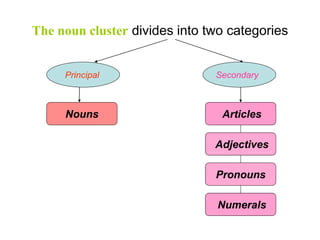
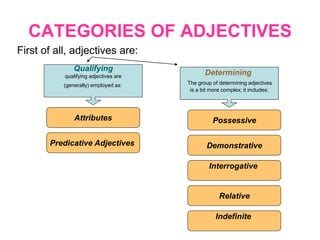
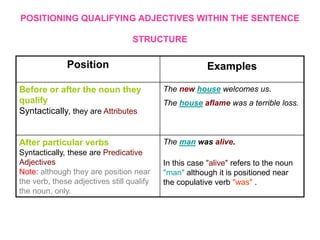
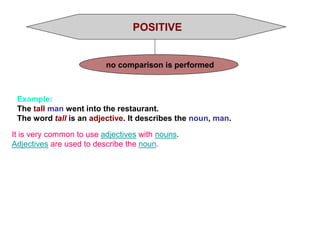
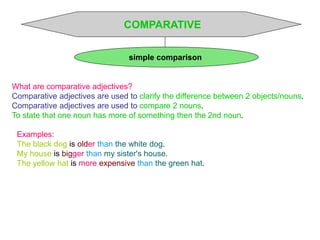
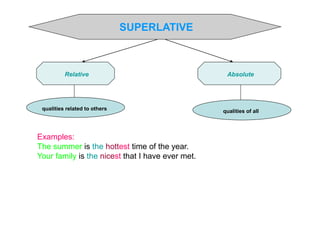
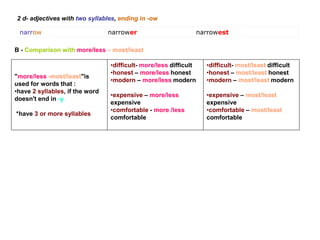
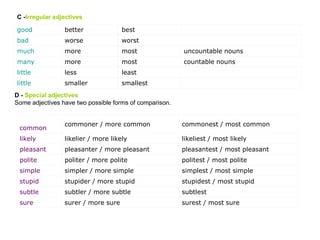
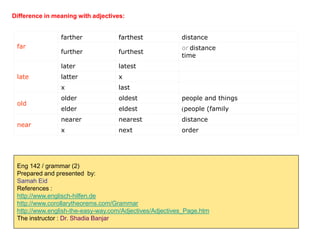
This document discusses different types of adjectives and how to use them correctly. It defines adjectives as words used to qualify or describe nouns. Adjectives are divided into two main categories: qualifying adjectives and determining adjectives. Qualifying adjectives can be used attributively or predicatively and can be compared using comparative and superlative forms with suffixes like -er/-est or more/most. Determining adjectives include possessive, demonstrative, interrogative, and relative adjectives. The document provides examples and guidelines for forming comparative and superlative adjectives regularly and irregularly. It also discusses the positioning of adjectives and differences in meanings between related terms.