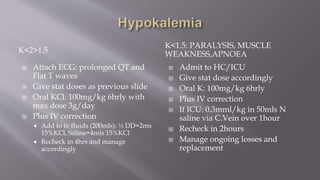
This document provides information on the management of acute diarrhea in children. It defines acute diarrhea and dysentery. The most common causes are viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections acquired through the fecal-oral route. Rotavirus is the leading cause and can cause dehydration. Signs and symptoms include diarrhea, vomiting, fever and abdominal pain. Complications include dehydration, electrolyte disturbances, and malnutrition. Management involves fluid resuscitation, continued feeding, zinc and vitamin A supplementation, and antibiotics for bacterial infections. Close monitoring of hydration and electrolytes is important.