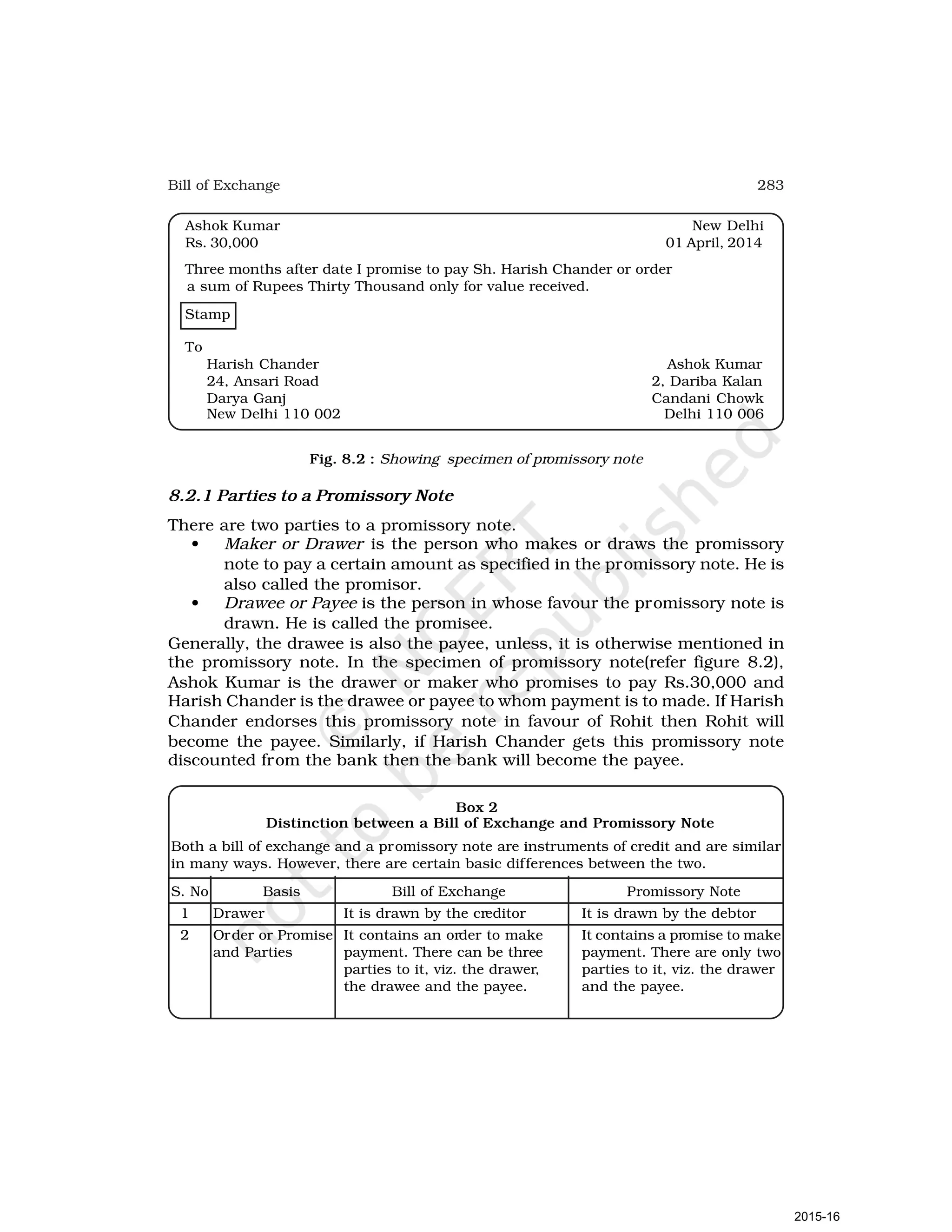
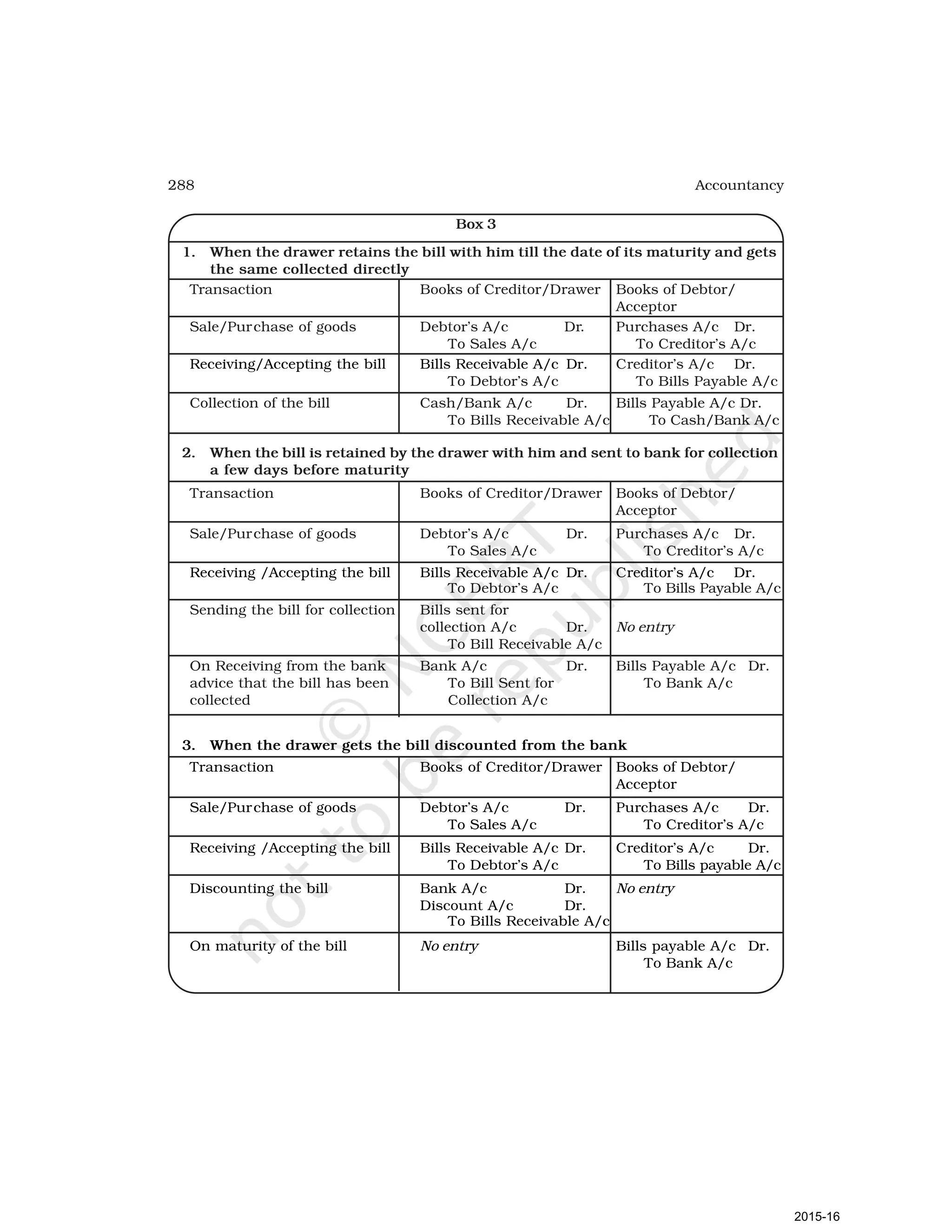
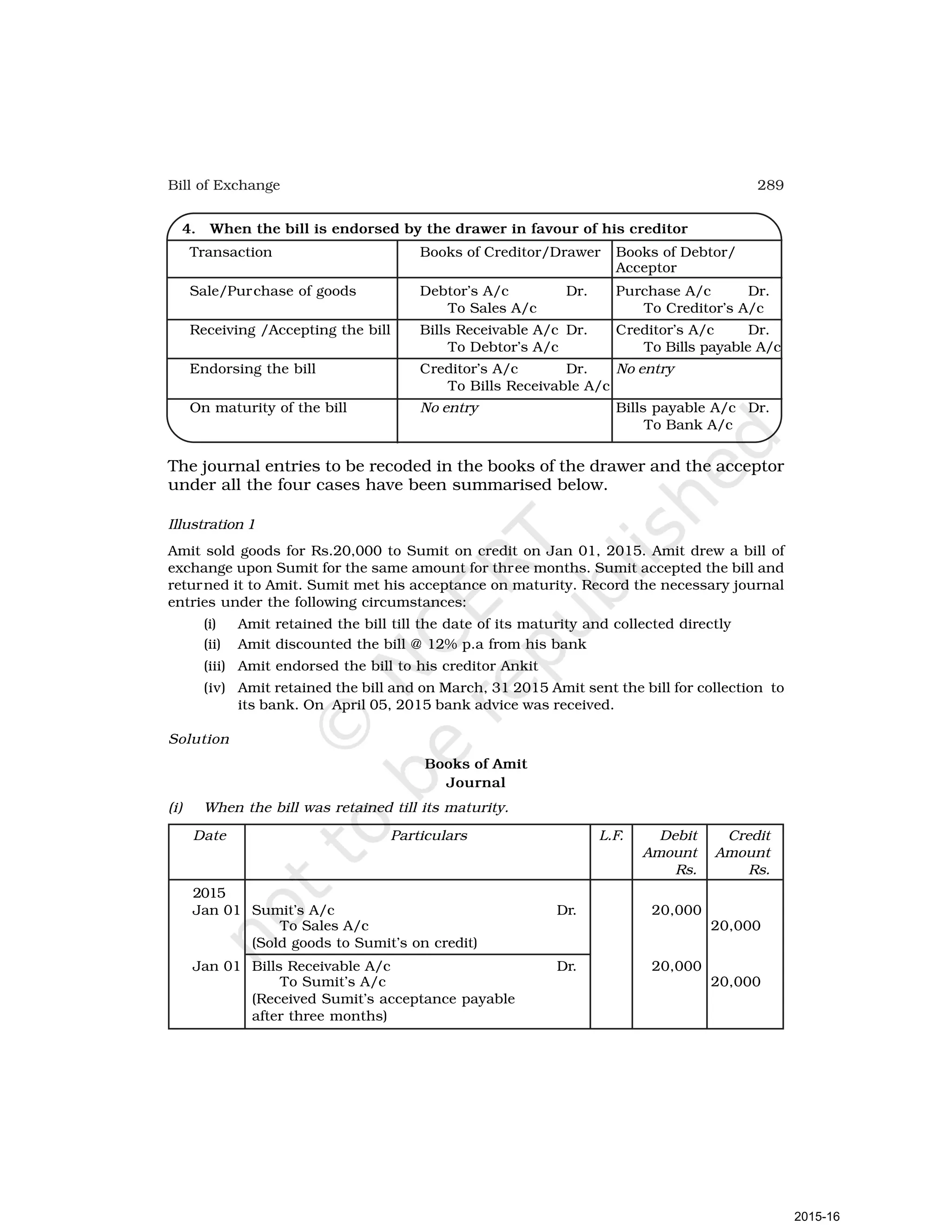
