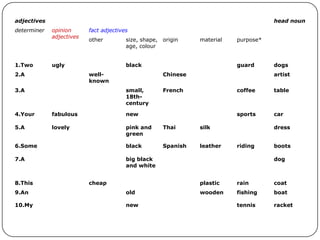
1. Adjectives modify nouns and provide additional information about them. Determiners like articles and possessives precede noun phrases.
2. There is generally an order for multiple adjectives before nouns - opinion adjectives come before fact adjectives, which follow a pattern of size, shape, age, color, origin, material, and purpose.
3. Comparative adjectives compare two things using "-er" or "more" and superlative adjectives express the highest degree using "-est" or "most".