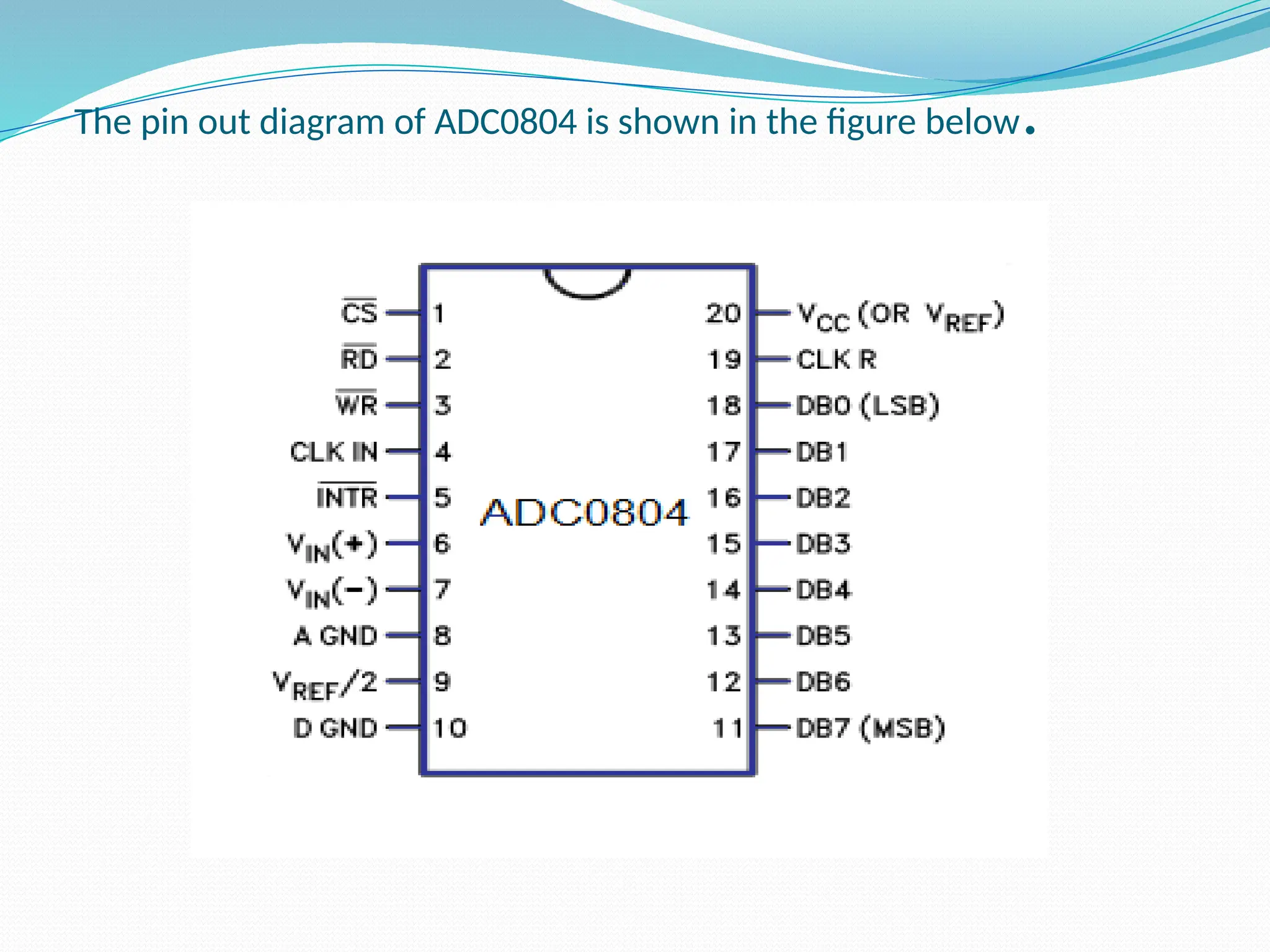
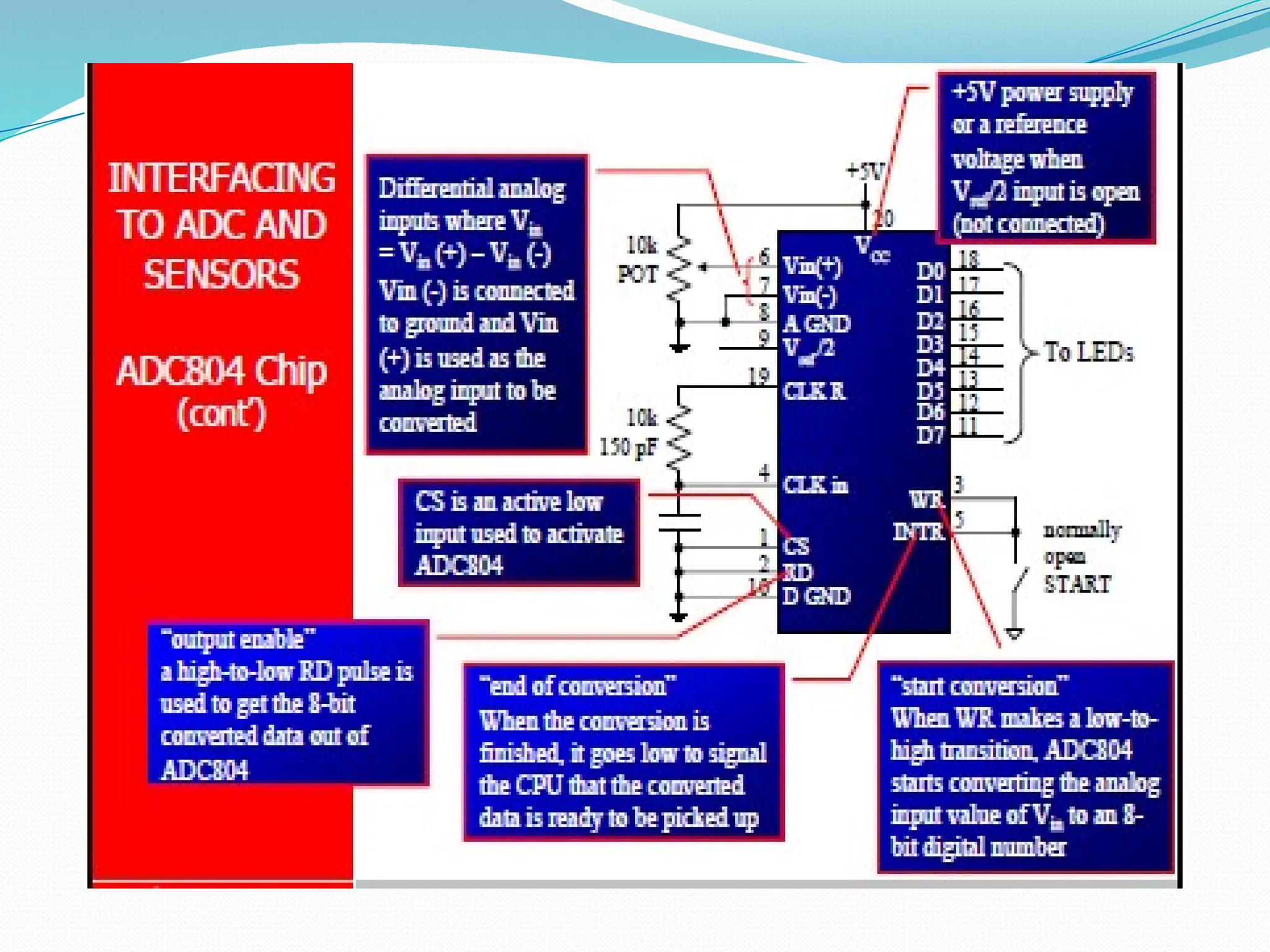
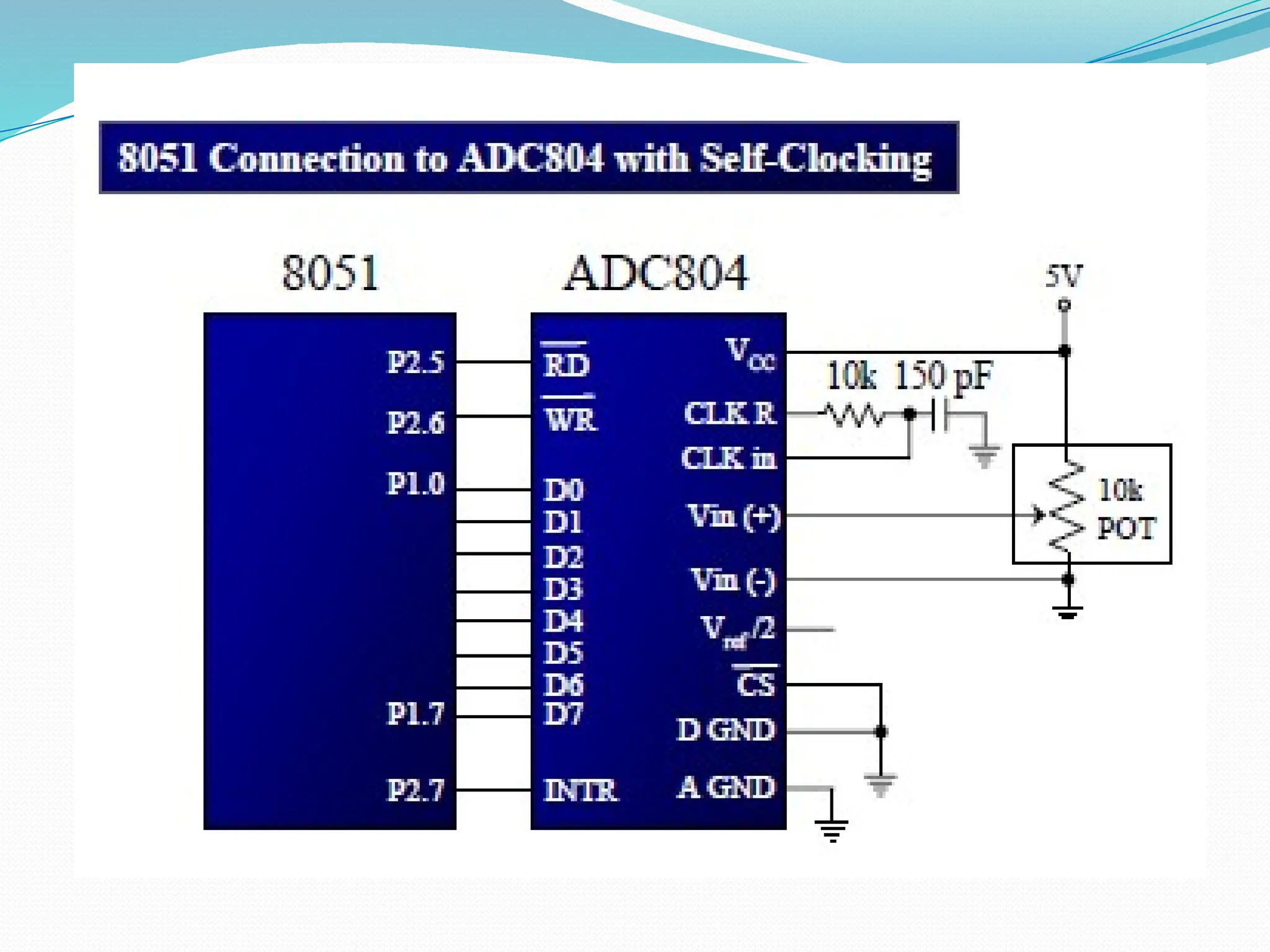
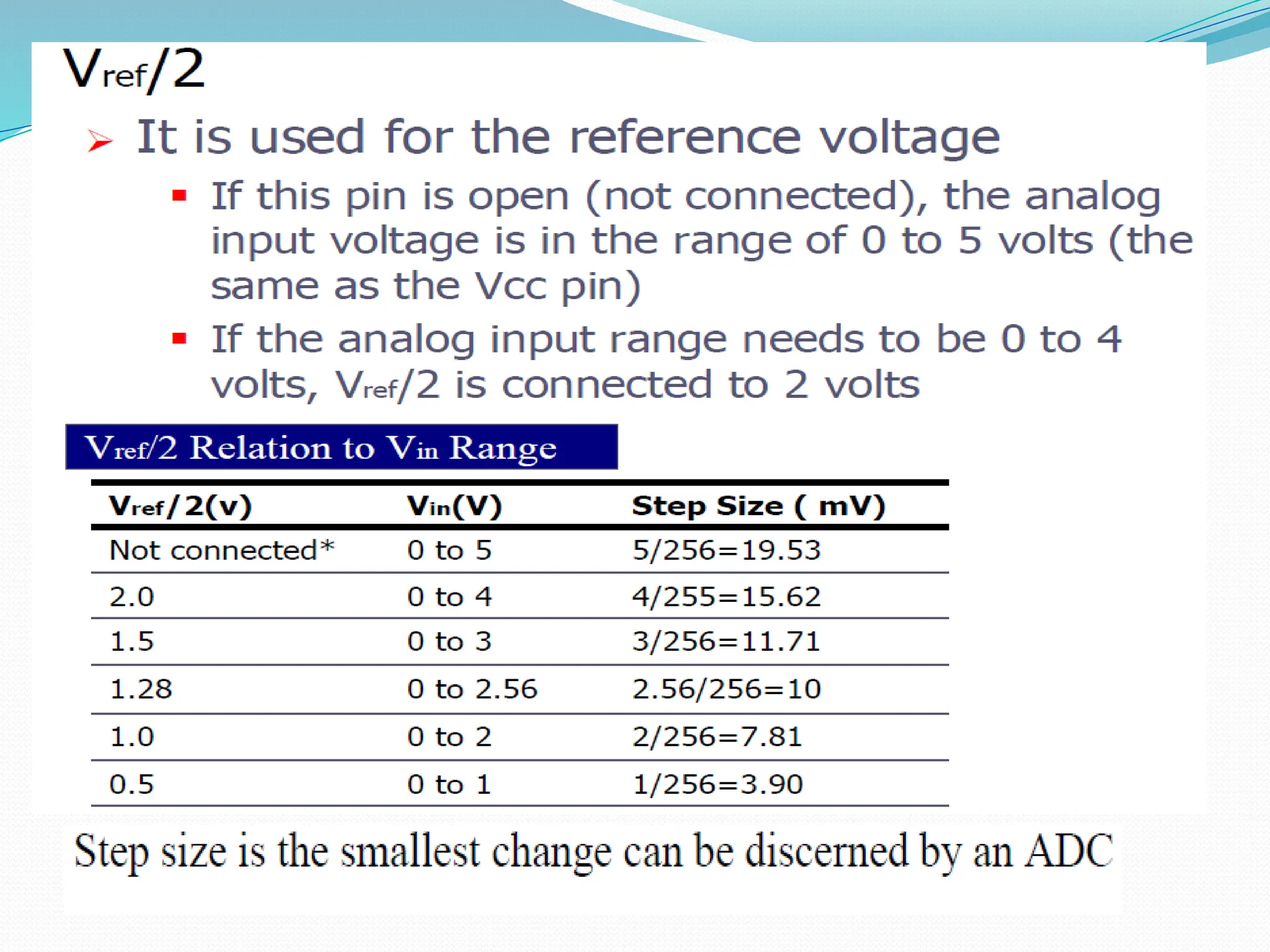