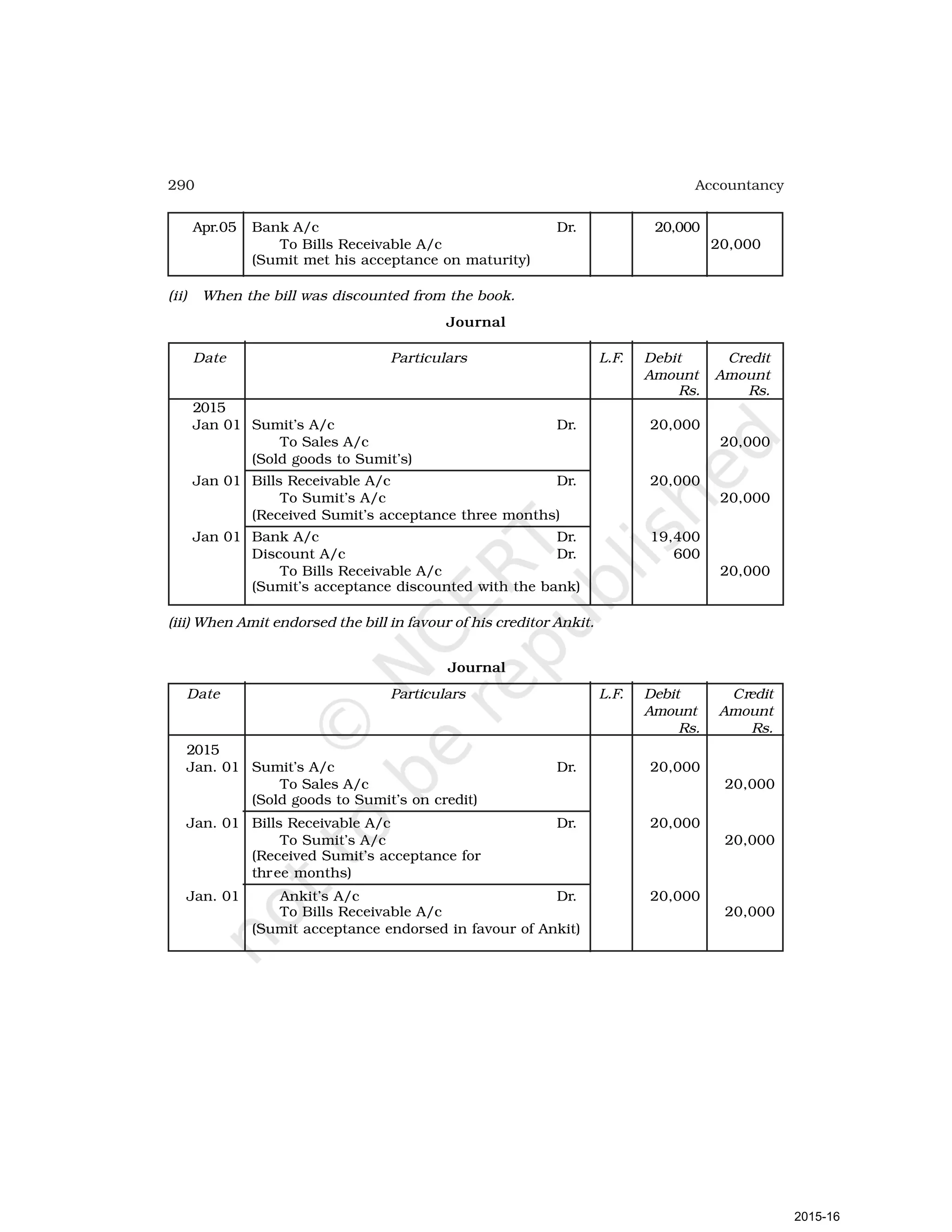
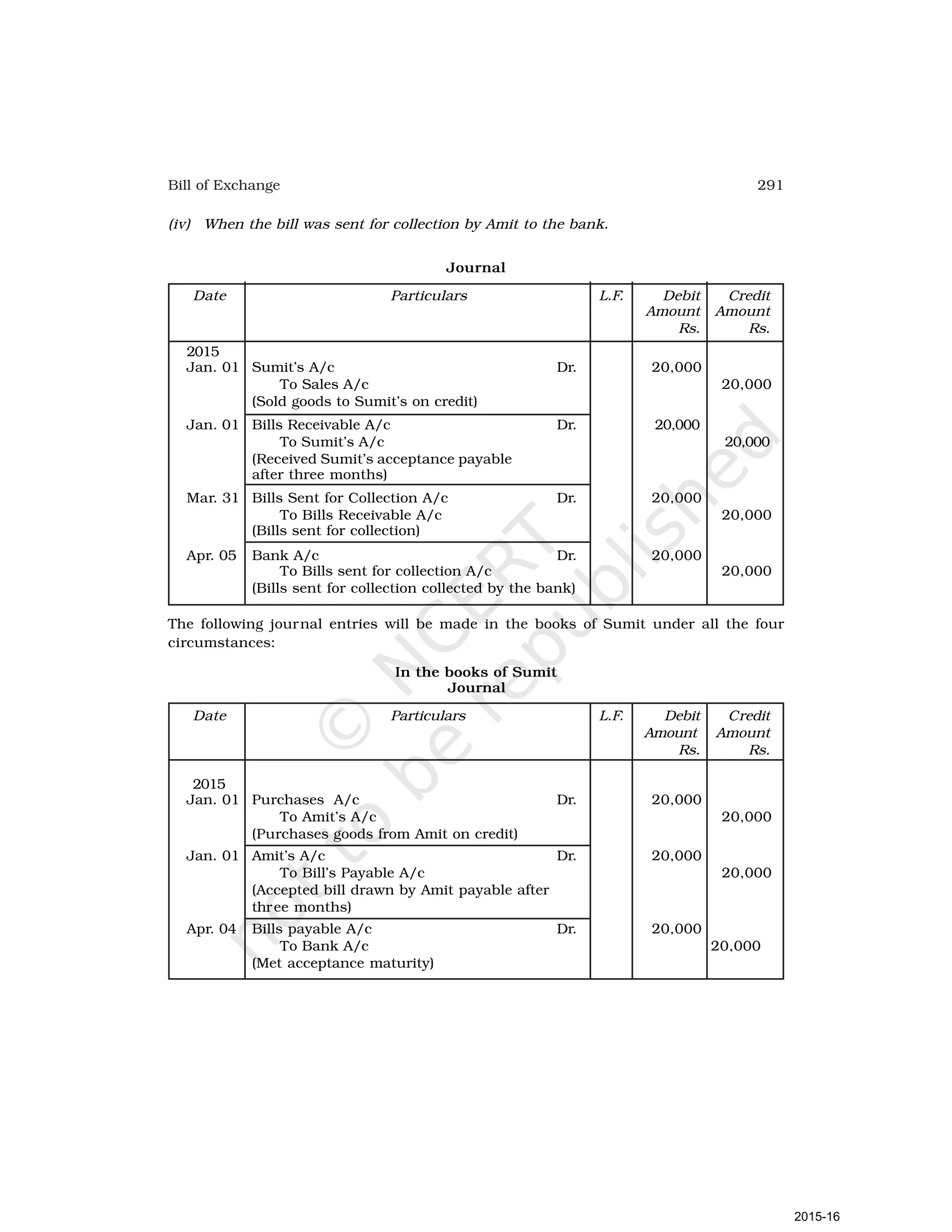
