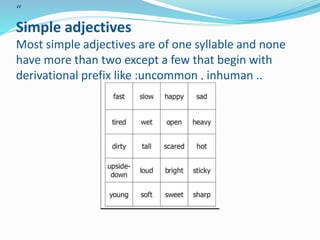
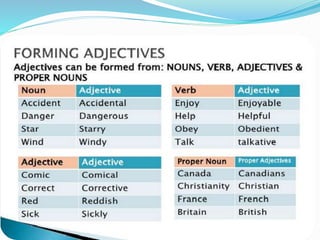
Adjectives are words that provide information about nouns, describing qualities like size, age, color, and more. In English, adjectives have the same form regardless of the number or gender of the noun. Adjectives can be simple one-syllable words, derived words formed with suffixes, participles, or compound words formed by combining two or more words. Adjectives function either attributively by coming before a noun, or predicatively by coming after a linking verb and complementing the subject.