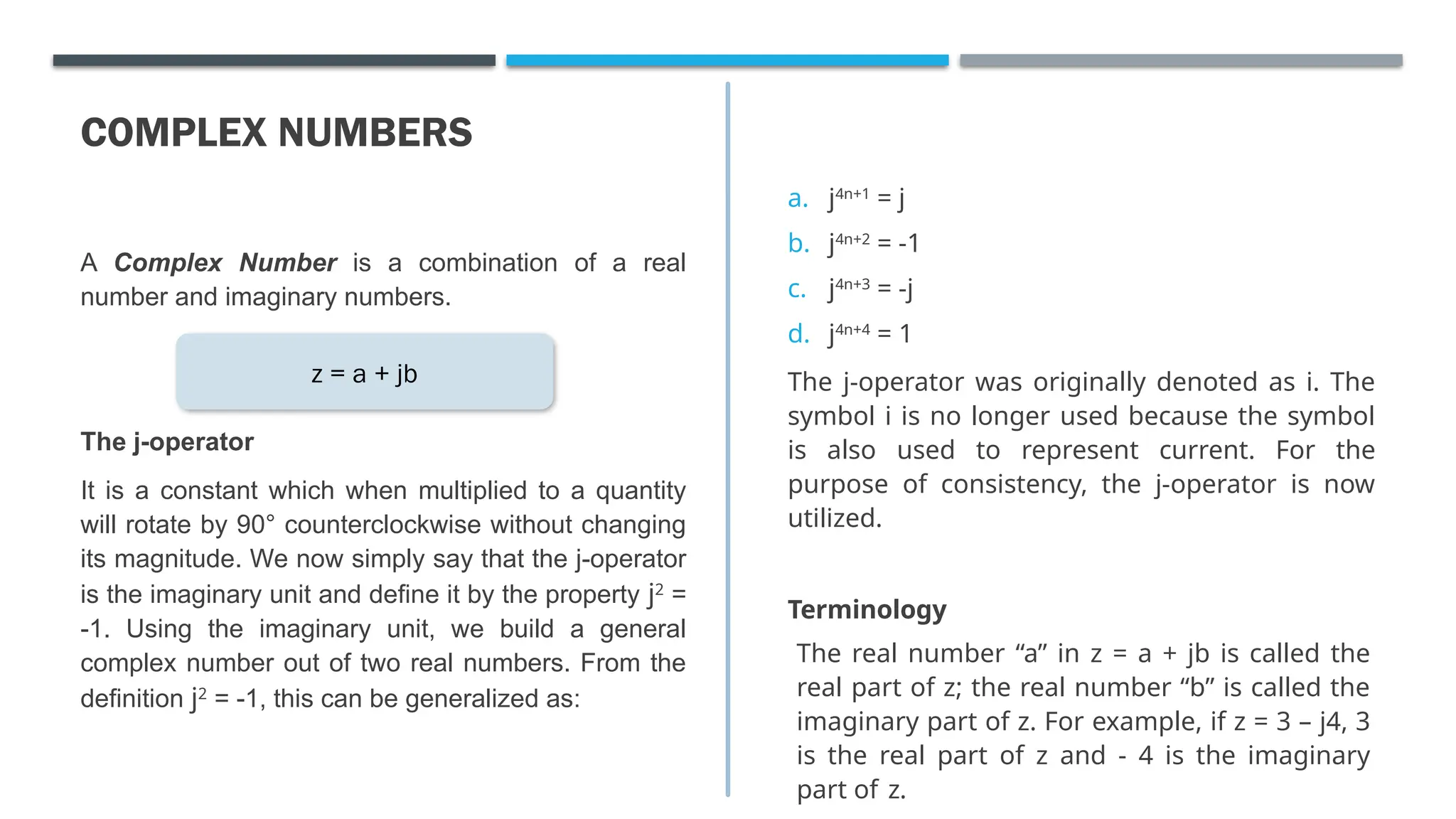
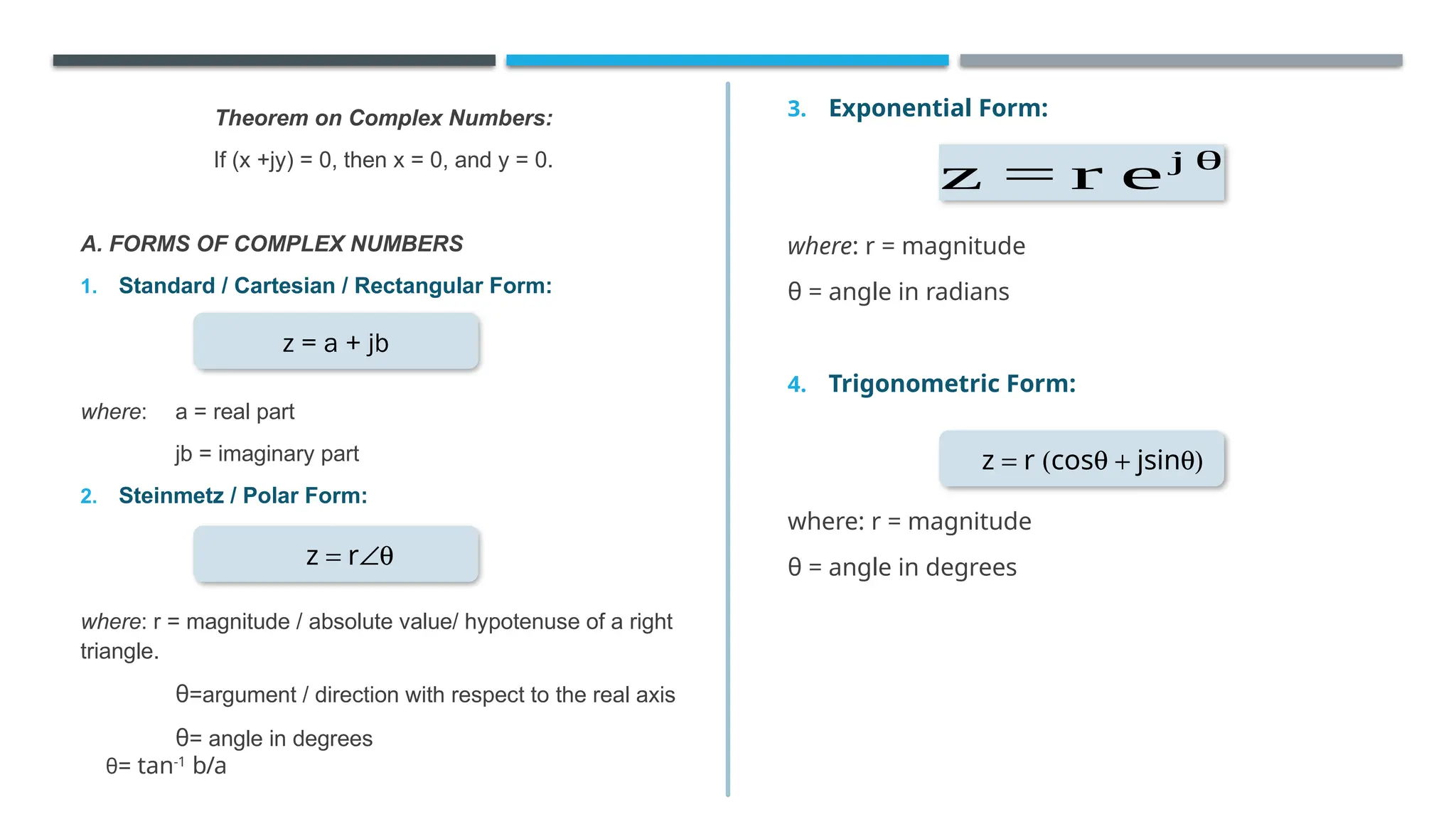
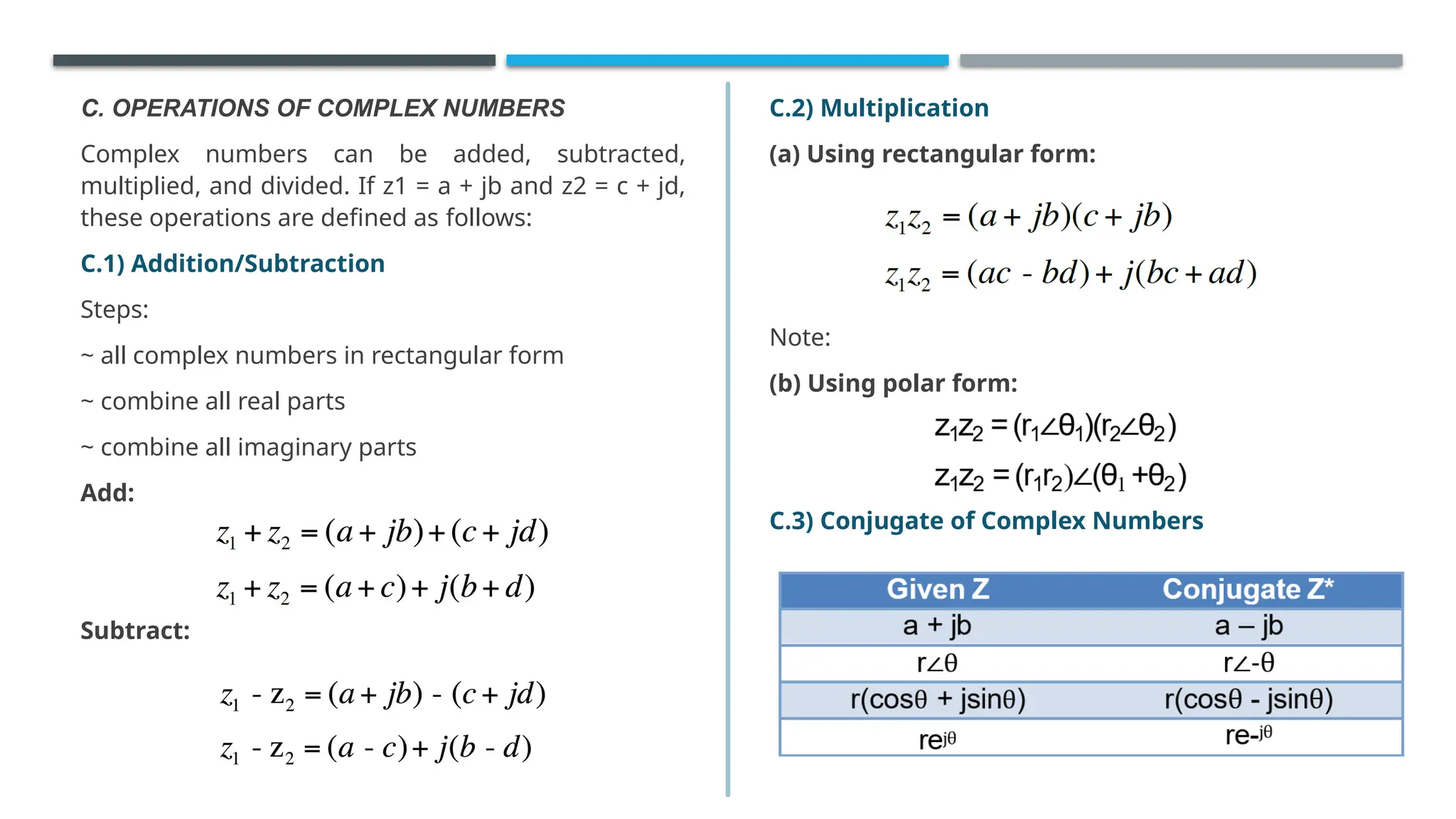
The document outlines the fundamentals of complex numbers, introducing the j-operator as an imaginary unit defined by the property j² = -1. It explains various forms of complex numbers, including standard, polar, exponential, and trigonometric forms, along with the methods for transforming between these forms and performing arithmetic operations. Additionally, it defines the real and imaginary parts of a complex number and presents the theorem stating that if (x + jy) = 0, then both x and y must equal zero.