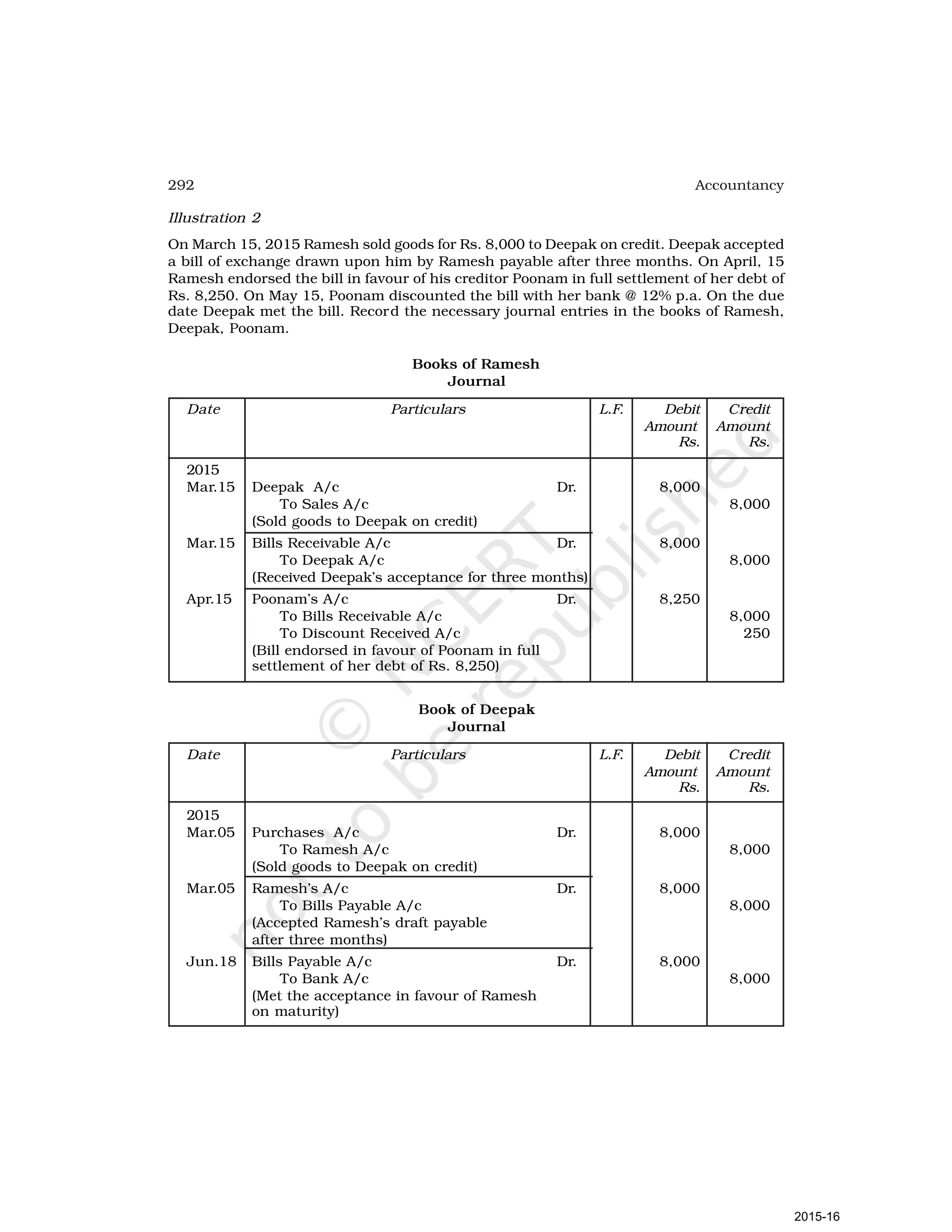
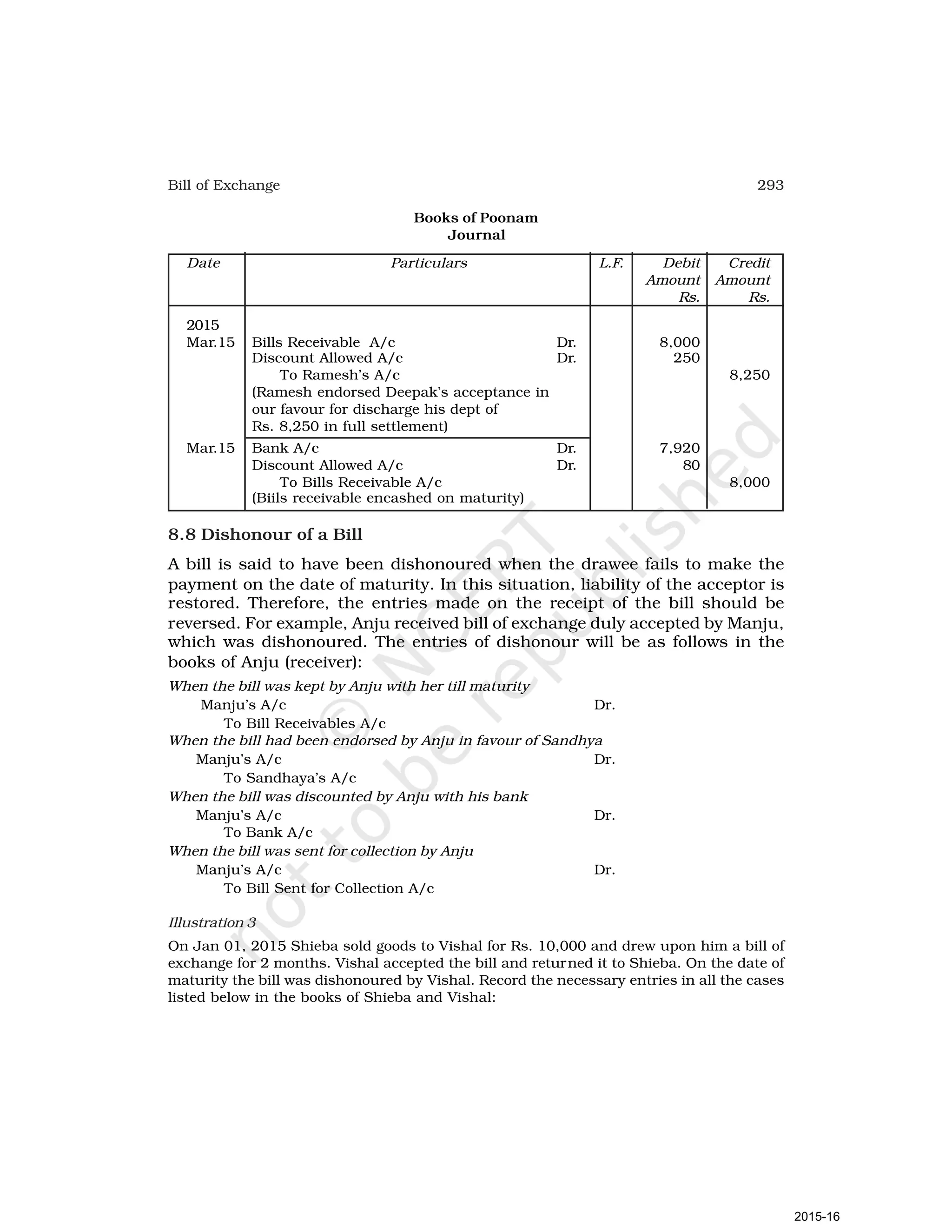
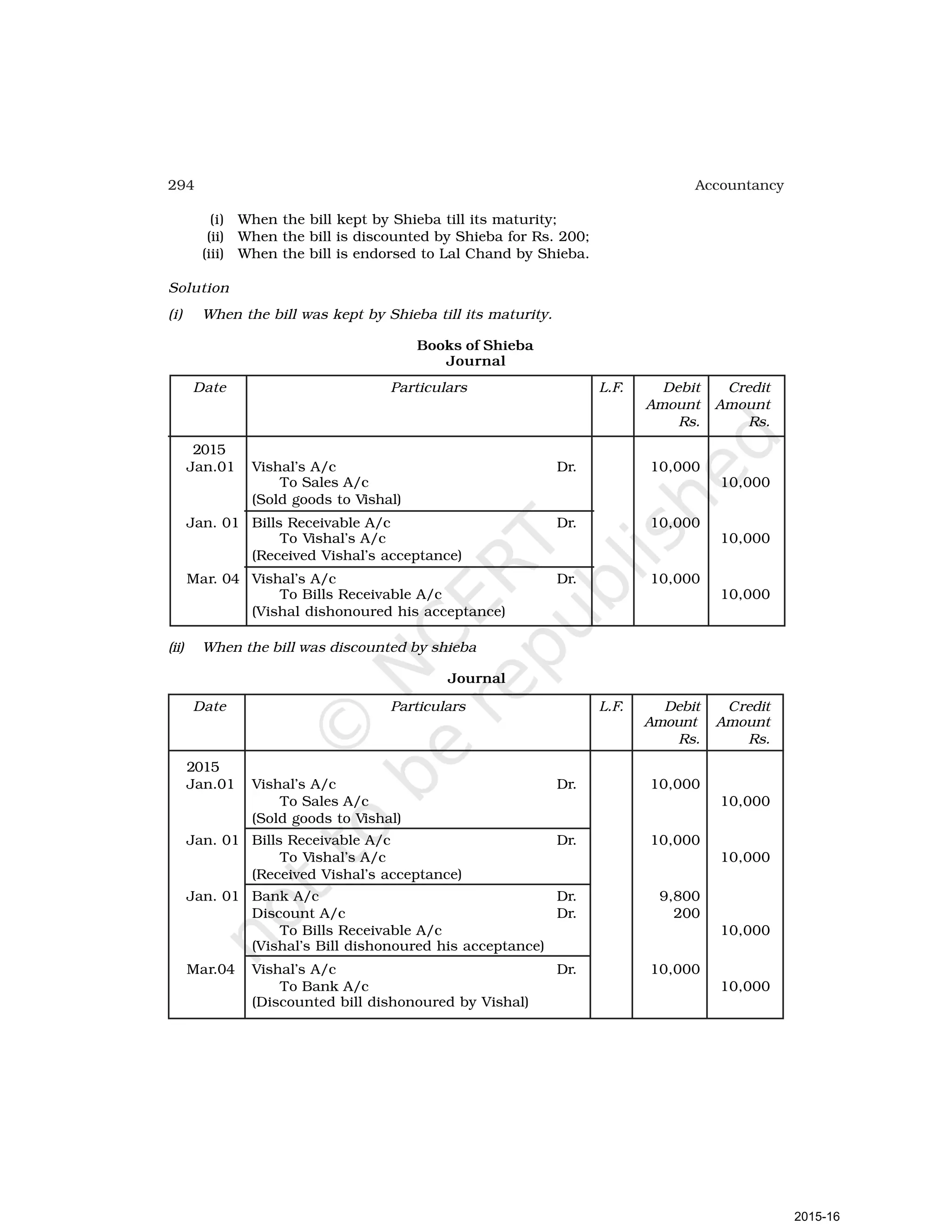
