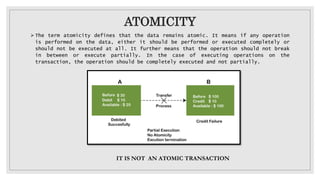
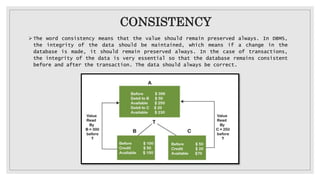
This document discusses the ACID properties that ensure reliable transactions in distributed database management systems. It defines each property: Atomicity guarantees transactions are treated as a single unit completed or rolled back. Consistency ensures data validity throughout transactions. Isolation prevents interference between concurrent transactions. Durability guarantees committed changes survive failures. Collectively, ACID properties provide reliability, consistency, and durability of data transactions in distributed databases.