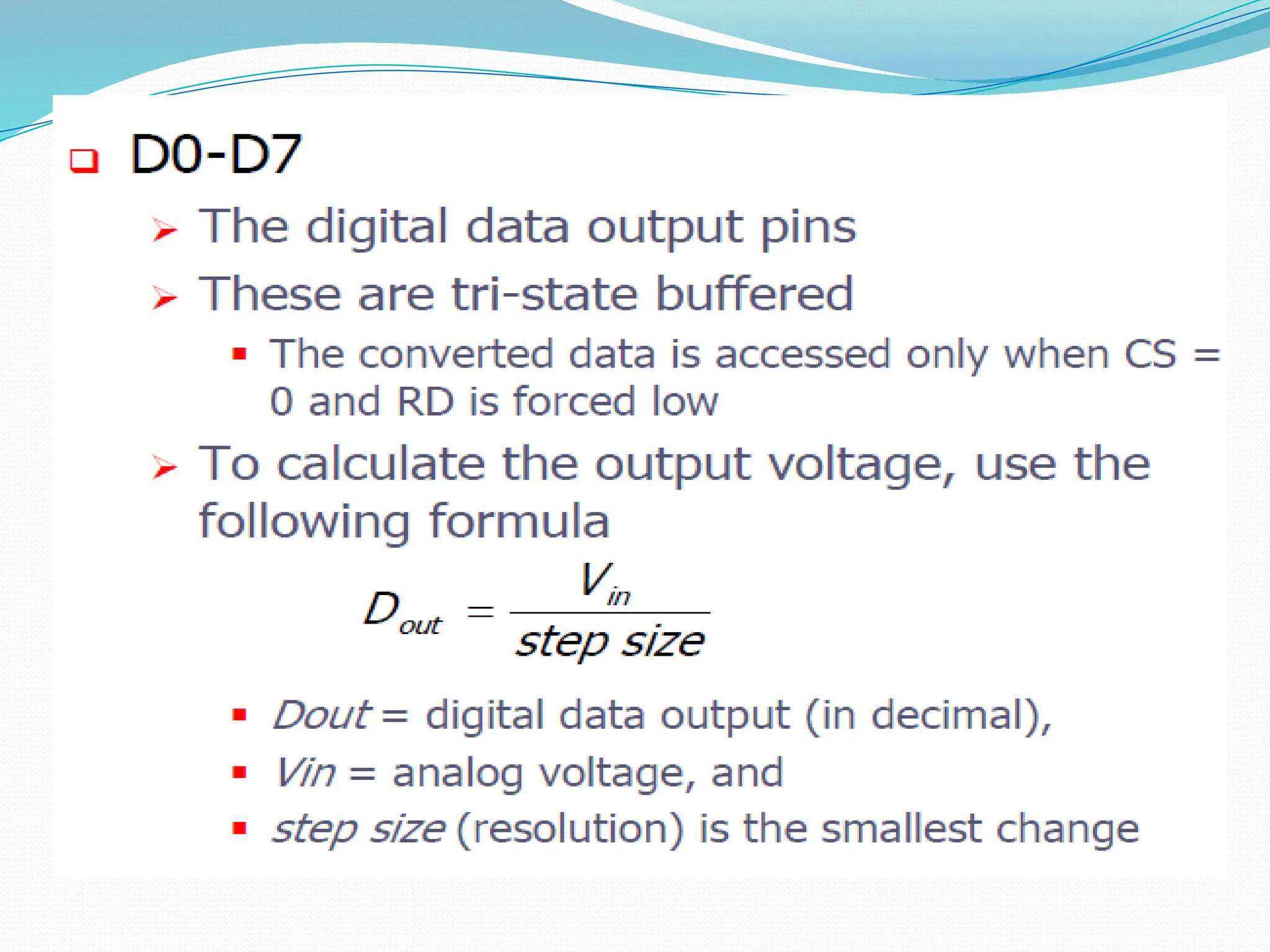
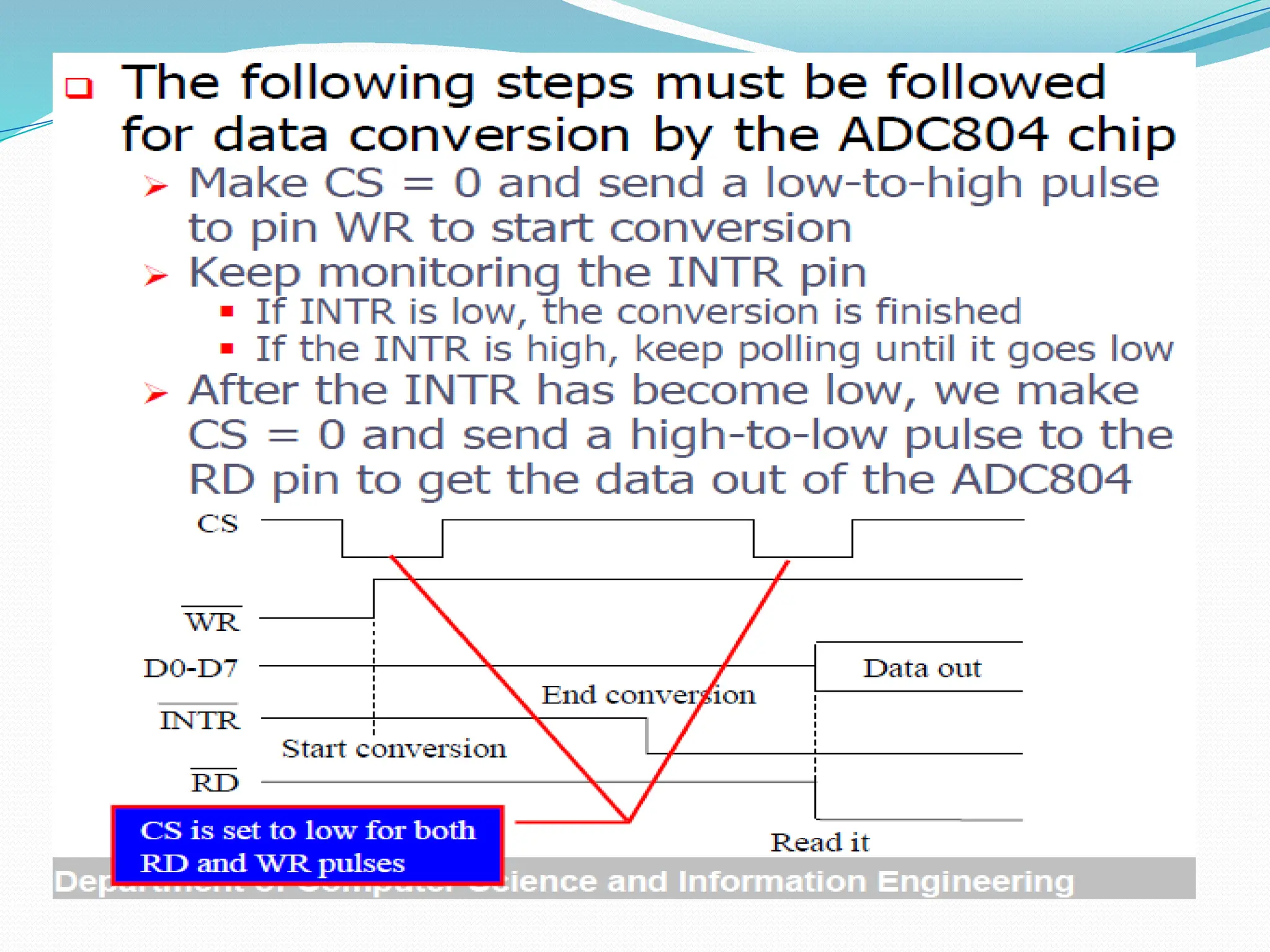
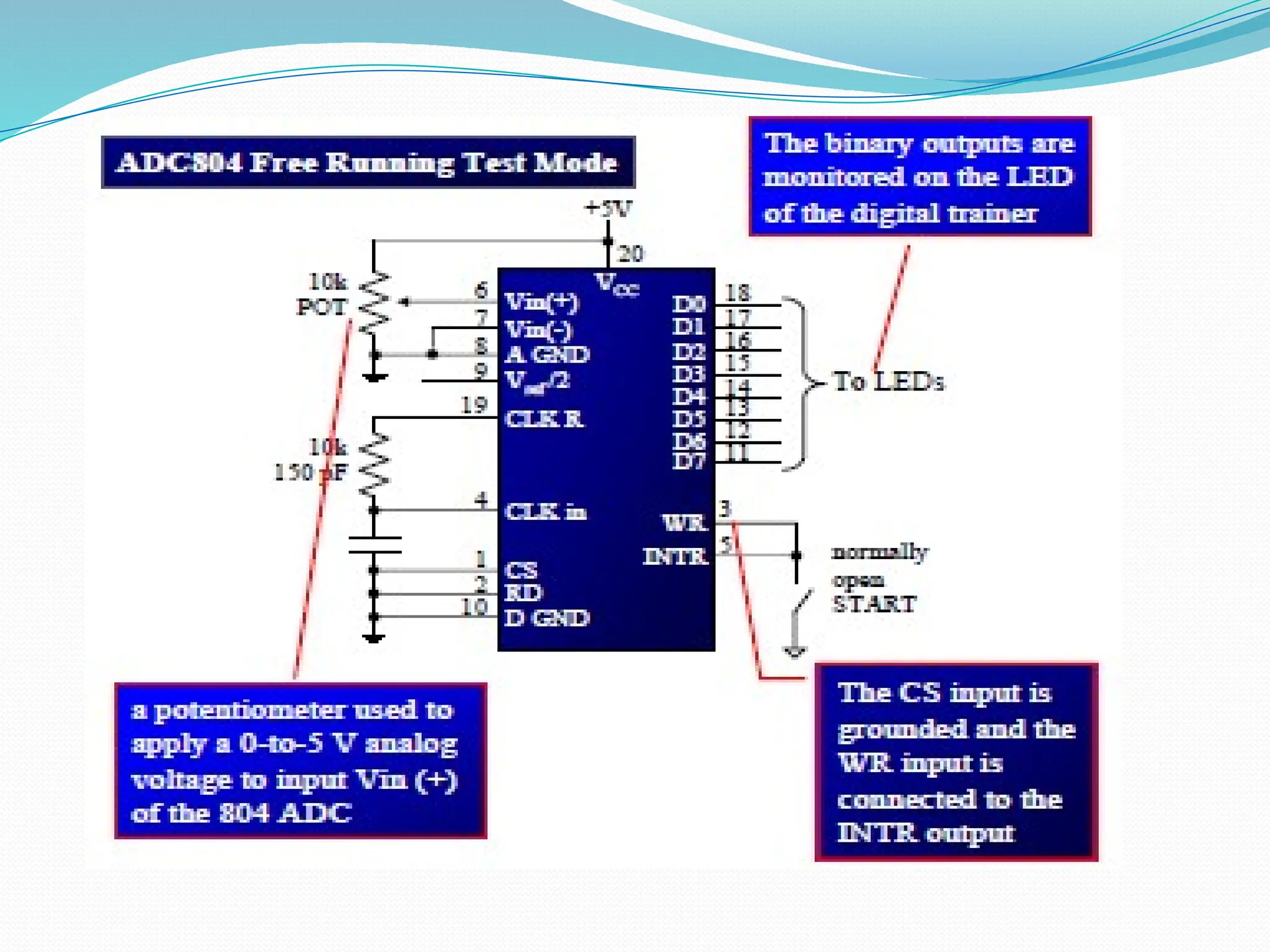
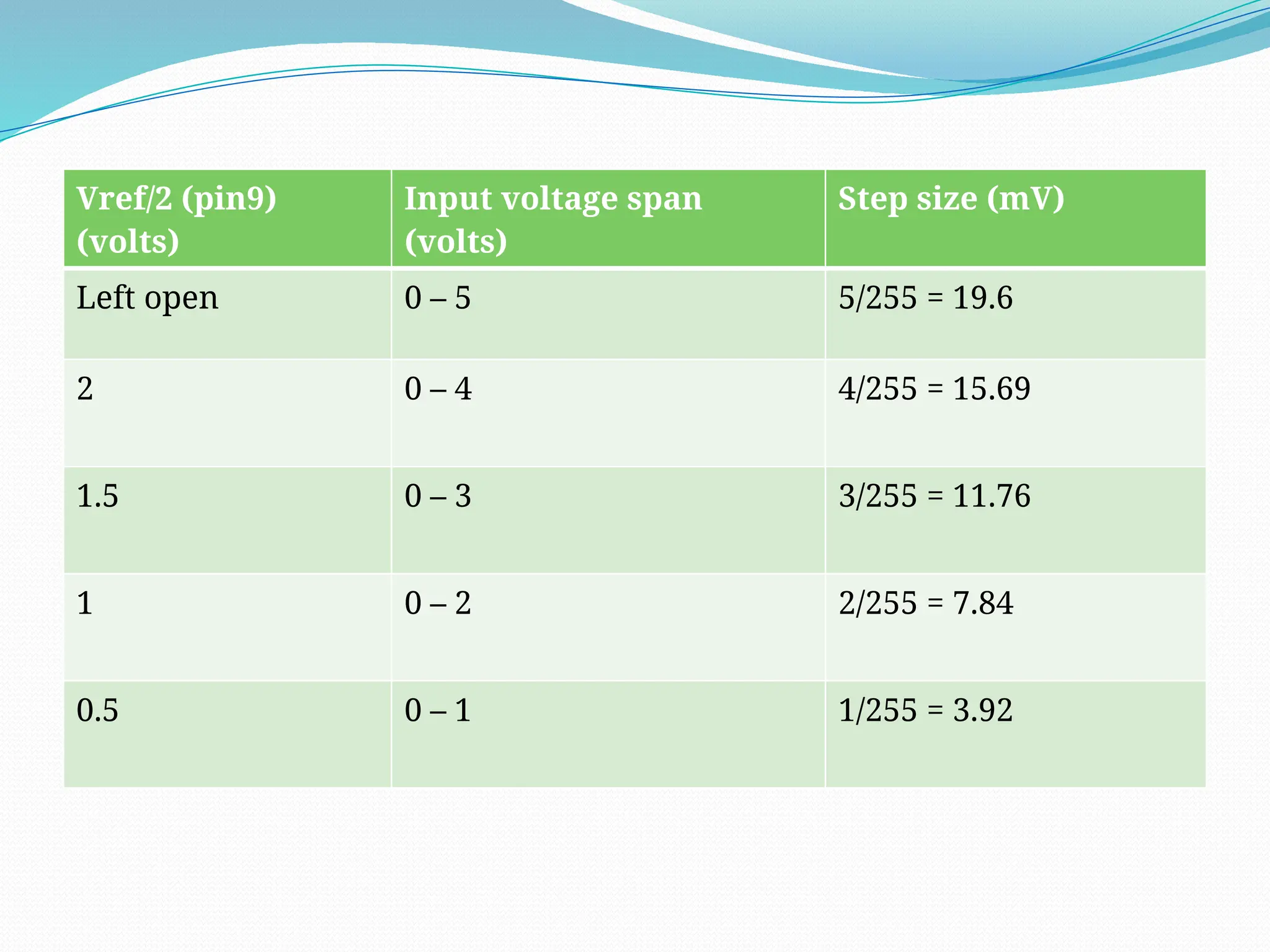
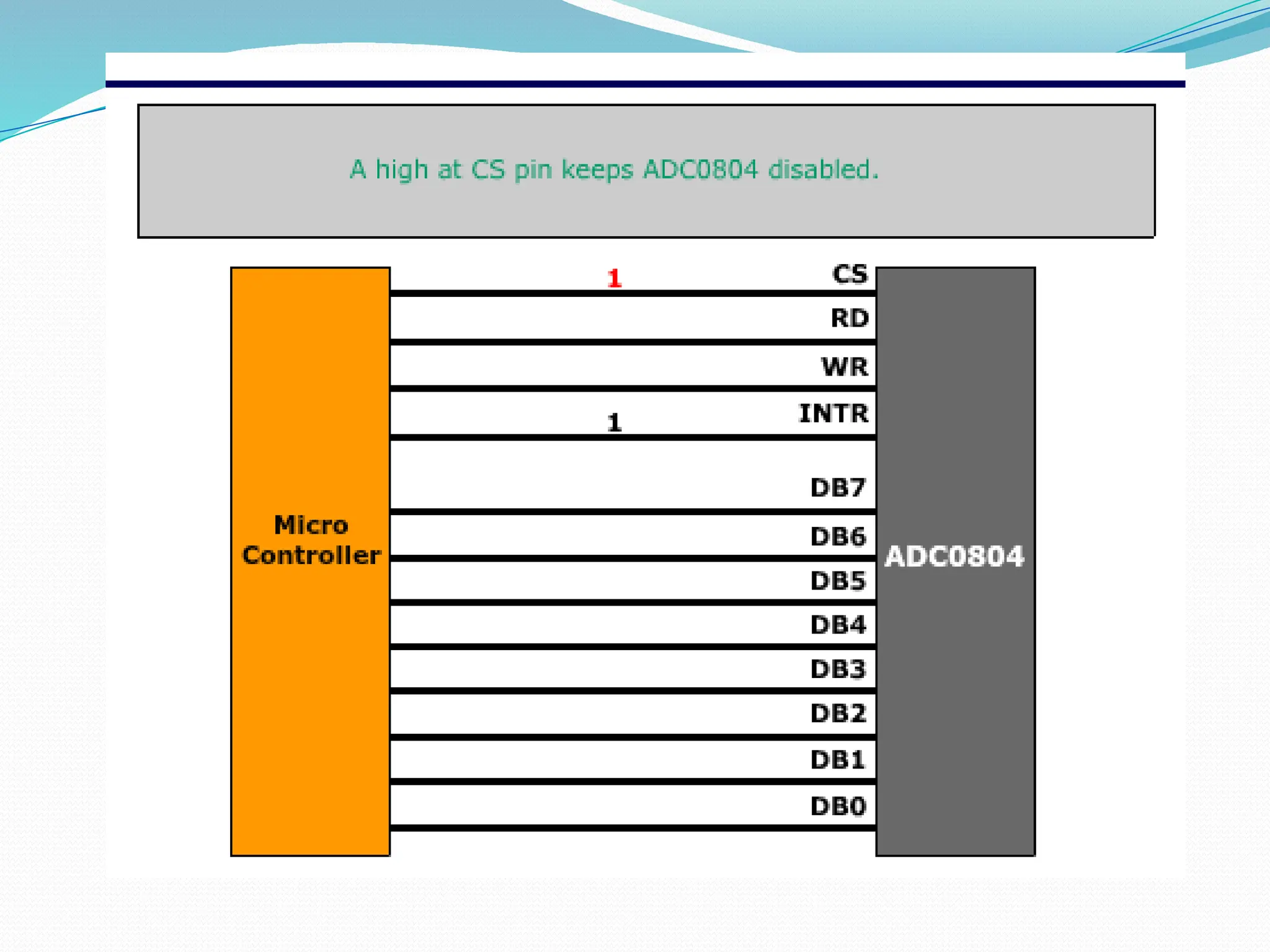