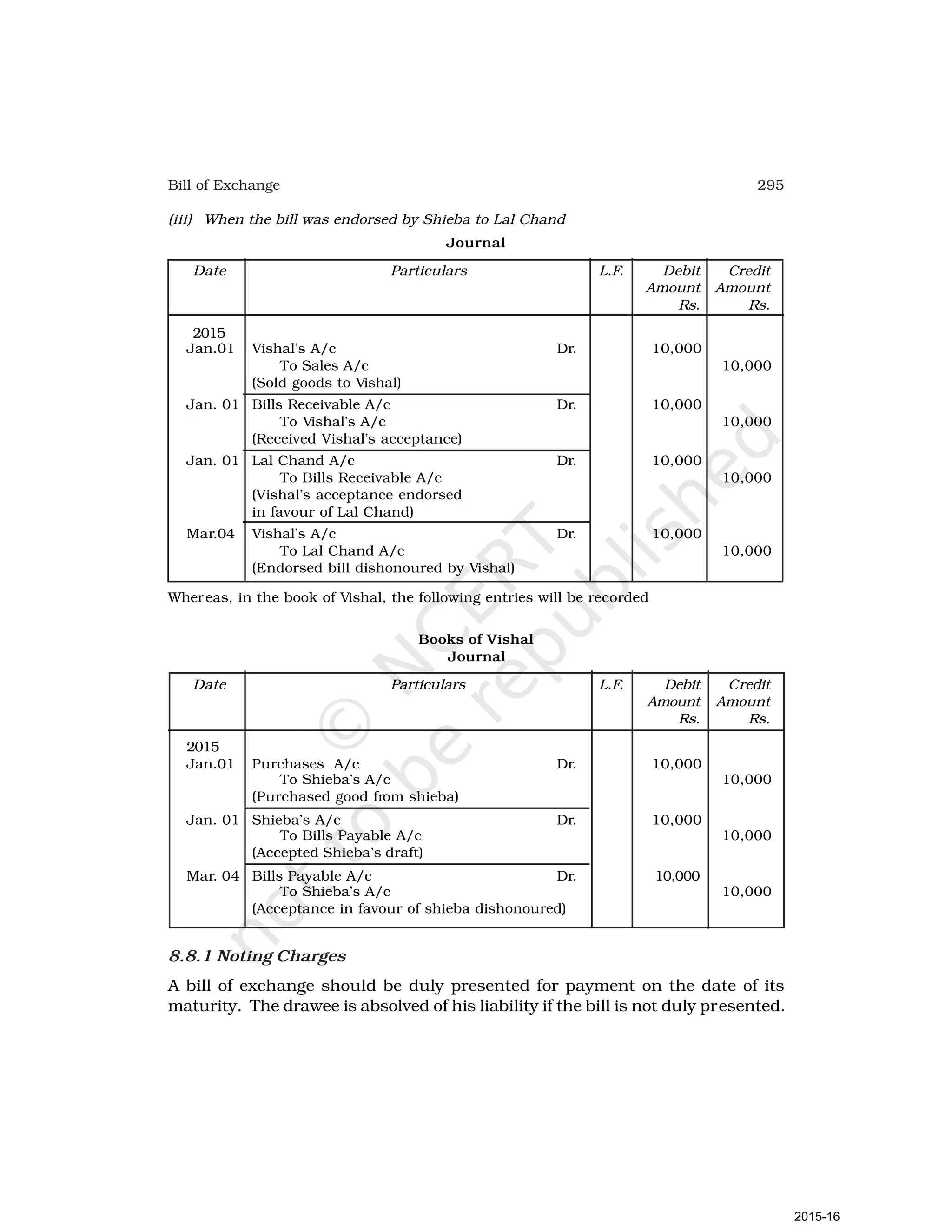
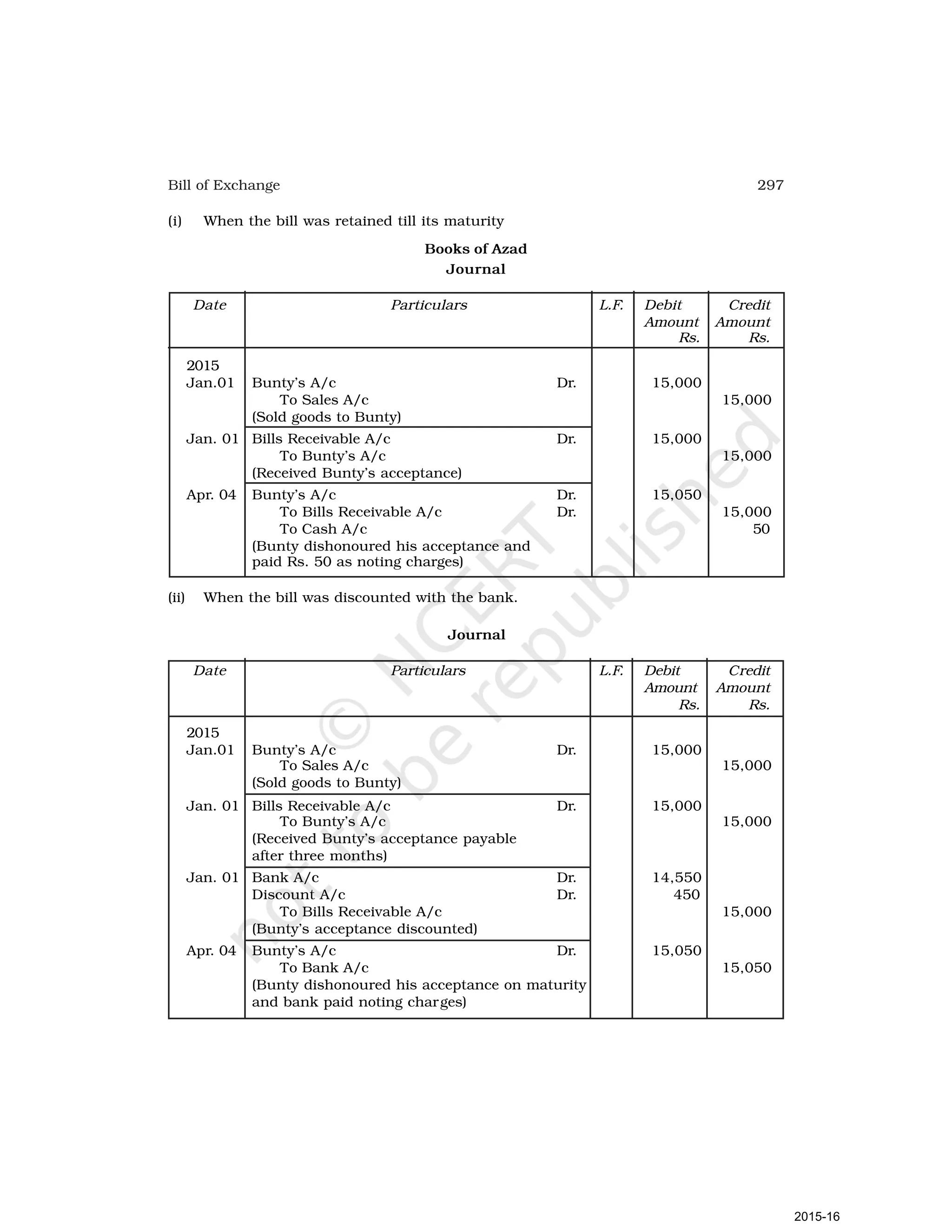
