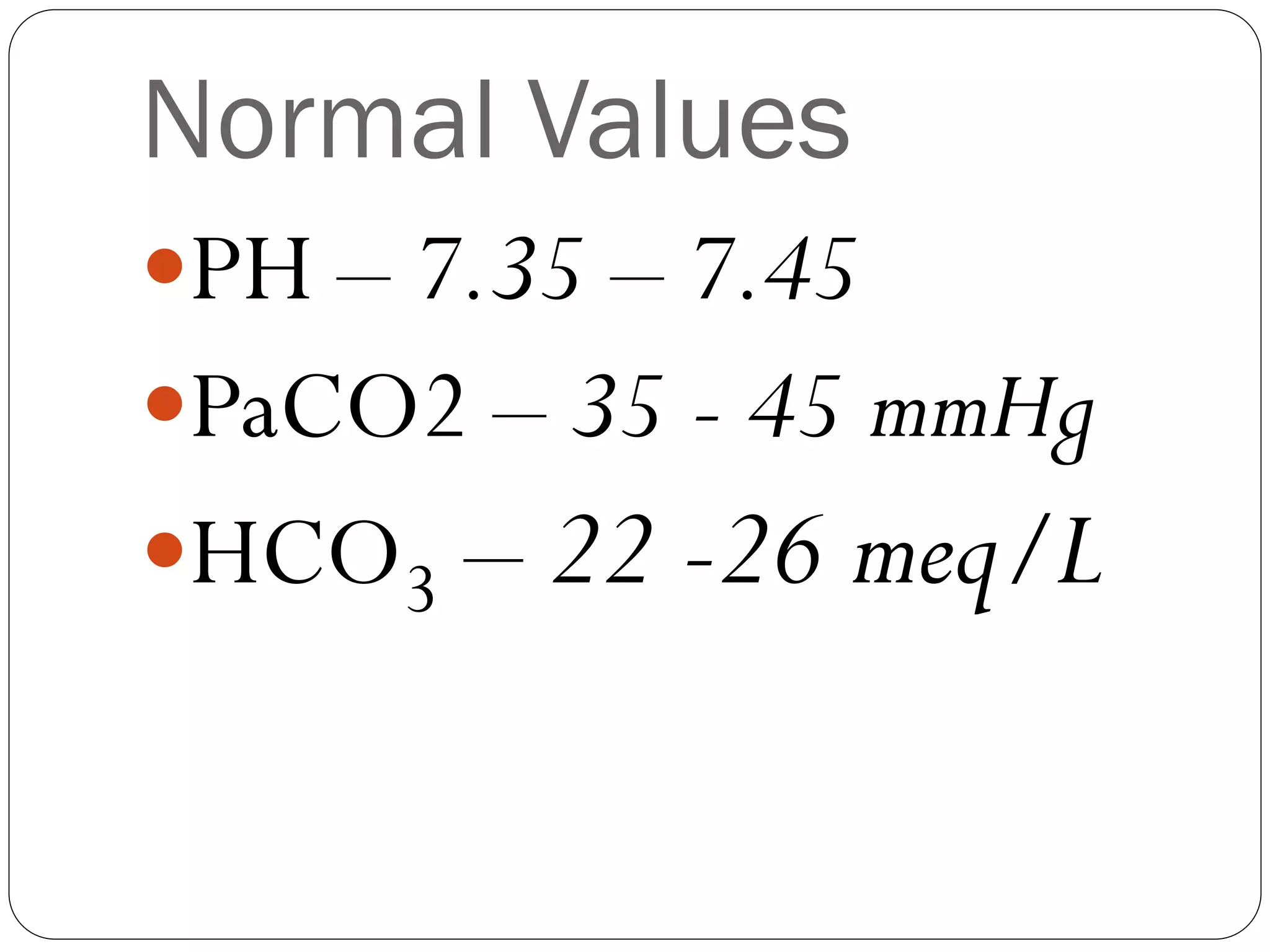
The document outlines the normal values for acid-base balance, specifically the pH, PaCO2, and HCO3 levels, and provides a framework for interpreting arterial blood gases (ABG) results. It details how to identify acidosis or alkalosis, determine the cause (respiratory or metabolic), and assess whether there is compensation present. Additionally, it includes examples of various ABG results with interpretations of their clinical significance.