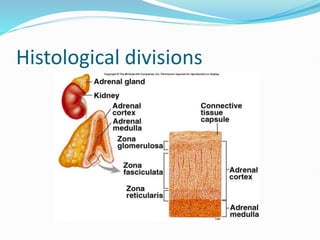
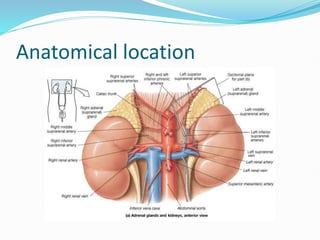
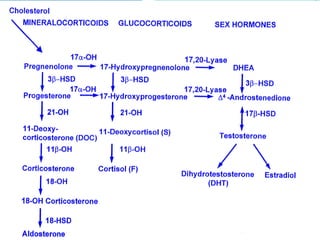
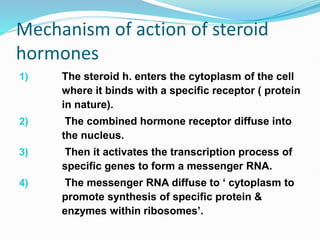
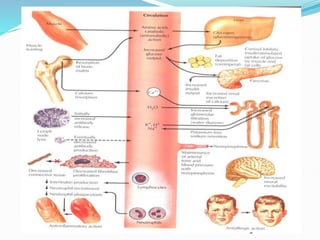
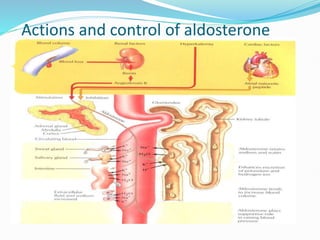
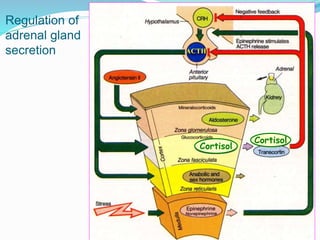
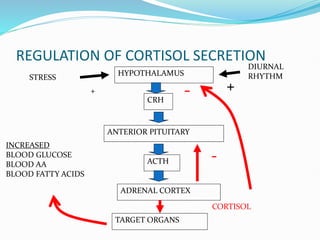
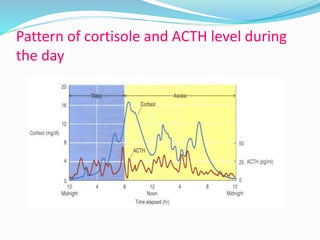
The document discusses the anatomy, histology, and functions of the adrenal glands. It describes the adrenal cortex and medulla. The adrenal cortex secretes corticosteroids like cortisol and aldosterone which regulate metabolism, immune function, and electrolyte balance. The adrenal medulla secretes catecholamines like epinephrine. Tests are discussed to evaluate hypercortisolism, hypoadrenalism, hyperaldosteronism, and pheochromocytoma.