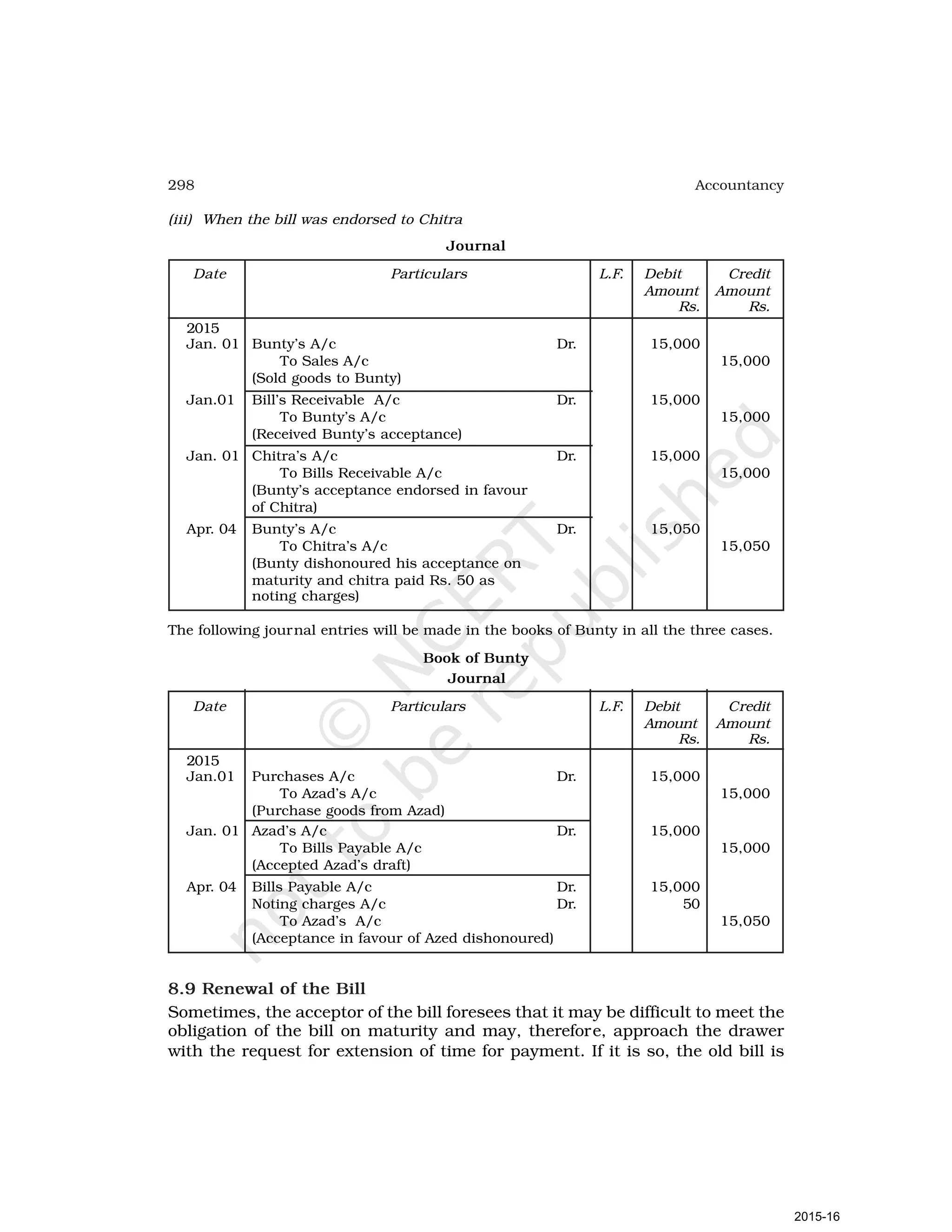
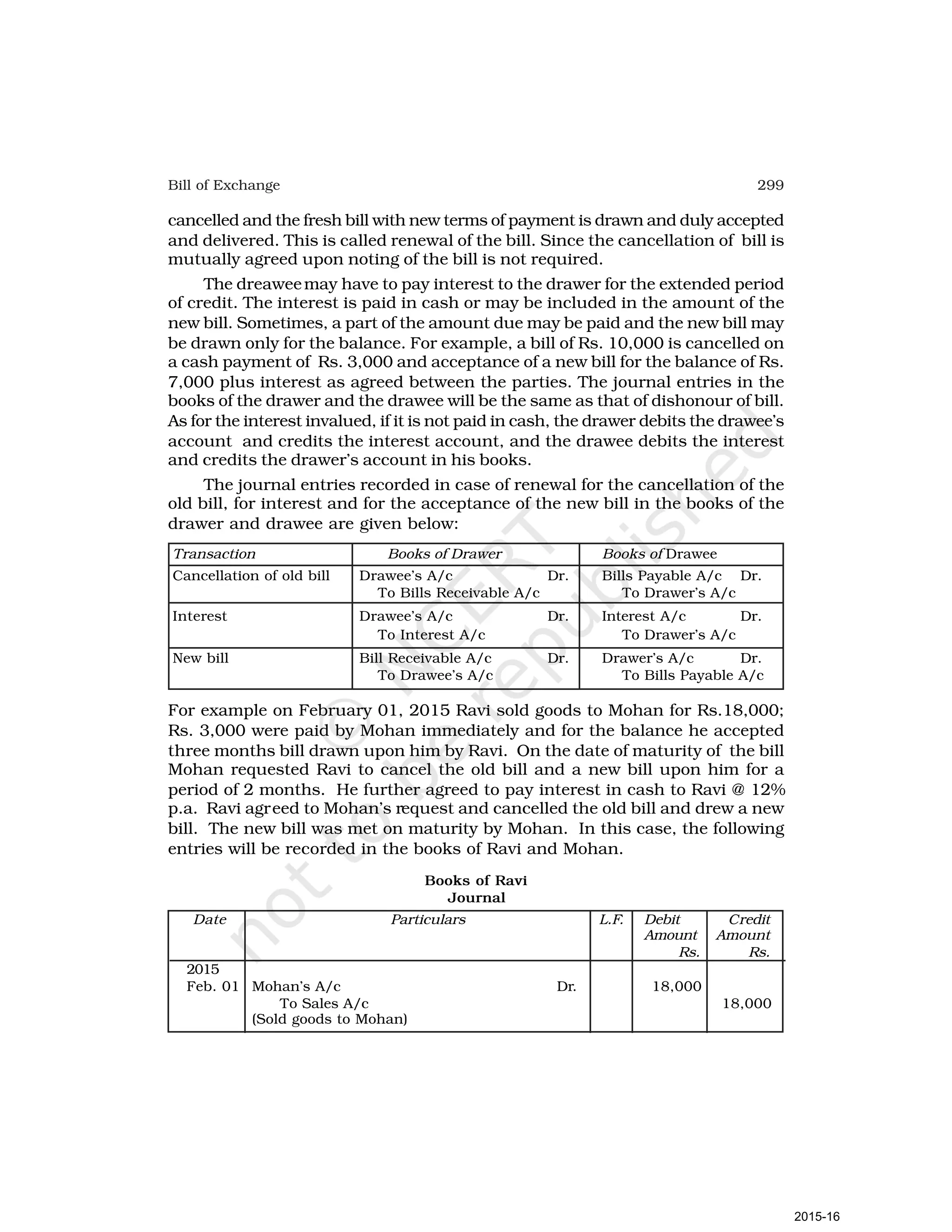
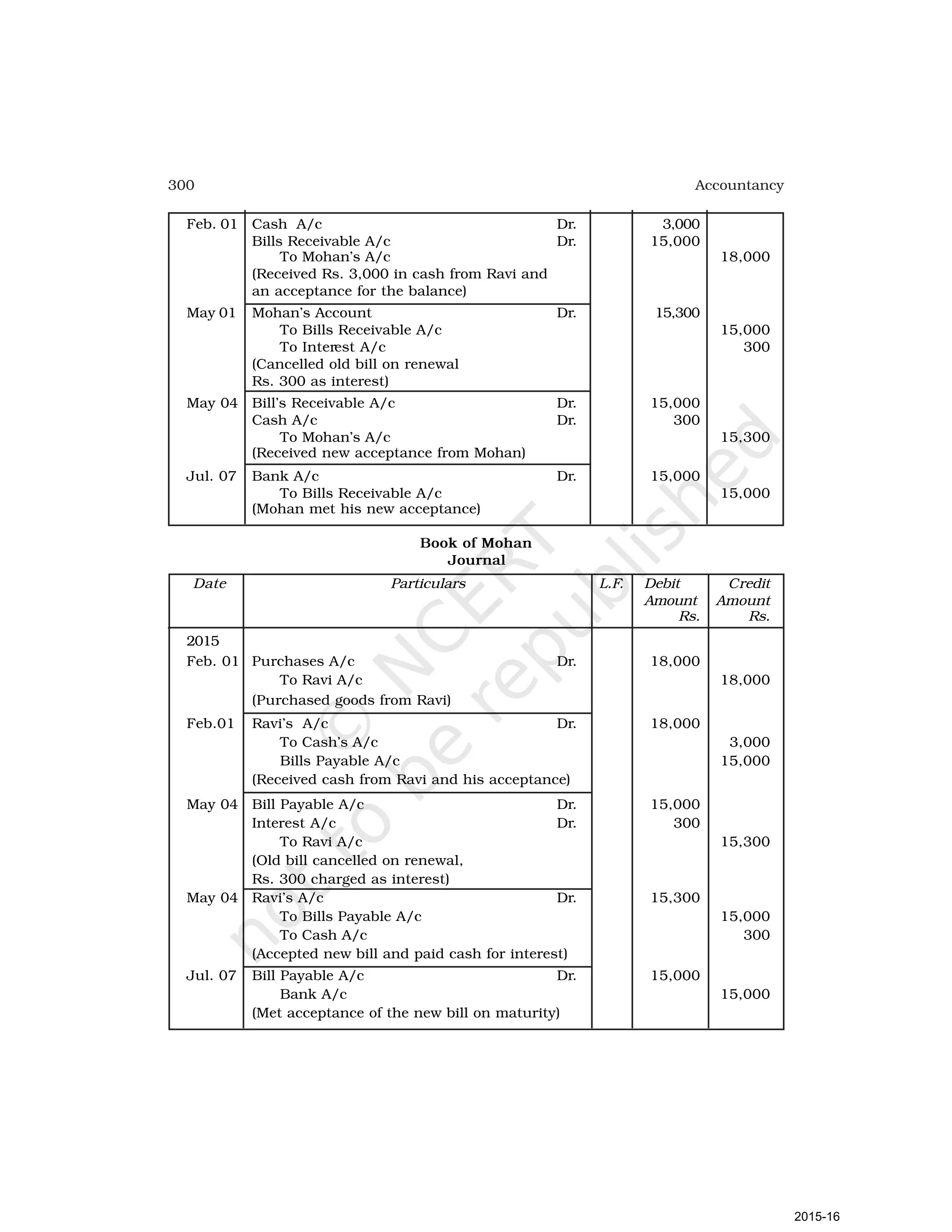
