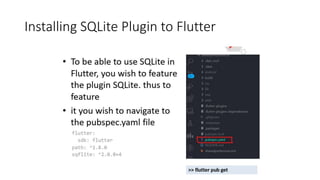
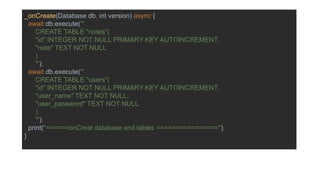
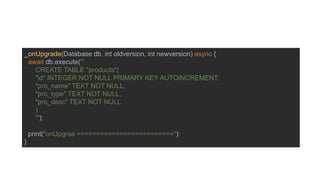
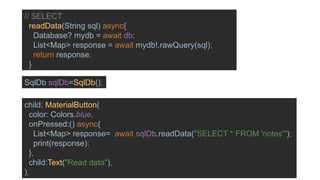
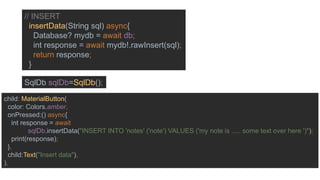
The document discusses advanced mobile application development focusing on local databases using Flutter, specifically highlighting the sqflite package for SQLite databases and its capabilities. It illustrates how to set up, create, read, update, and delete database entries with relevant code snippets. SQLite is emphasized as a widely used, serverless database engine suitable for mobile applications.