phpapp02/85/Advanced-Google-Analytics-16-320.jpg)






























![<a href="#"
onClick="_gaq.push(['_trackEvent', 'Guides', 'Dow
nload', 'Intro to Genealogy
Research']);”>Download the guide</a>
Category = Guides
Action = Download
Label = Intro to Genealogy Research](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gaadvanced-final1-120327073556-phpapp02/85/Advanced-Google-Analytics-48-320.jpg)



