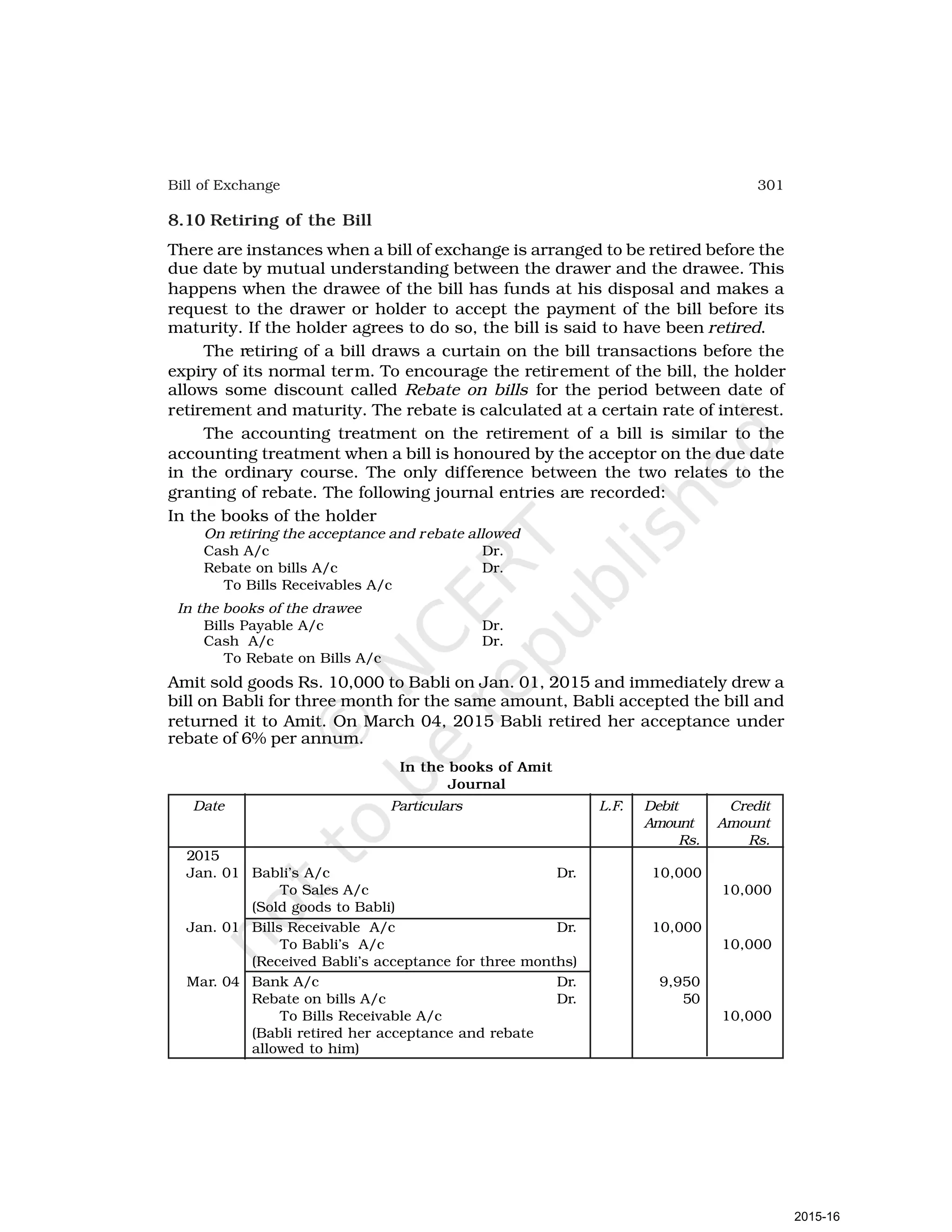
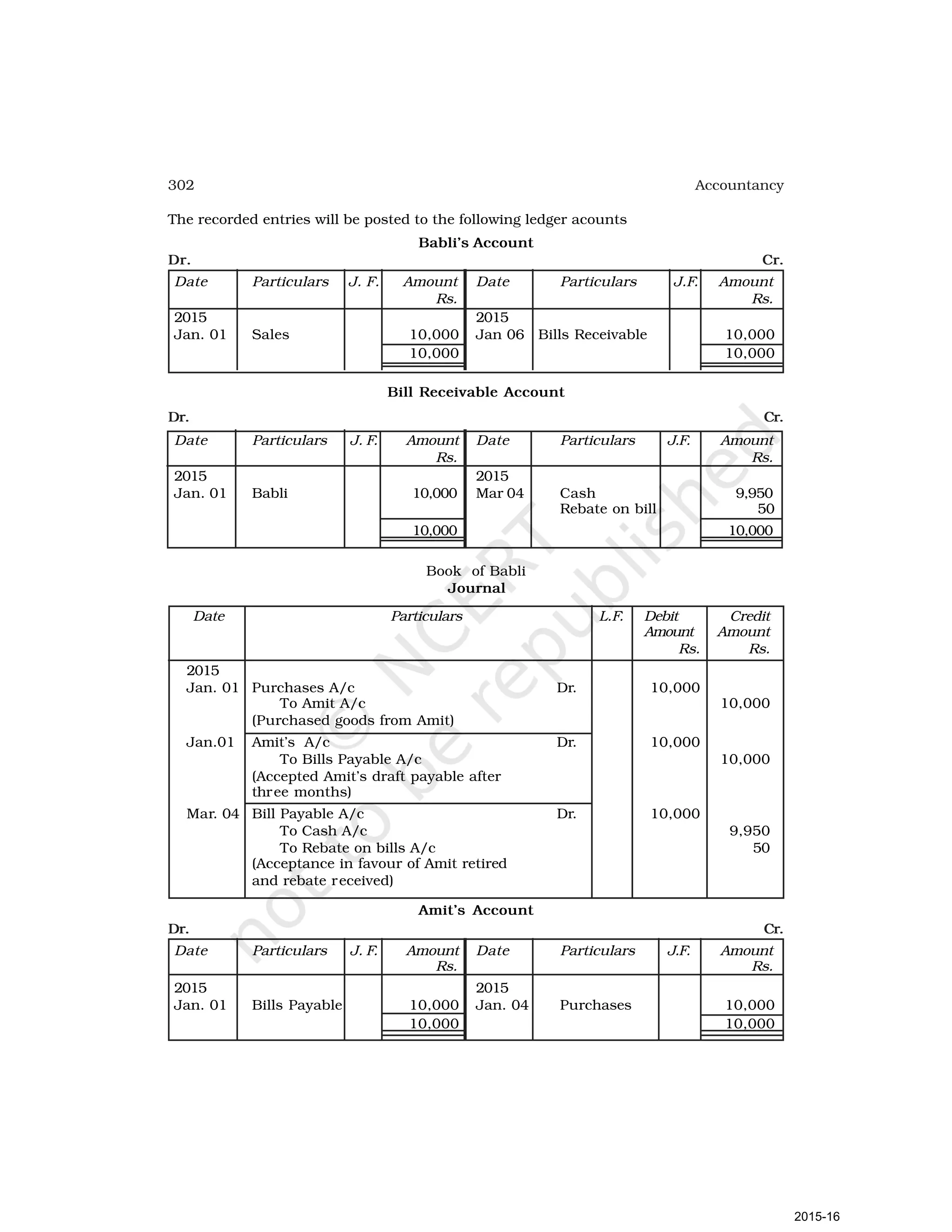
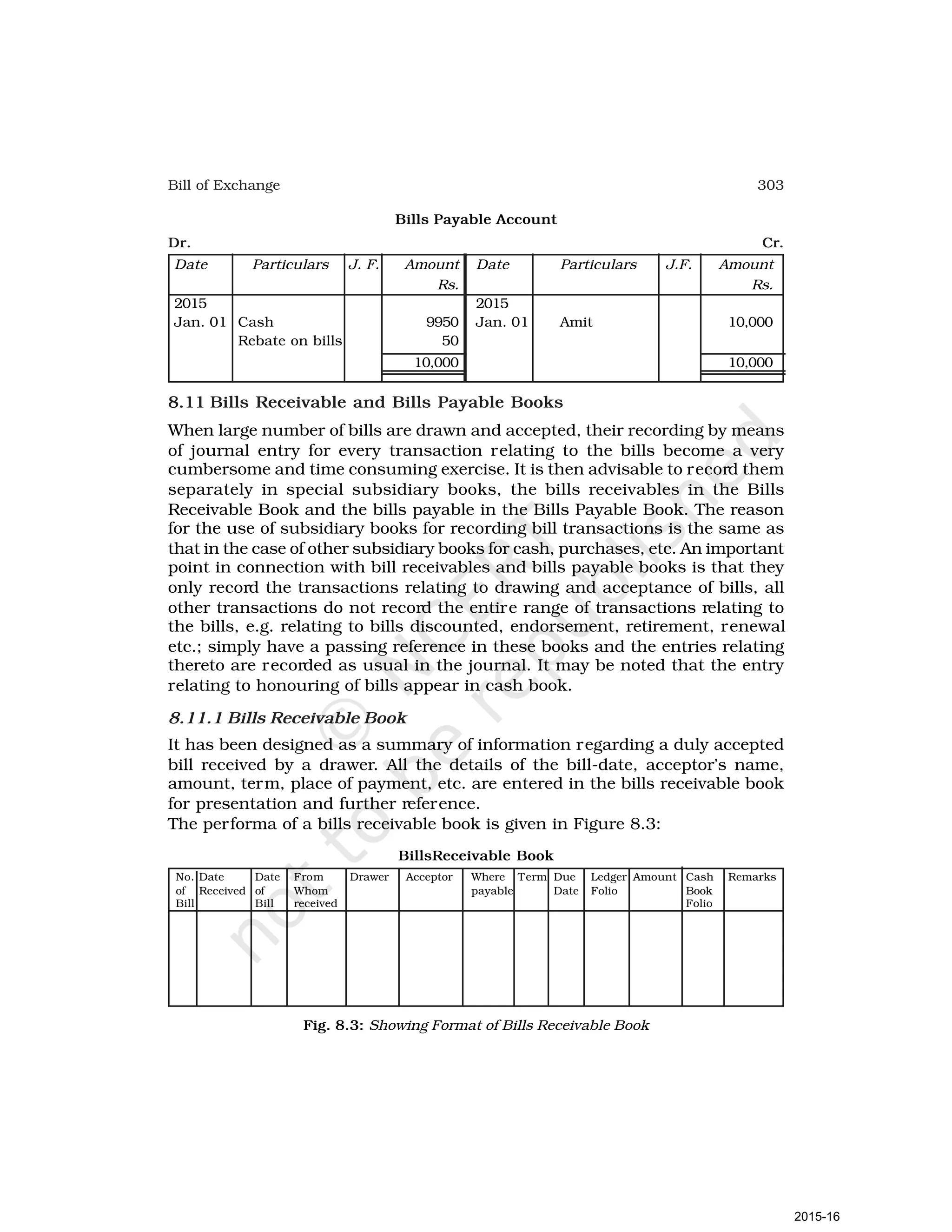