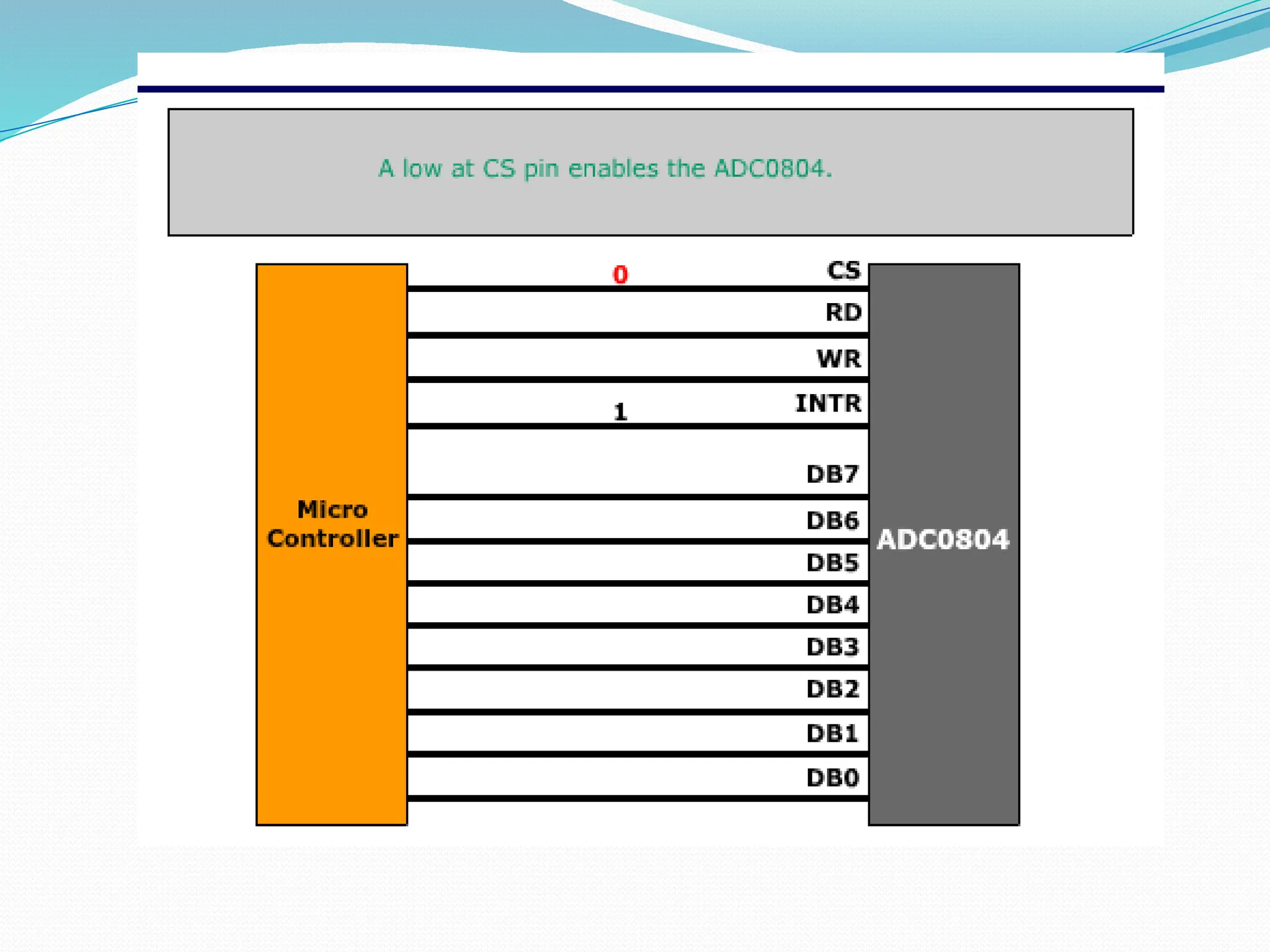
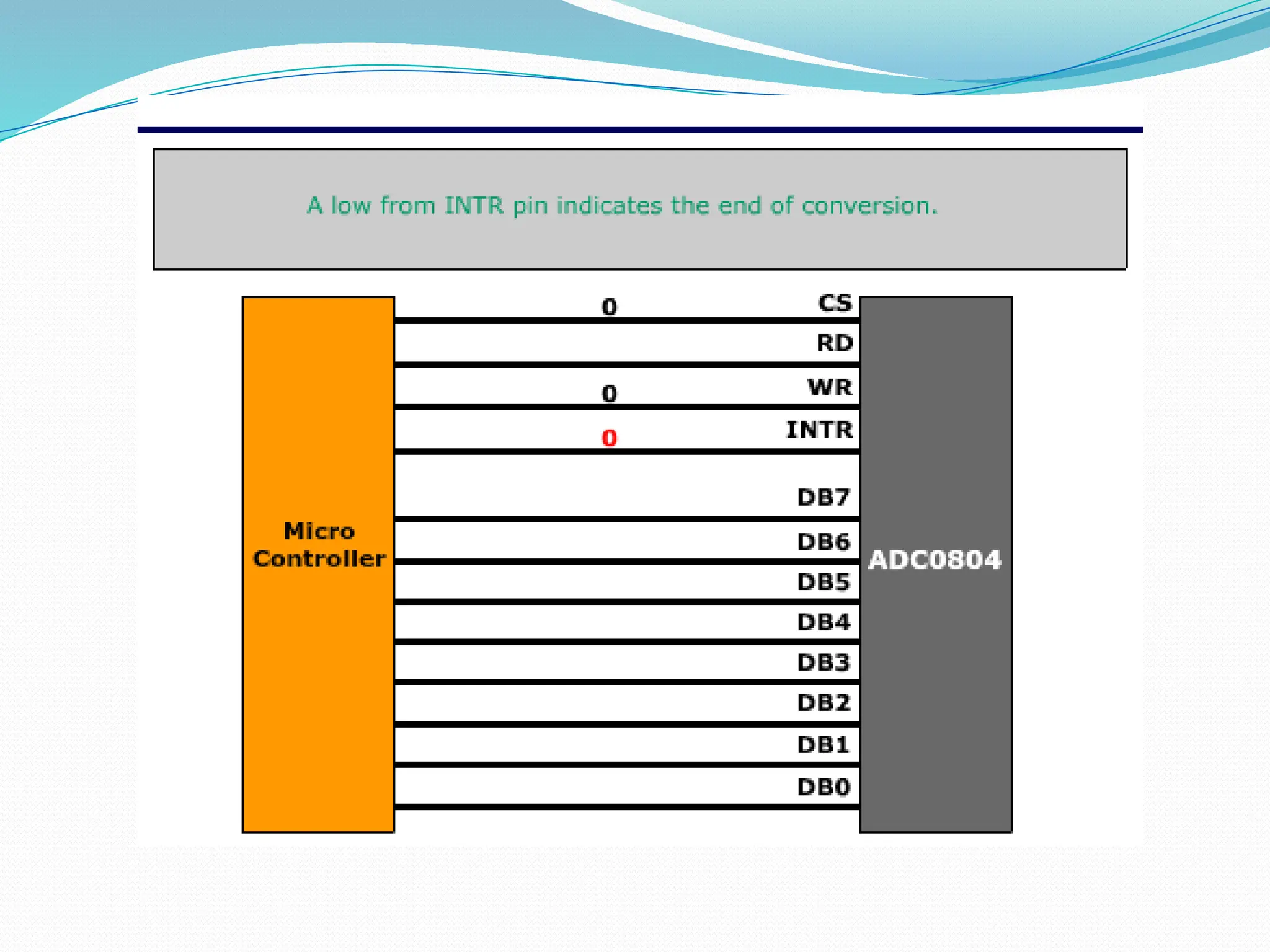
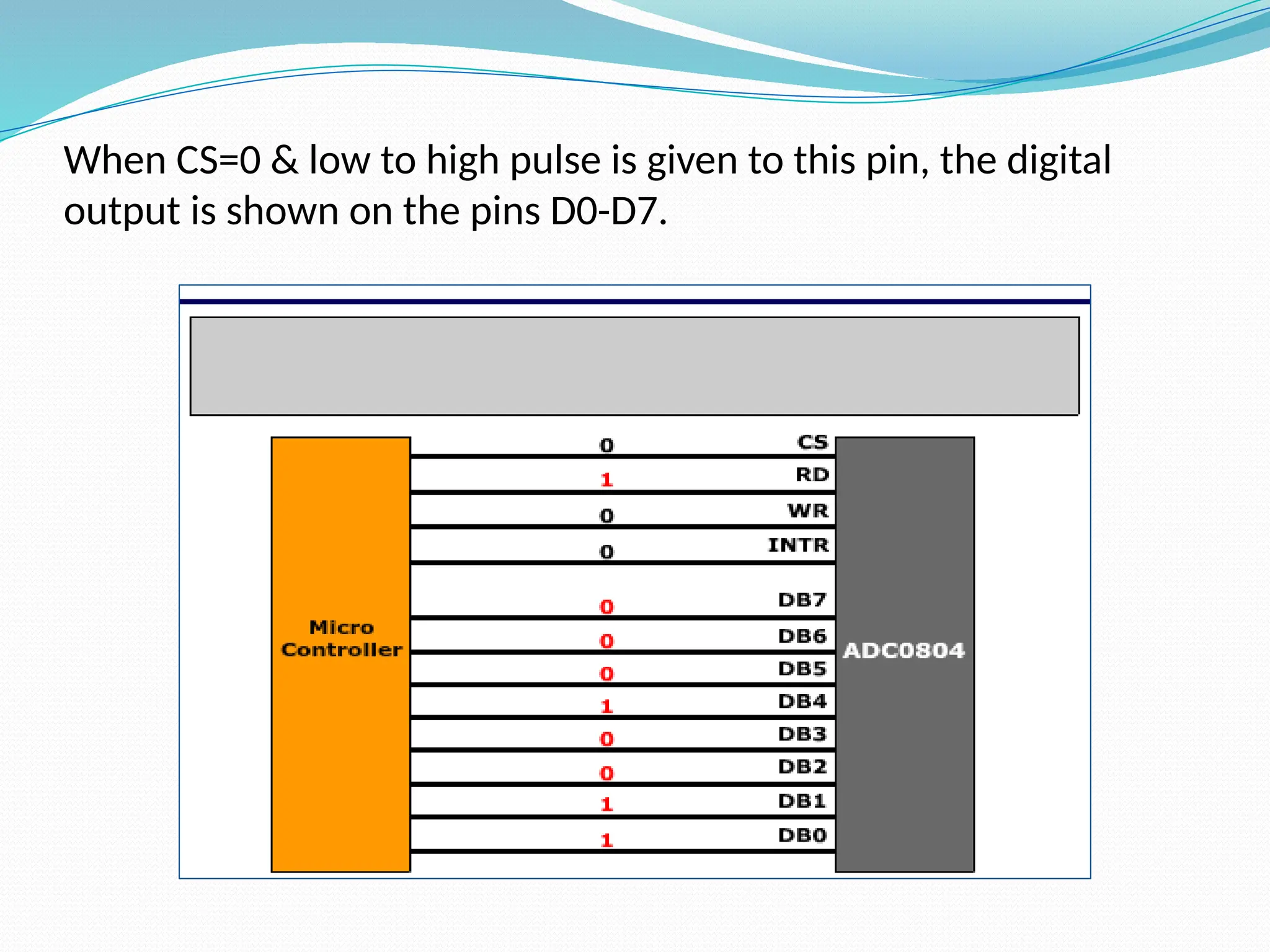
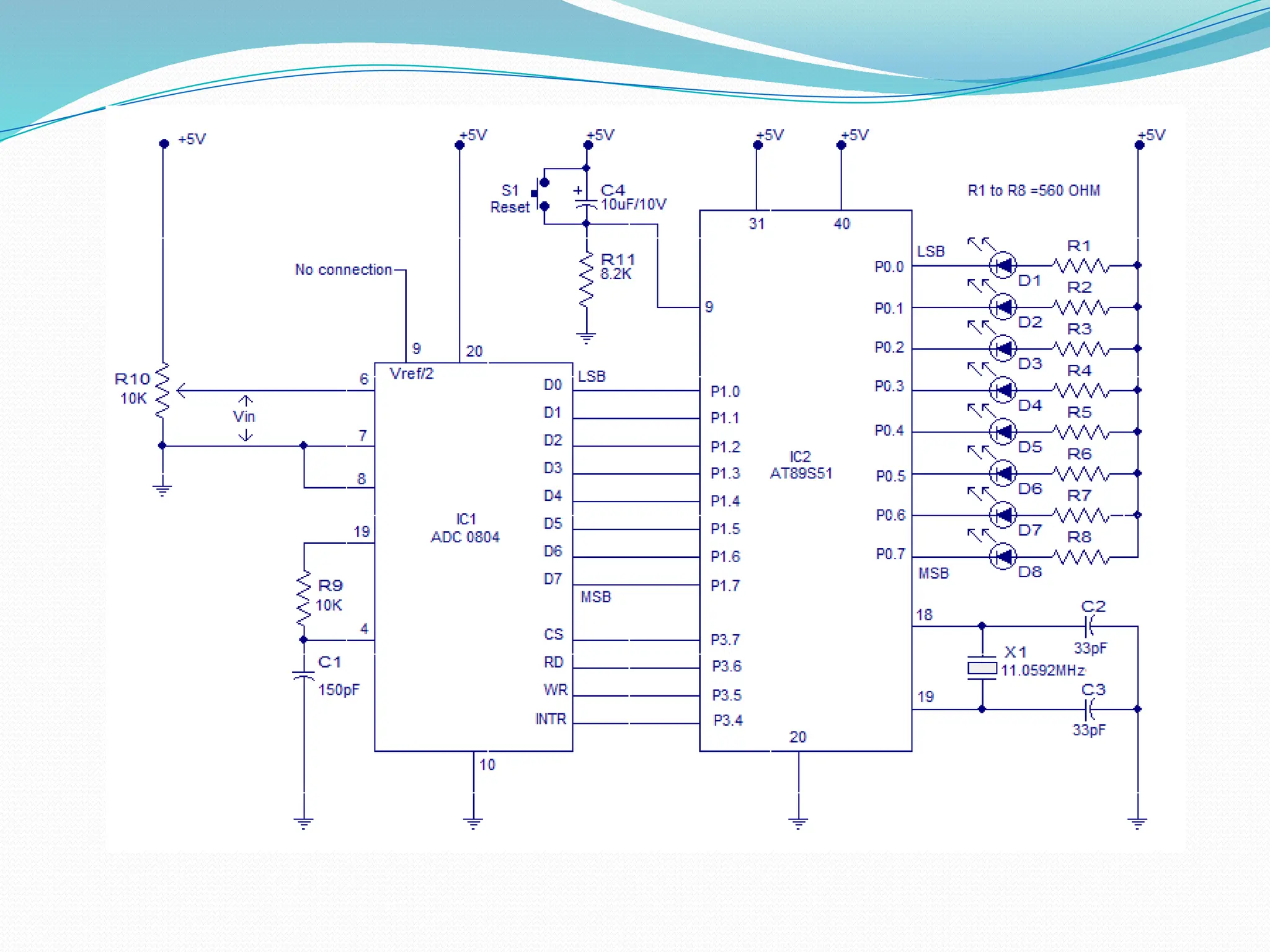
