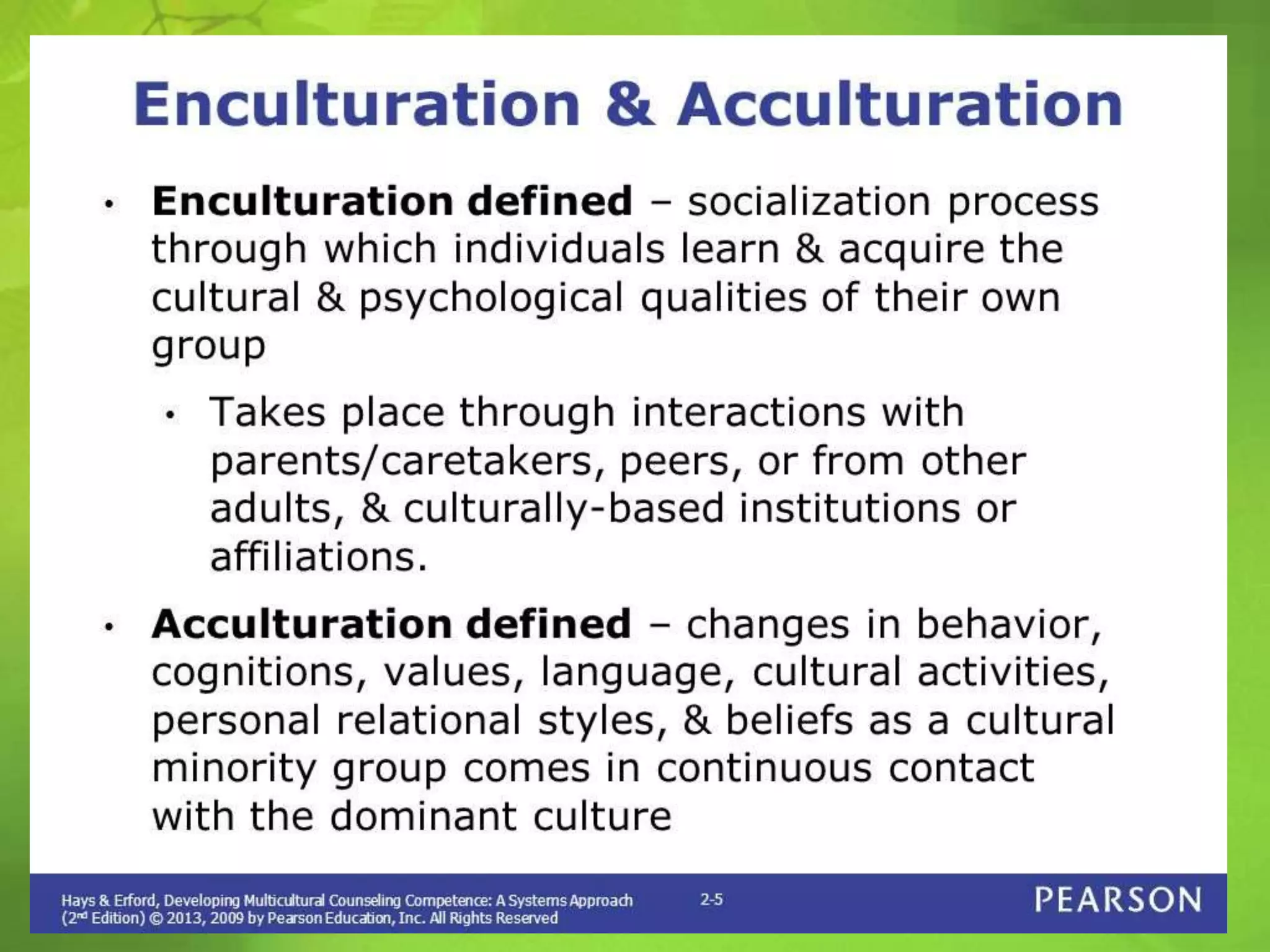
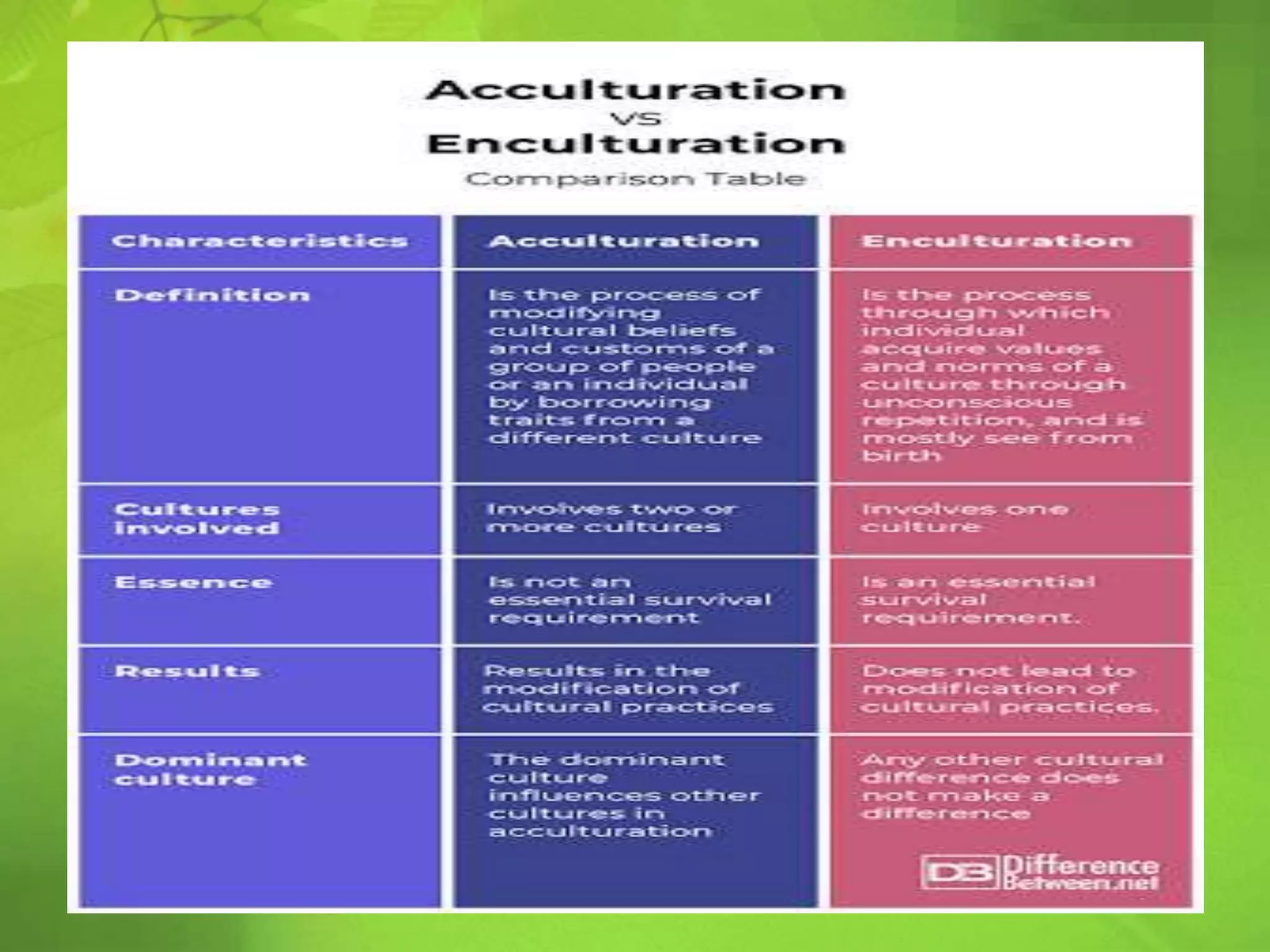
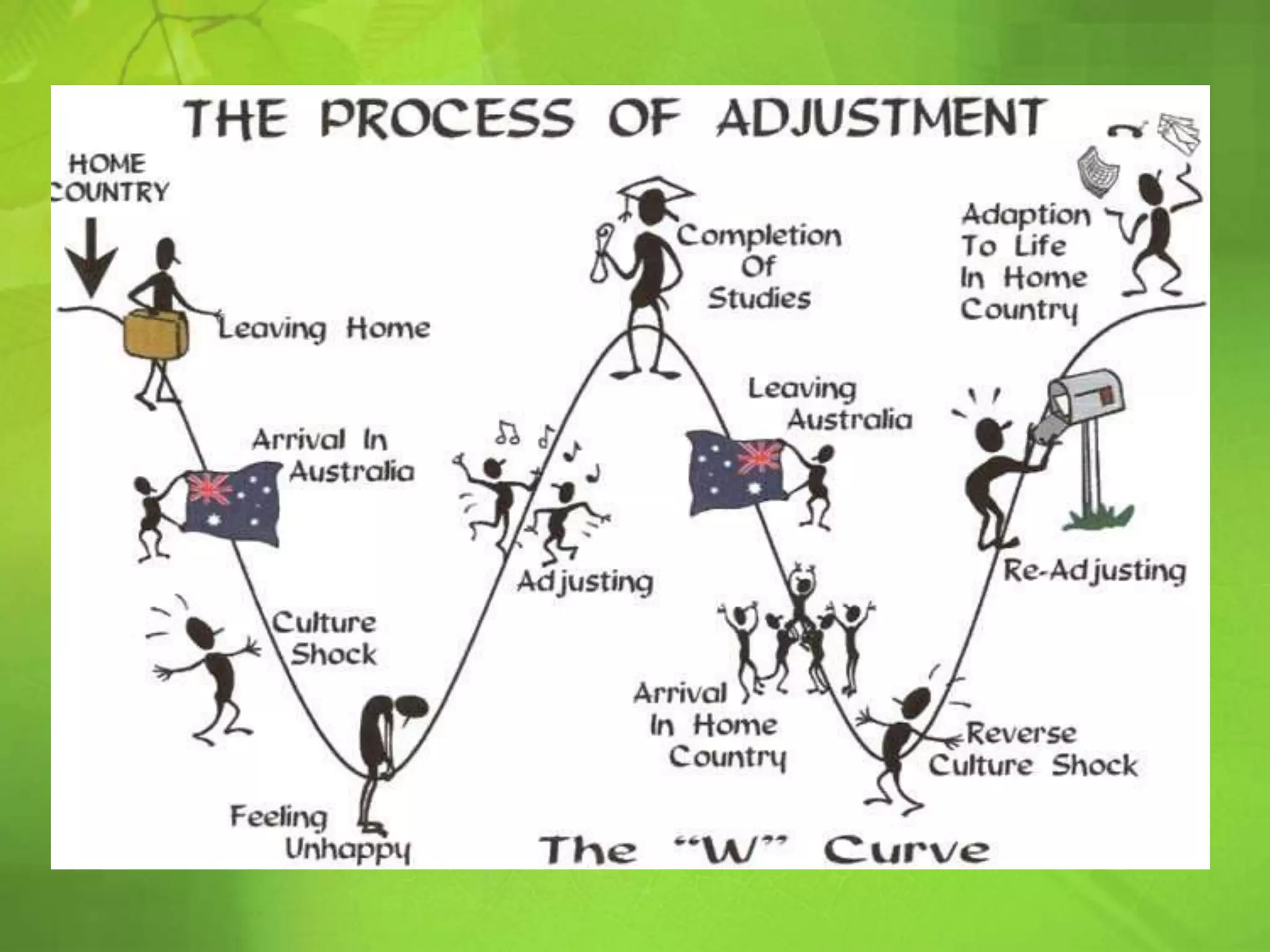
The document defines key concepts related to cultural interactions, including diffusion, cultural lag, cultural shock, acculturation, and cultural assimilation. It explains how cultural assimilation involves the integration and loss of distinct traits among groups, while acculturation allows cultures to interact without losing their core identities. Additionally, it discusses the implications of multiculturalism and the challenges posed by cultural lag in adapting to technological changes.