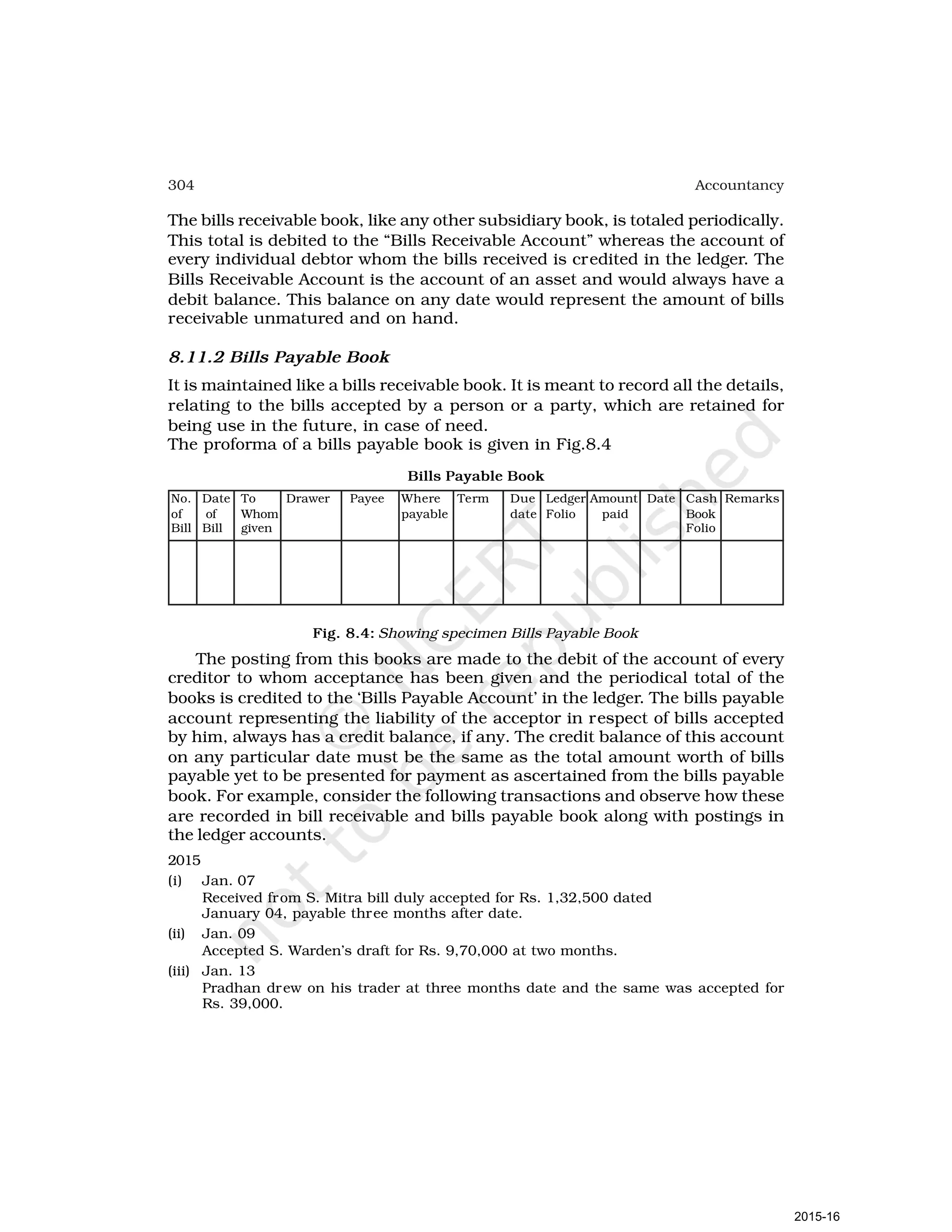
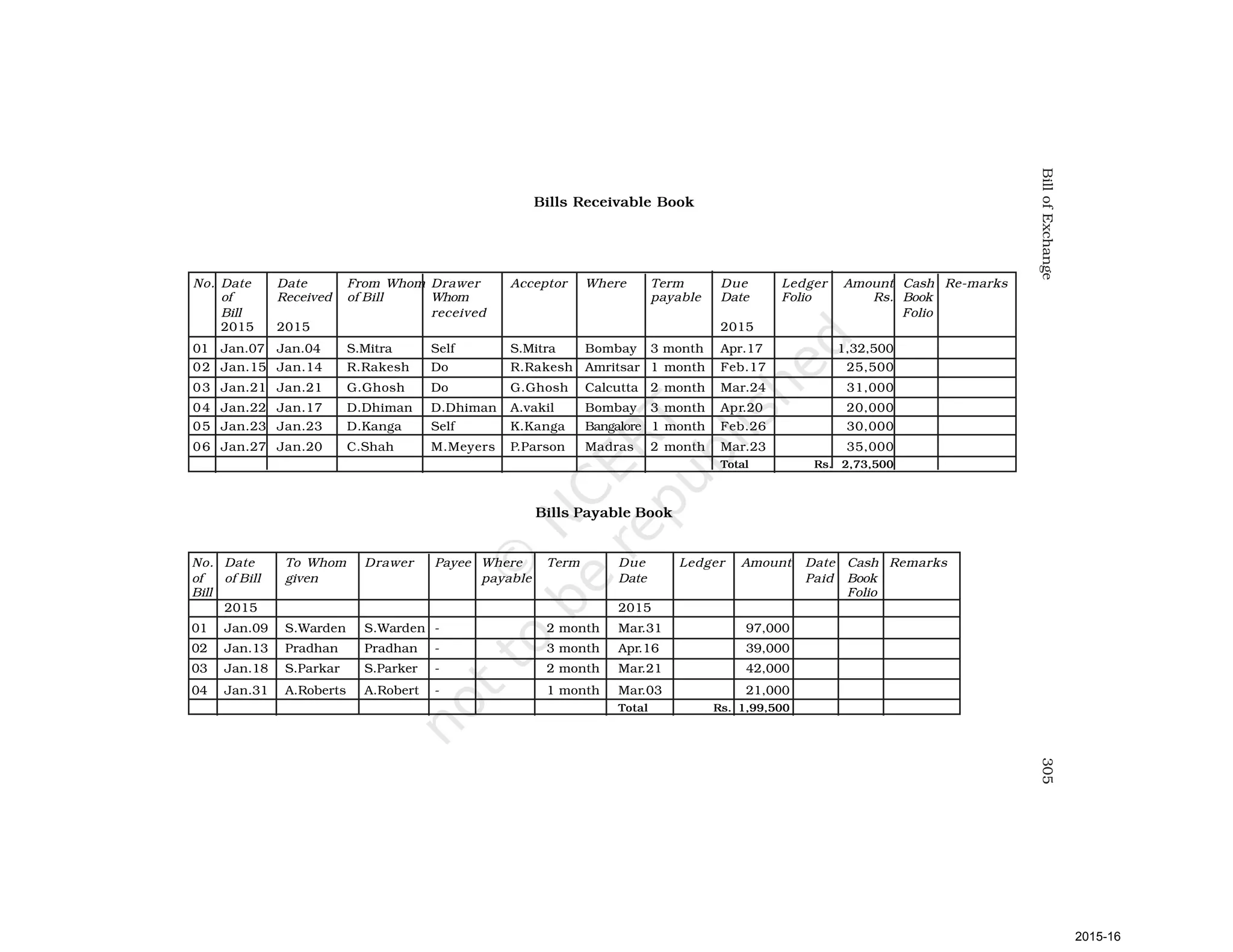