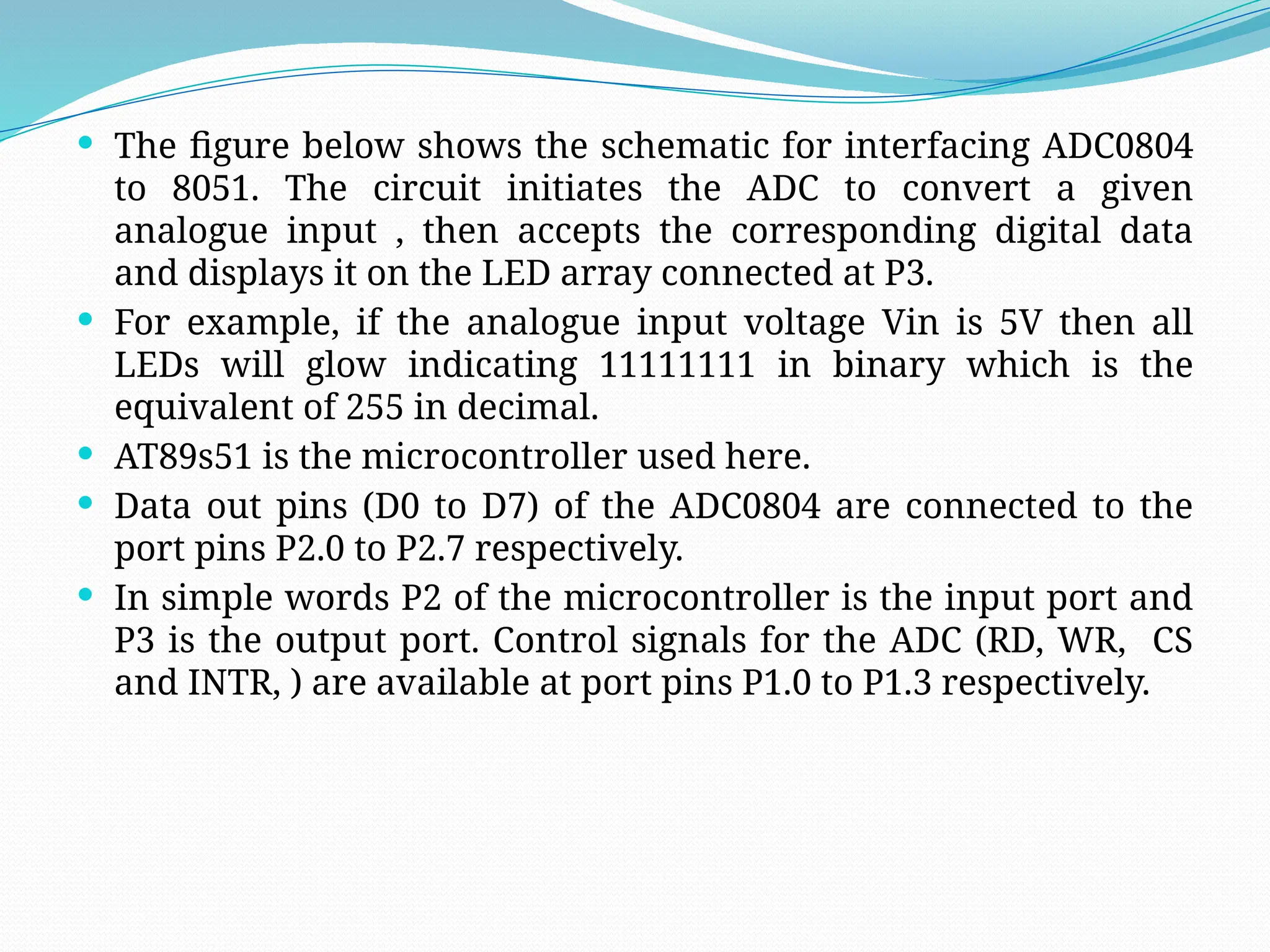
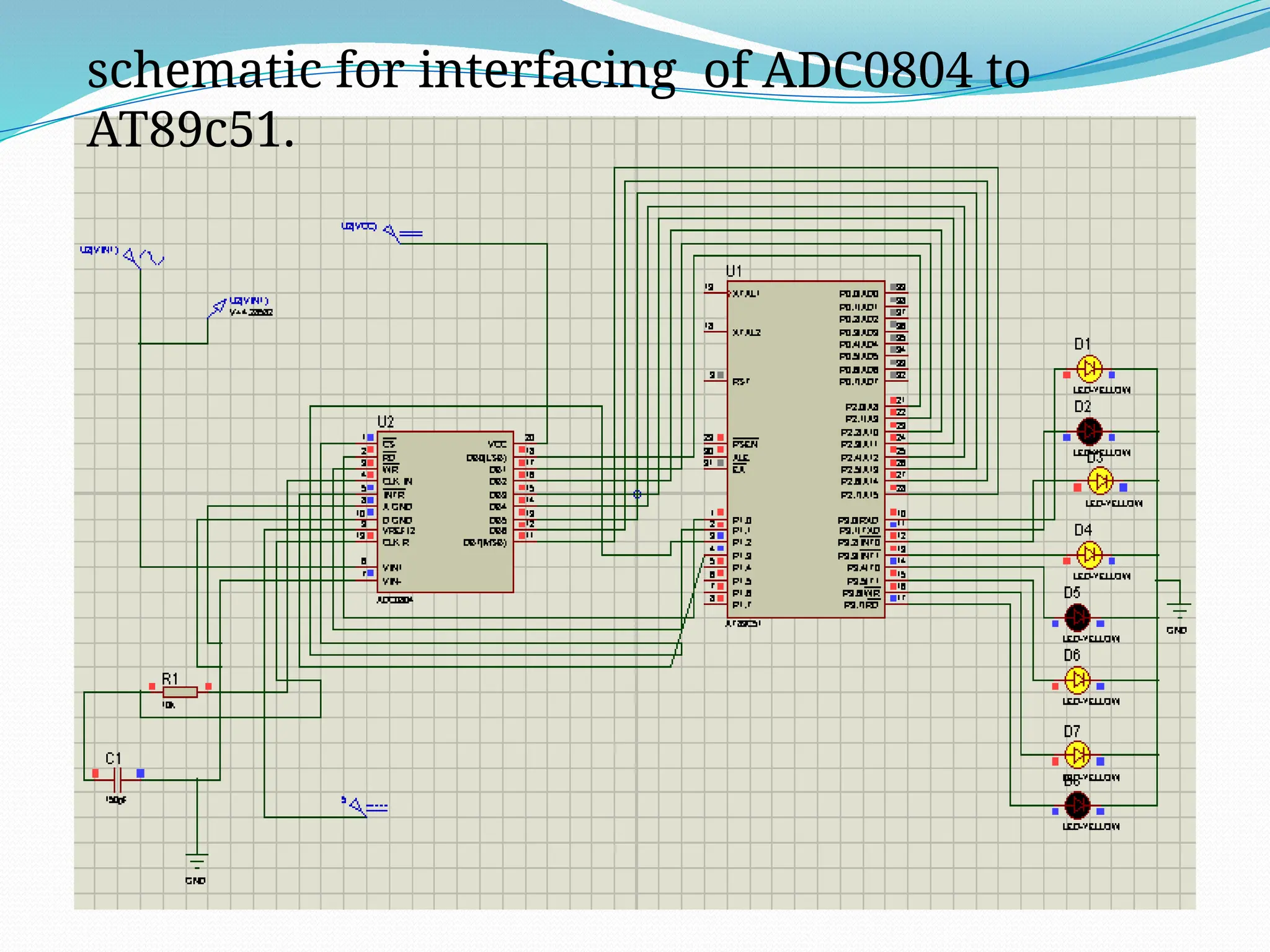
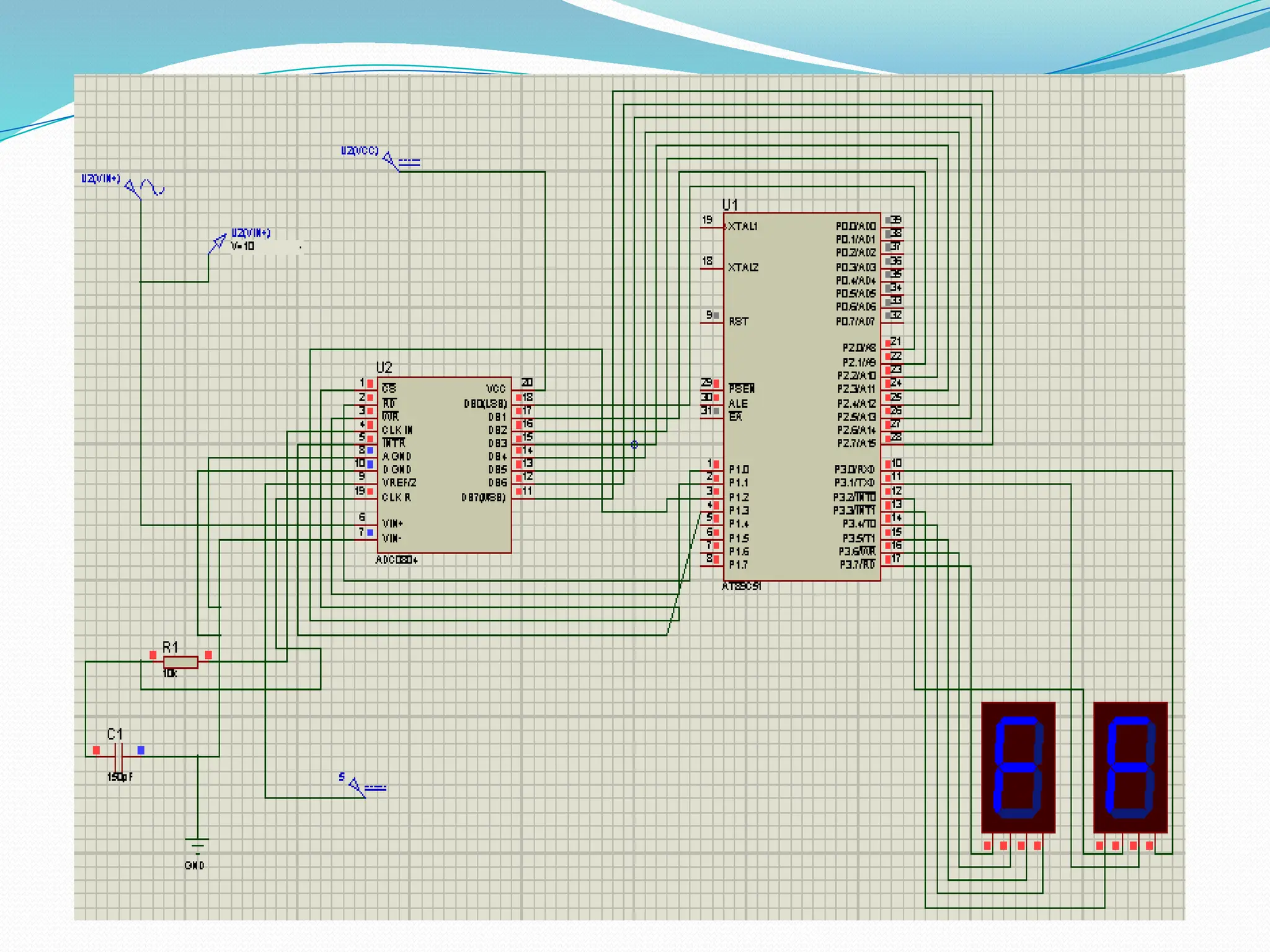
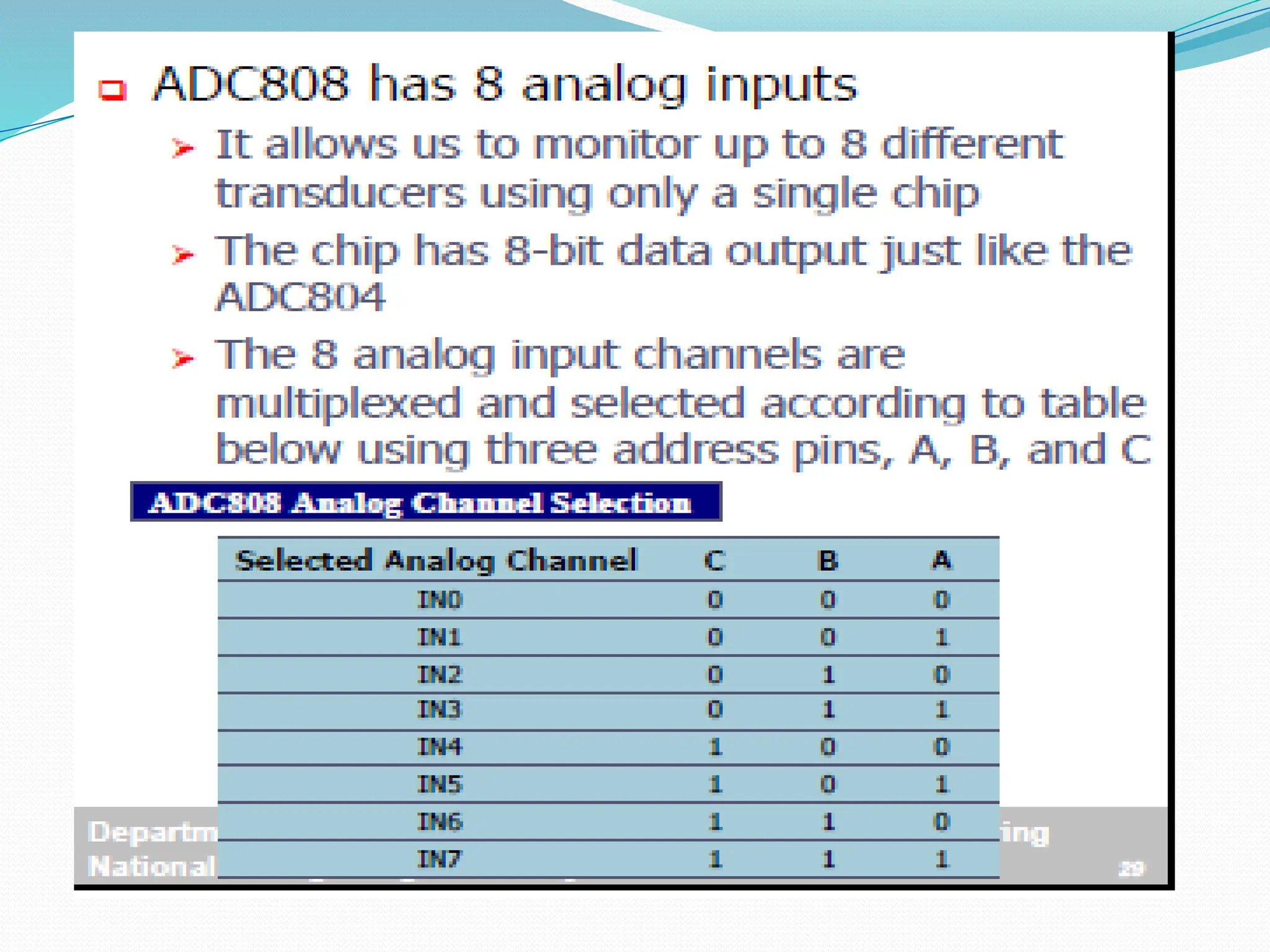
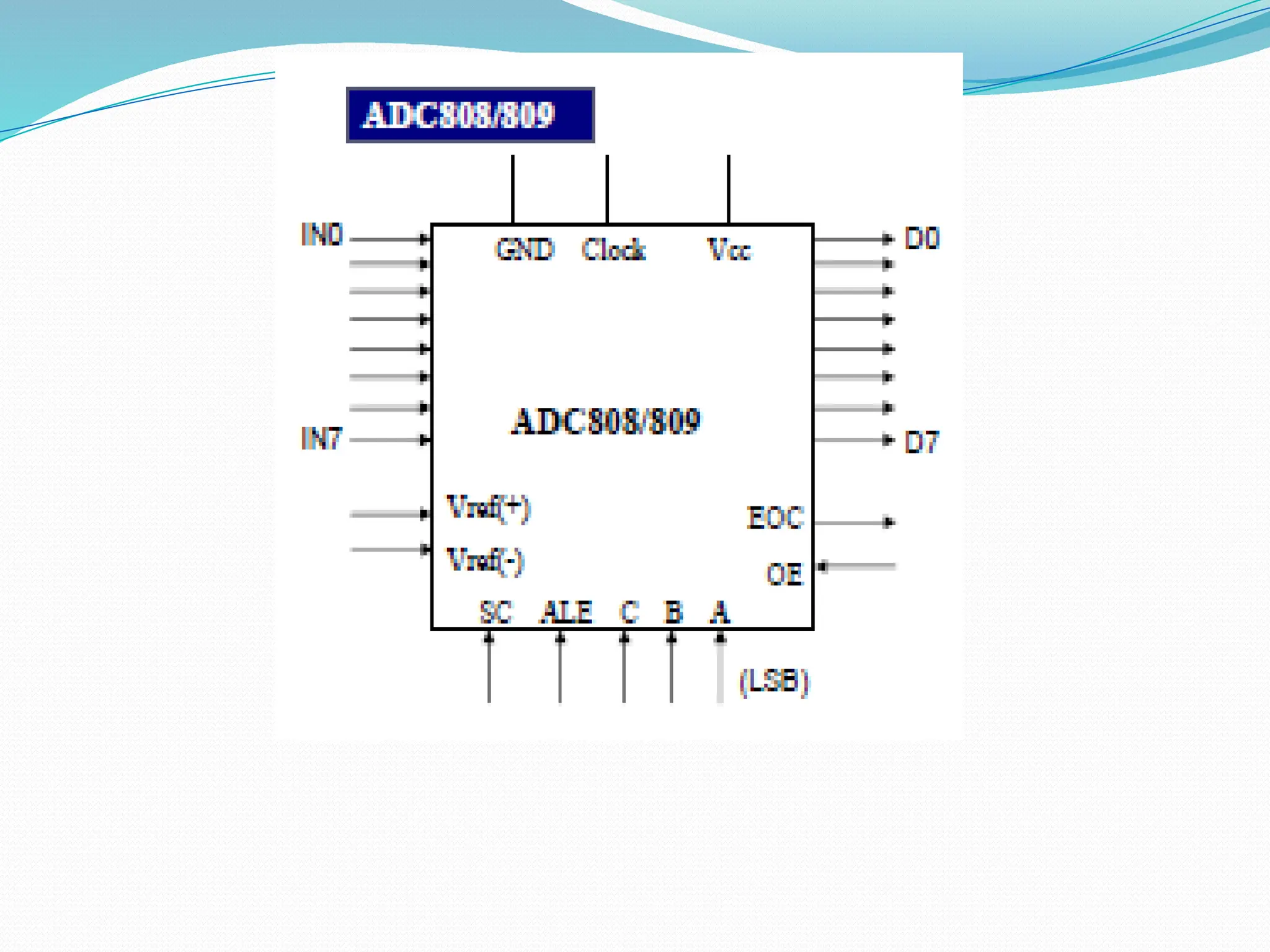
