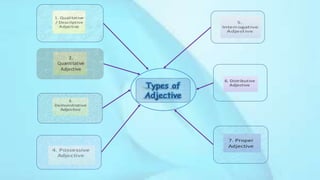
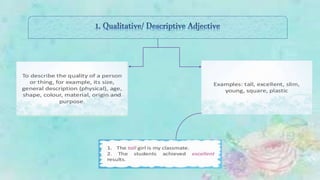
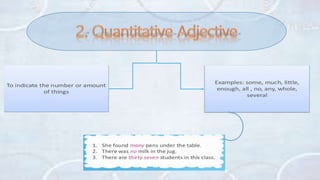
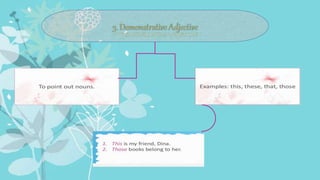
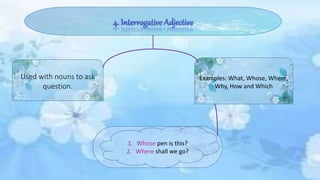
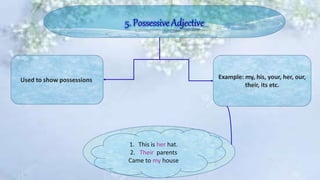
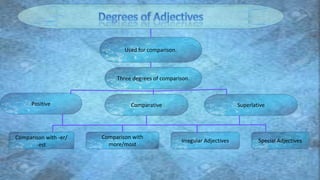
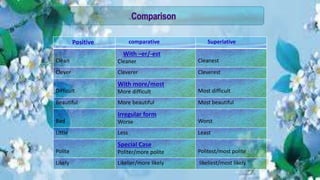
An adjective is a part of speech that describes, identifies, or quantifies a noun or pronoun. There are several types of adjectives including descriptive adjectives, demonstrative adjectives, possessive adjectives, interrogative adjectives, distributive adjectives, and proper adjectives. Adjectives can also be compared using degrees of comparison such as positive, comparative, and superlative forms. When using multiple adjectives, there is generally a standard order with adjectives describing opinion, size, age, and other attributes coming before those of color, origin, or purpose.