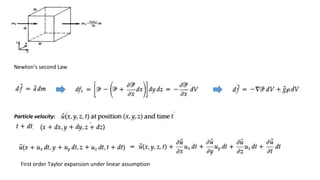
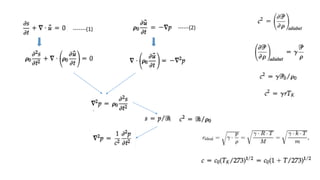
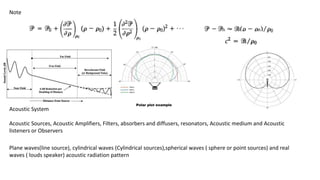
Sound is the propagation of mechanical vibrations in the form of pressure waves through a medium. The wave equation, derived from continuum mechanics equations, describes sound mathematically from a physics point of view. Linear and nonlinear wave equations can explain linear and nonlinear acoustic phenomena. Sound propagates as plane, cylindrical, spherical, or real waves depending on the source, and can be reflected, refracted, attenuated, or interfere through the superposition principle.