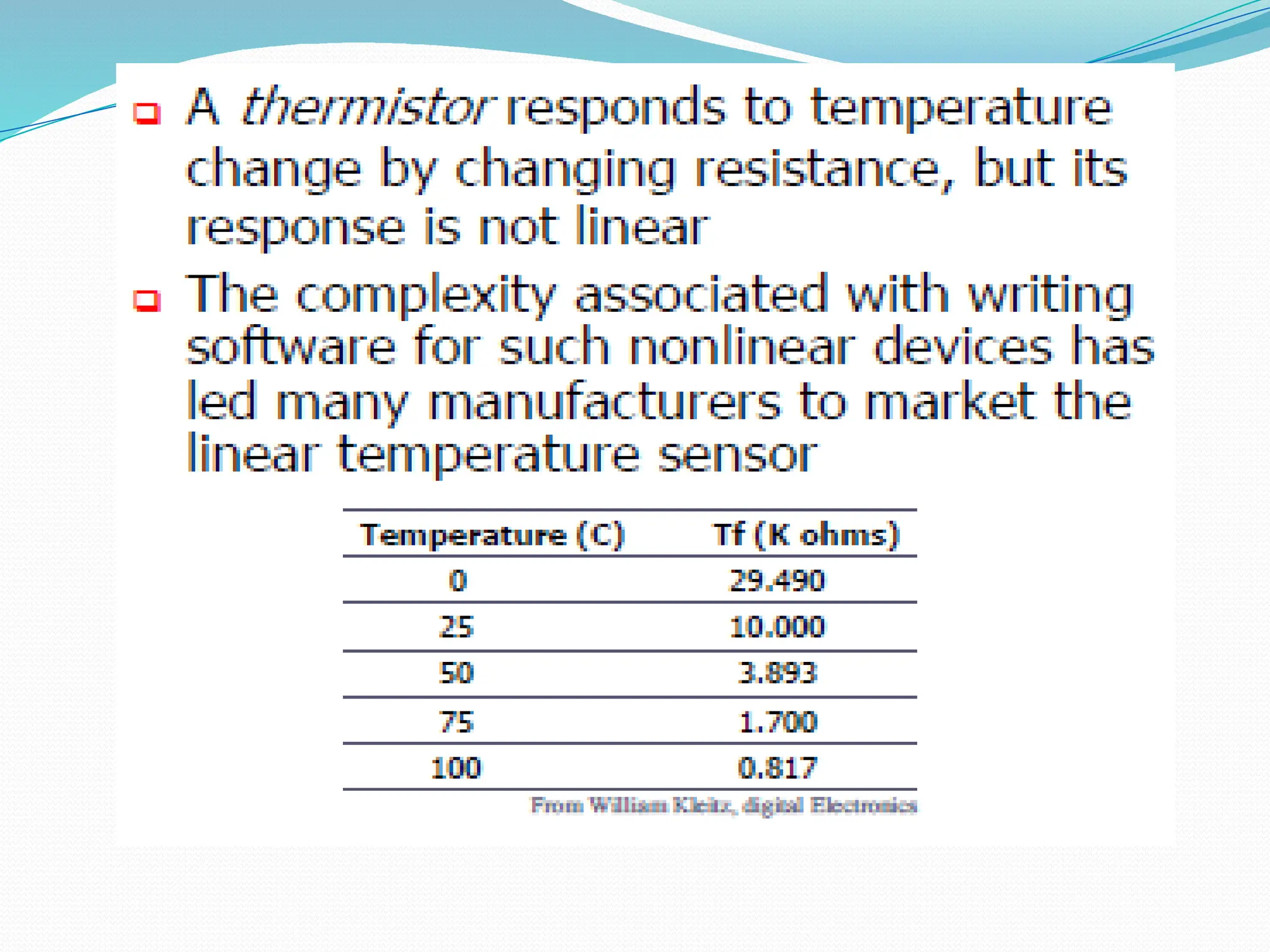
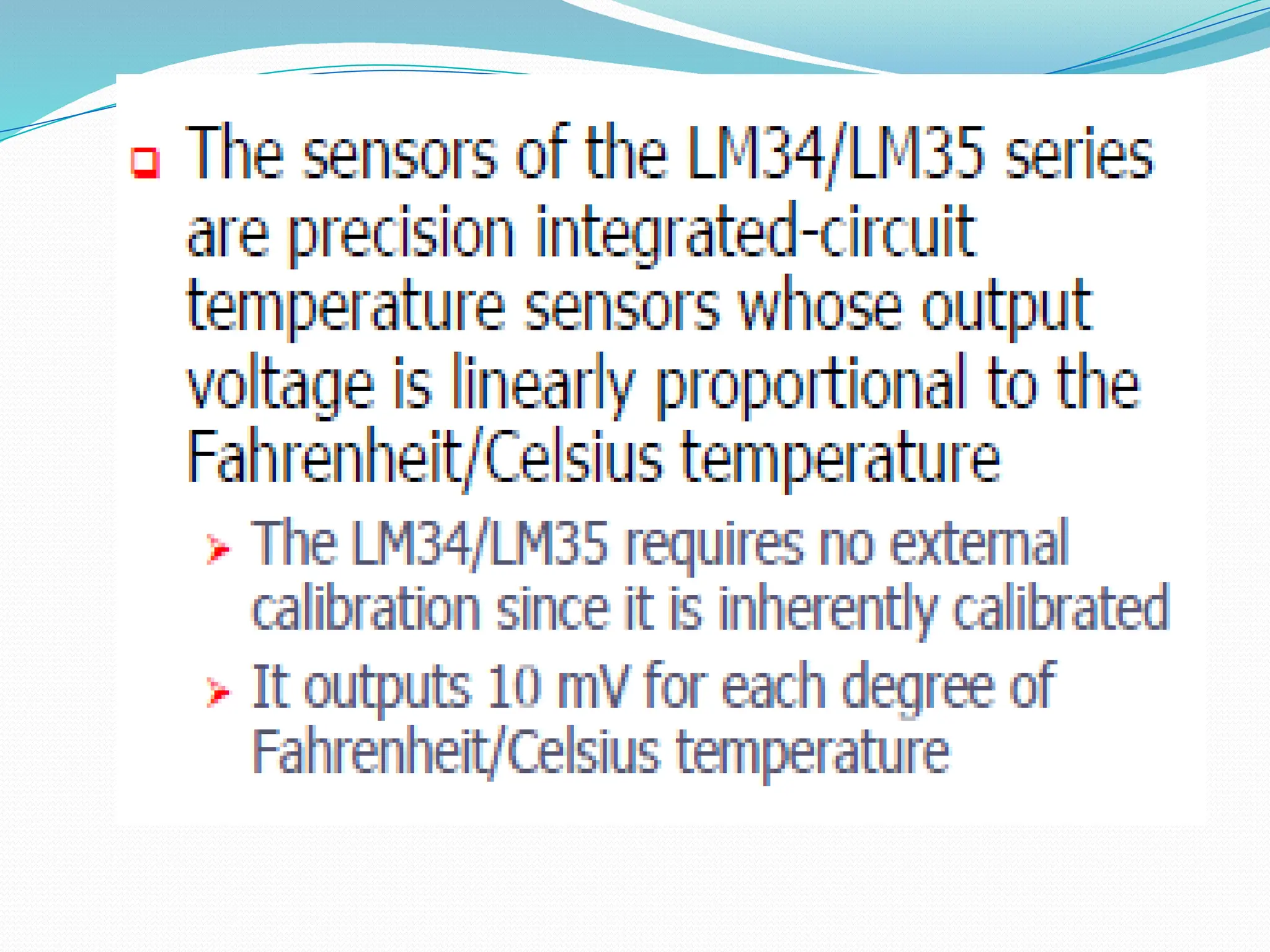
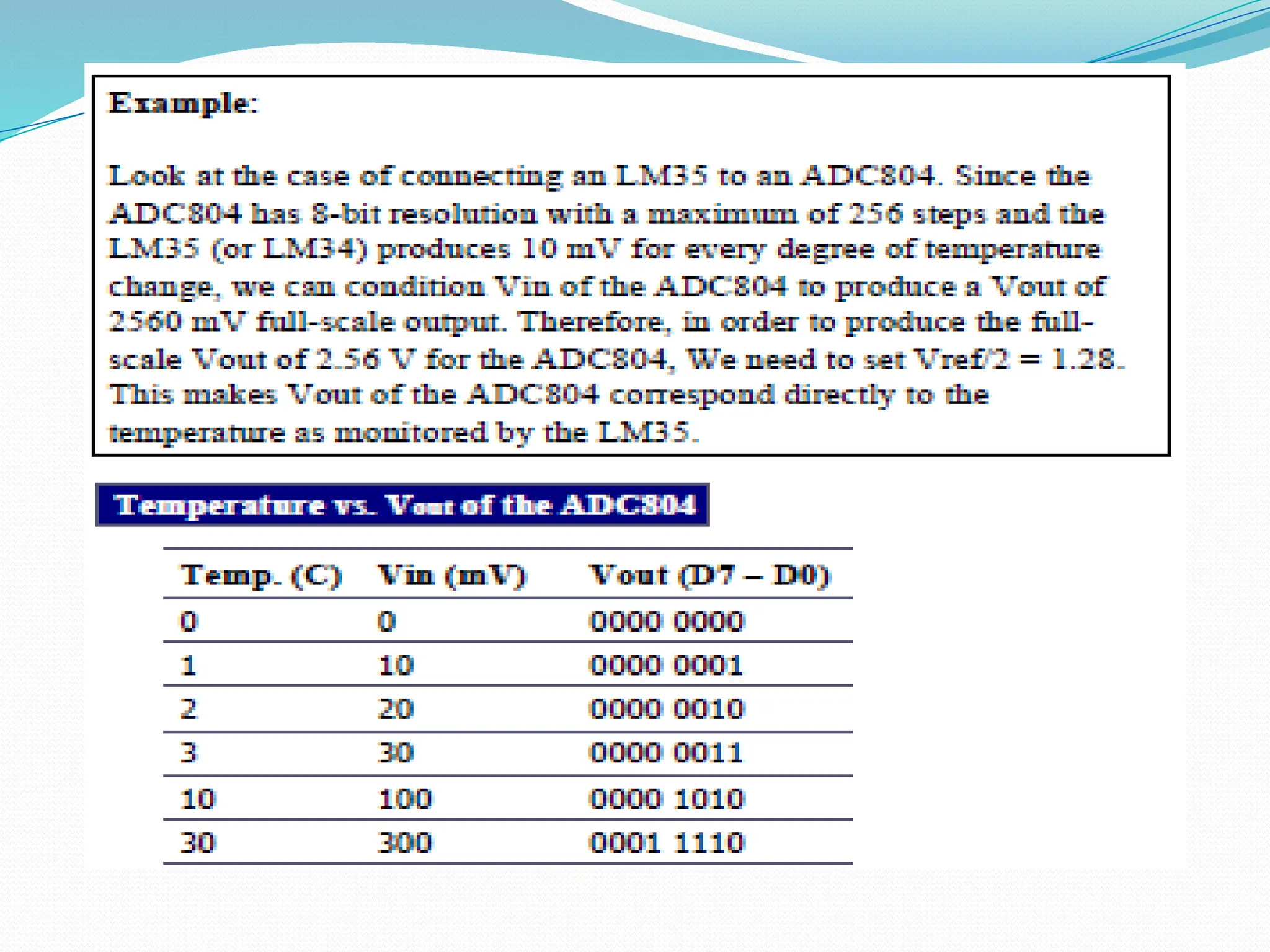
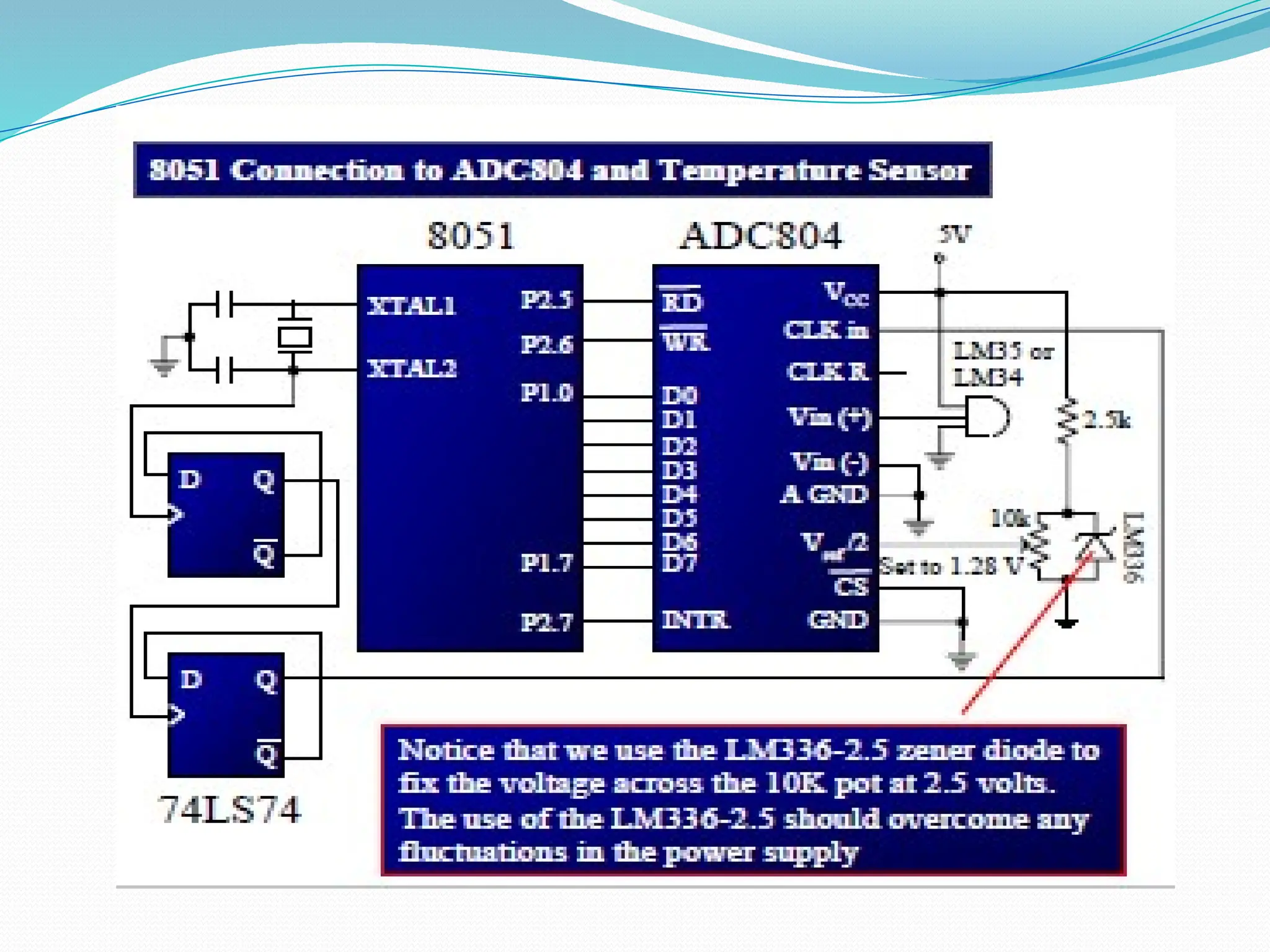
