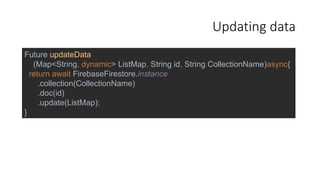
The document covers advanced mobile application development using Firebase, focusing on data management methods such as addition, retrieval, updating, and deletion of data through Firestore in a Flutter environment. It elaborates on the use of streams and StreamBuilder for real-time updates to the UI, emphasizing lifecycle methods such as initState for data initialization. Additionally, it provides example code snippets for various functionalities, showcasing the integration of Firebase Firestore with Flutter widgets.




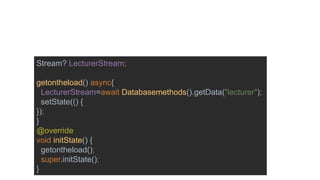

![Building the vessel for the data
Widget allLecDetails(){
return StreamBuilder(
>>> Stream builder settings <<<
? ListView.builder(
>>>ListView setting<<<
return Material(
>>> the card or material elements<<<
);
}):Container();
});
}
>>> Stream builder settings <<<
return StreamBuilder(
stream: LecturerStream,
builder:(context, AsyncSnapshot snapshot){
return snapshot.hasData
? ListView.builder(
>>>ListView setting<<<
? ListView.builder(
itemCount: snapshot.data.docs.length,
itemBuilder: (context, index){
DocumentSnapshot ds=snapshot.data.docs[index];
return Material(](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advmobdev-c05-240305215000-156a9821/85/Advance-Mobile-Application-Development-class-05-7-320.jpg)

![return Material(
elevation: 5.0,
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(10),
child: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(20),
width: MediaQuery.of(context).size.width,
decoration: BoxDecoration(color: Colors.white,borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(10)),
child: Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
Text("name : "+ds["lecName"],
style:TextStyle(color: Colors.blue,fontSize: 20.0, fontWeight: FontWeight.bold) ),
Text("college : "+ds["lecCol"],
style:TextStyle(color: Colors.blue,fontSize: 20.0, fontWeight: FontWeight.bold) ),
Text("Department : "+ds["lecDept"],
style:TextStyle(color: Colors.blue,fontSize: 20.0, fontWeight: FontWeight.bold) ),
Text("Phone No. : "+ds["lecPhNo"],
style:TextStyle(color: Colors.blue,fontSize: 20.0, fontWeight: FontWeight.bold) ),
],
),
),
);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advmobdev-c05-240305215000-156a9821/85/Advance-Mobile-Application-Development-class-05-9-320.jpg)
![@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
backgroundColor: Theme.of(context).colorScheme.inversePrimary,
title: Text(“Lecturers of Seiyun University"),
),
body: Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16.0),
child: Column(
children: [
Expanded(child: allLecDetails()),
]
)
)
);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advmobdev-c05-240305215000-156a9821/85/Advance-Mobile-Application-Development-class-05-10-320.jpg)

![child: Column(
children: [
TextField(
controller: collectionname,
),
TextField(
controller: docname,
),
TextField(
controller: docvalue,
),
ElevatedButton(
child: Text(
""بحث,
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 16.0,
),
),
),
]
)
onPressed: () async{
LecturerStream=await Databasemethods()
.getselectedData(collectionname.text,docname.text,docvalue.text)
.then((value) {
Navigator.push(
context,
MaterialPageRoute(
builder: (context) => Showdata(LecturerStream: value),
),
);
});
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advmobdev-c05-240305215000-156a9821/85/Advance-Mobile-Application-Development-class-05-12-320.jpg)