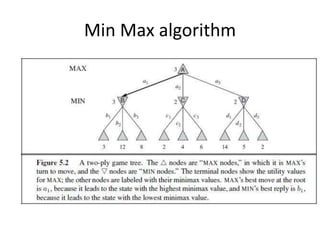
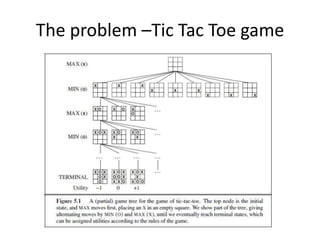
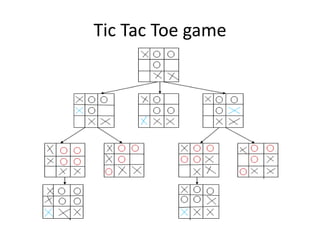
The document describes the minimax algorithm and alpha-beta pruning for a Tic Tac Toe game. It explains that minimax finds the best possible move by assuming the opponent plays optimally to minimize utility. Alpha-beta pruning improves upon minimax by pruning branches that cannot influence the final decision. It then provides pseudocode for the minimax and alpha-beta algorithms. Finally, it shows code for implementing a Tic Tac Toe game that uses minimax with alpha-beta pruning to choose moves.






![#Class TicTacToe
• from math import inf as infinity
• class TicTacToe:
• def __init__(self):
• self.initialize_board()
• def initialize_board(self):
• self.current_state = [['-','-','-'],
• ['-','-','-'],
• ['-','-','-']]
• # Player X always plays first
• self.player_turn = 'X'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aci-webinar-3-minmaxalphabetapruning-tictactoe-240320001754-3eb90e7f/85/ACI-Webinar-3-MinMaxAlphaBetaPruning-TicTacToe-pptx-10-320.jpg)
![#Class TicTacToe – Draw the board
• def draw_board(self):
• for i in range(0, 3):
• for j in range(0, 3):
• print('{}|'.format(self.current_state[i][j]),
end=" ")
• print()
• print()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aci-webinar-3-minmaxalphabetapruning-tictactoe-240320001754-3eb90e7f/85/ACI-Webinar-3-MinMaxAlphaBetaPruning-TicTacToe-pptx-11-320.jpg)
![# Determines if the made move is a
legal move
• def is_validmove(self, px, py):
• if px < 0 or px > 2 or py < 0 or py > 2:
• return False
• elif self.current_state[px][py] != '-':
• return False
• else:
• return True](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aci-webinar-3-minmaxalphabetapruning-tictactoe-240320001754-3eb90e7f/85/ACI-Webinar-3-MinMaxAlphaBetaPruning-TicTacToe-pptx-12-320.jpg)
![# Checks if the game has ended and returns the
winner in each case - #is_endofgame() function
• def is_endofgame(self):
• # Check for column-wise win
• for i in range(0, 3):
• if (self.current_state[0][i] != '-' and
• self.current_state[0][i] ==
self.current_state[1][i] and
• self.current_state[1][i] ==
self.current_state[2][i]):
• return self.current_state[0][i]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aci-webinar-3-minmaxalphabetapruning-tictactoe-240320001754-3eb90e7f/85/ACI-Webinar-3-MinMaxAlphaBetaPruning-TicTacToe-pptx-13-320.jpg)
![is_endofgame() function
• # Check for row-wise win
• for i in range(0, 3):
• if (self.current_state[i] == ['X', 'X', 'X']):
• return 'X'
• elif (self.current_state[i] == ['O', 'O',
'O']):
• return 'O'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aci-webinar-3-minmaxalphabetapruning-tictactoe-240320001754-3eb90e7f/85/ACI-Webinar-3-MinMaxAlphaBetaPruning-TicTacToe-pptx-14-320.jpg)
![# is_endofgame() function
• # Check for win over the Main diagonal
• if (self.current_state[0][0] != '-' and
• self.current_state[0][0] ==
self.current_state[1][1] and
• self.current_state[0][0] ==
self.current_state[2][2]):
• return self.current_state[0][0]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aci-webinar-3-minmaxalphabetapruning-tictactoe-240320001754-3eb90e7f/85/ACI-Webinar-3-MinMaxAlphaBetaPruning-TicTacToe-pptx-15-320.jpg)
![# is_endofgame() function
• # Check for win over the Second diagonal
• if (self.current_state[0][2] != '-' and
• self.current_state[0][2] ==
self.current_state[1][1] and
• self.current_state[0][2] ==
self.current_state[2][0]):
• return self.current_state[0][2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aci-webinar-3-minmaxalphabetapruning-tictactoe-240320001754-3eb90e7f/85/ACI-Webinar-3-MinMaxAlphaBetaPruning-TicTacToe-pptx-16-320.jpg)
![# is_endofgame() function
• # Is whole board full?
• for i in range(0, 3):
• for j in range(0, 3):
• # There's an empty field, we continue the game
• if (self.current_state[i][j] == '-'):
• return None
• # It's a tie!
• return '-'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aci-webinar-3-minmaxalphabetapruning-tictactoe-240320001754-3eb90e7f/85/ACI-Webinar-3-MinMaxAlphaBetaPruning-TicTacToe-pptx-17-320.jpg)

![#Max player - #Testing for best remaining moves,
calculating the utility function and updating alpha
• for i in range(0, 3):
• for j in range(0, 3):
• if self.current_state[i][j] == '-':
• self.current_state[i][j] = 'O'
• (m, min_i, min_j) = self.min_alpha_beta(alpha,
beta)
• if m > maxv: #Update Maxvalue
• maxv = m
• px = i
• py = j
• #After checking reset to empty state
• self.current_state[i][j] = '-'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aci-webinar-3-minmaxalphabetapruning-tictactoe-240320001754-3eb90e7f/85/ACI-Webinar-3-MinMaxAlphaBetaPruning-TicTacToe-pptx-19-320.jpg)




![#Playing the game (Min turn)
• #px, py, qx and qy represent the board positions as x and y
coordinates
• if self.player_turn == 'X':
• while True:
• (m, qx, qy) = self.min_alpha_beta(-infinity, infinity)
• px = int(input('Insert the X coordinate: '))
• py = int(input('Insert the Y coordinate: '))
• qx = px
• qy = py
• if self.is_validmove(px, py):
• self.current_state[px][py] = 'X'
• self.player_turn = 'O'
• break
• else:
• print('The move is not valid! Try again.')](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aci-webinar-3-minmaxalphabetapruning-tictactoe-240320001754-3eb90e7f/85/ACI-Webinar-3-MinMaxAlphaBetaPruning-TicTacToe-pptx-24-320.jpg)
![#Playing the game (Max turn)
• else:
• (m, px, py) =
• self.max_alpha_beta(-infinity, infinity)
• self.current_state[px][py] = 'O'
• self.player_turn = 'X'
•](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aci-webinar-3-minmaxalphabetapruning-tictactoe-240320001754-3eb90e7f/85/ACI-Webinar-3-MinMaxAlphaBetaPruning-TicTacToe-pptx-25-320.jpg)