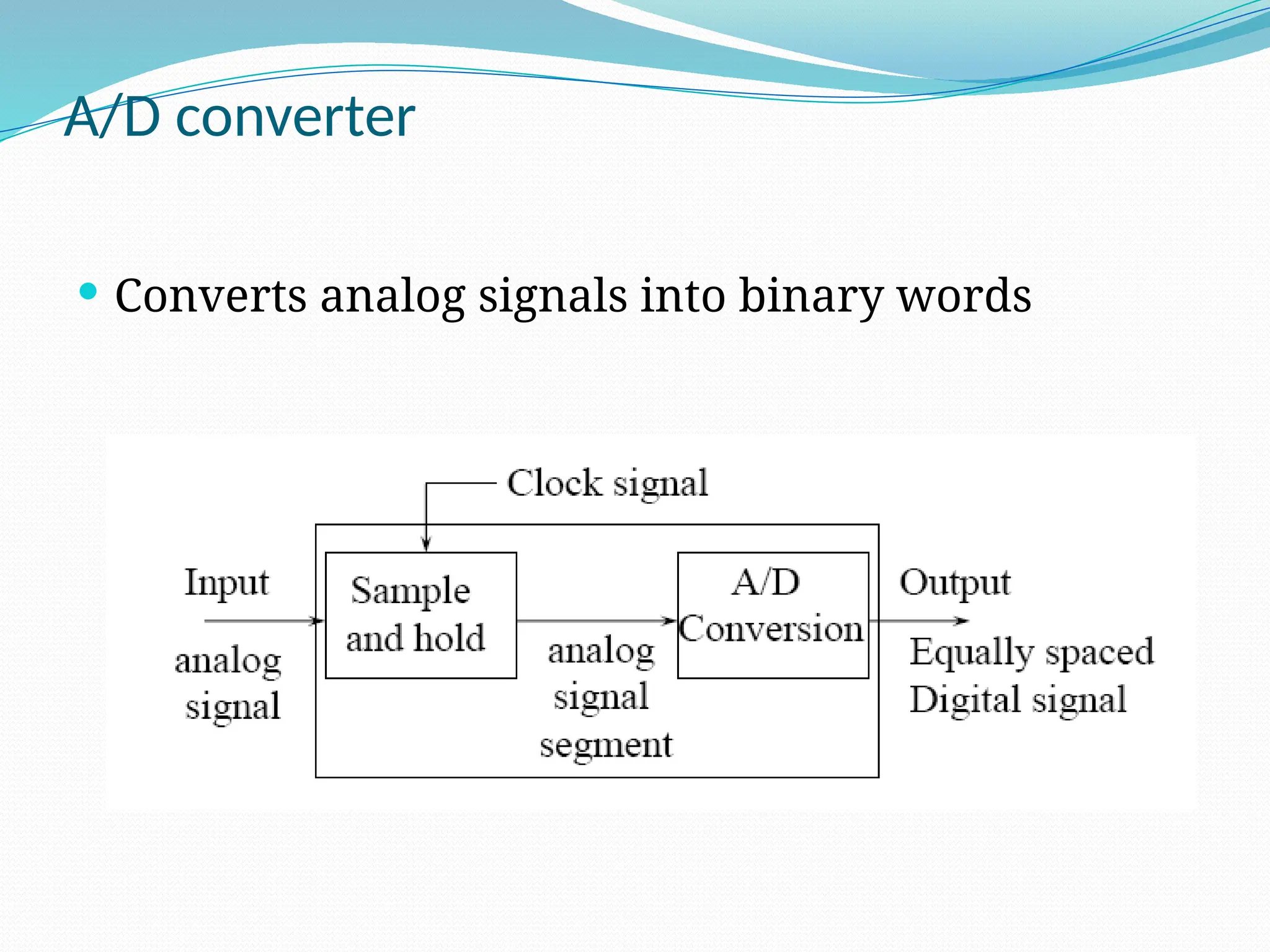
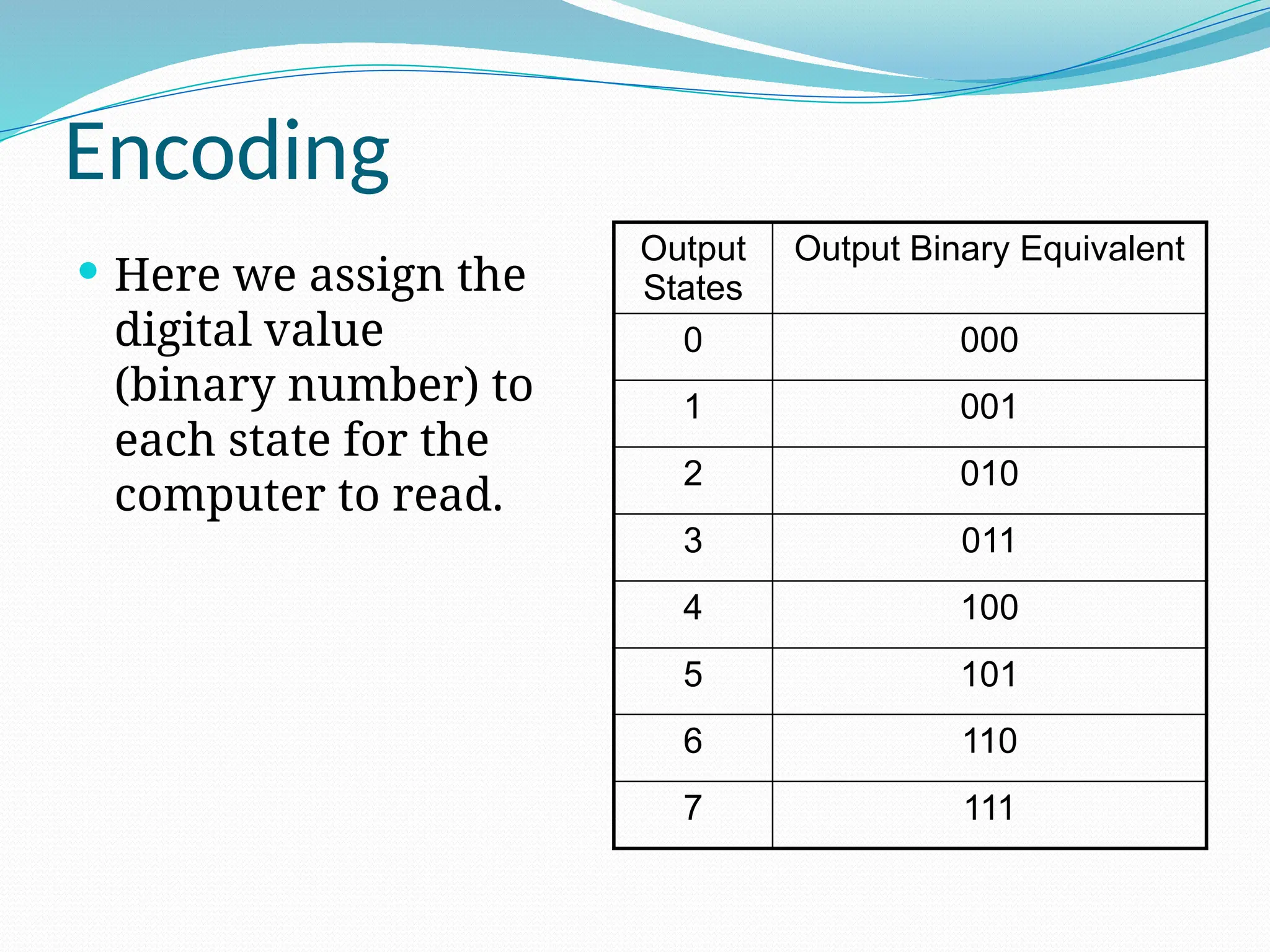
The document discusses the interfacing of the ADC0804 analog to digital converter with the AT89C51 microcontroller, detailing its features, pin configuration, and typical applications. It explains the conversion process from analog to digital, including the steps to initiate and read outputs, as well as coding examples for implementation. Additionally, it covers quantization and encoding processes, emphasizing resolution and accuracy in A/D conversions.