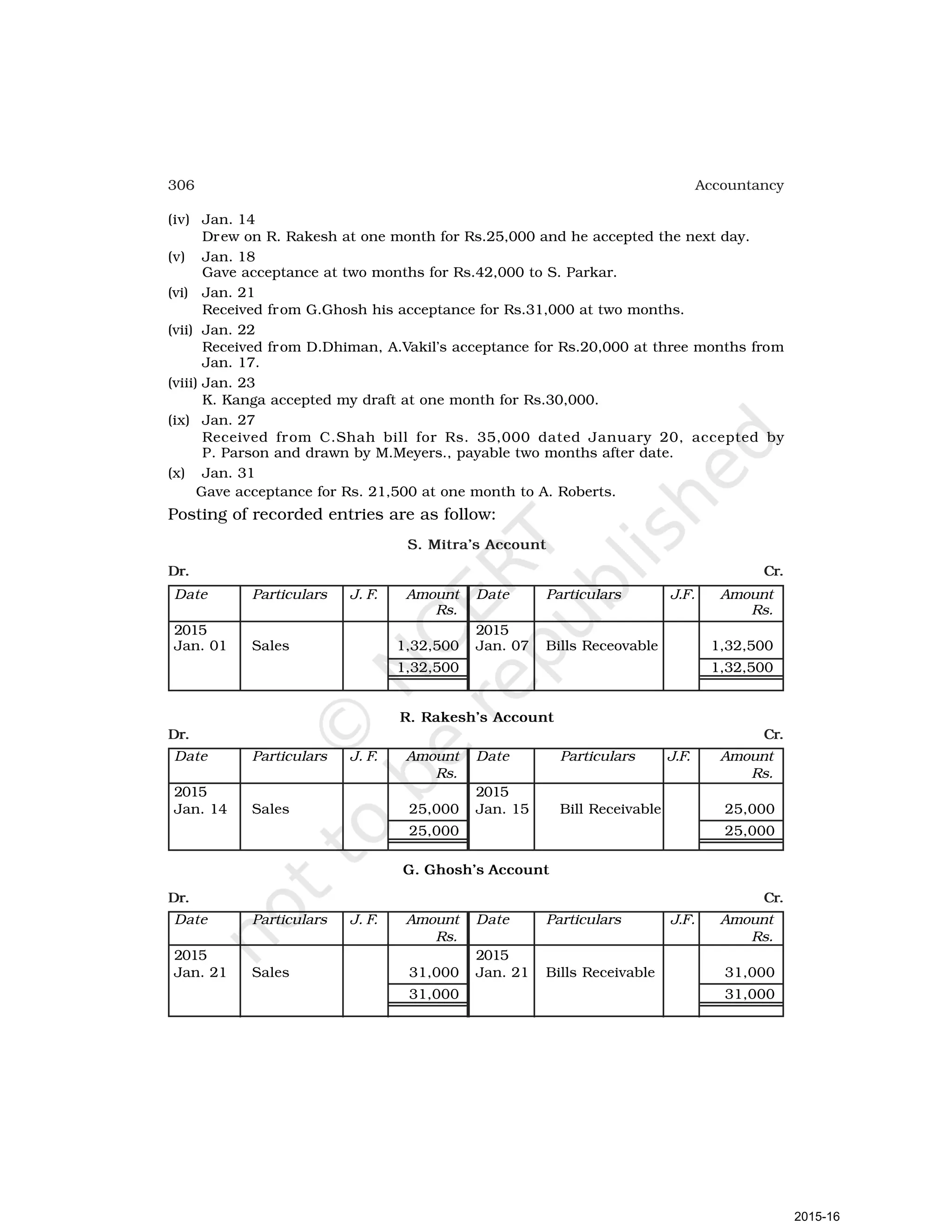
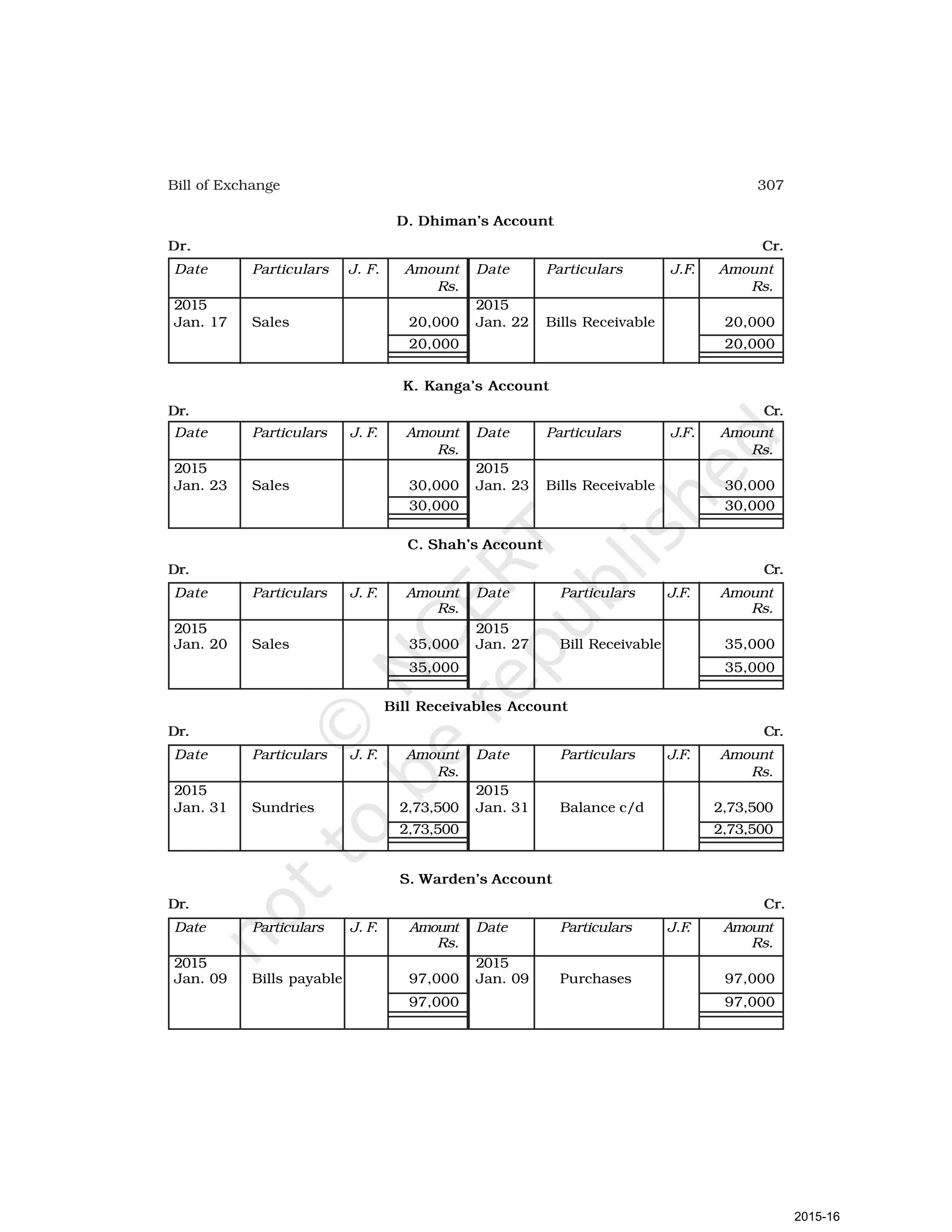
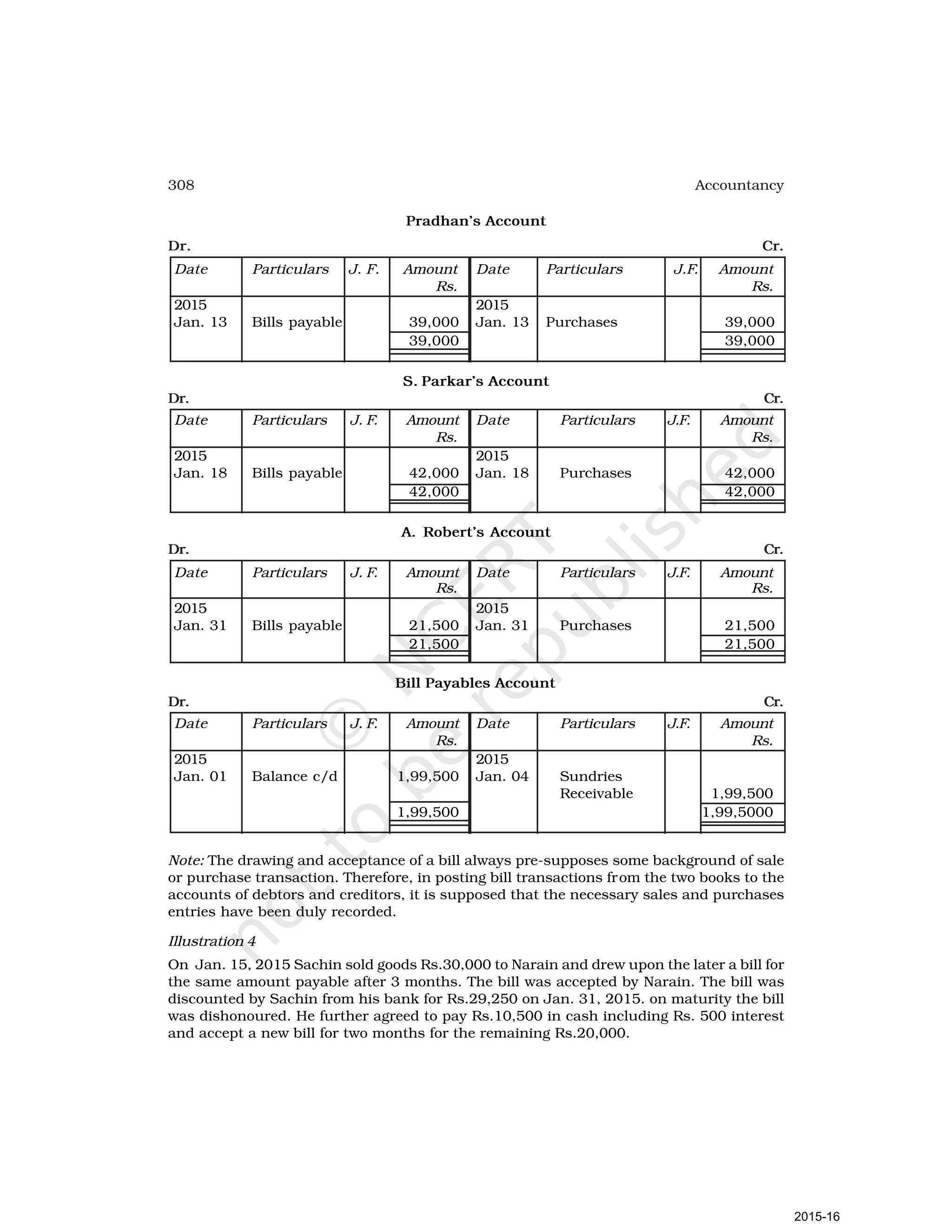
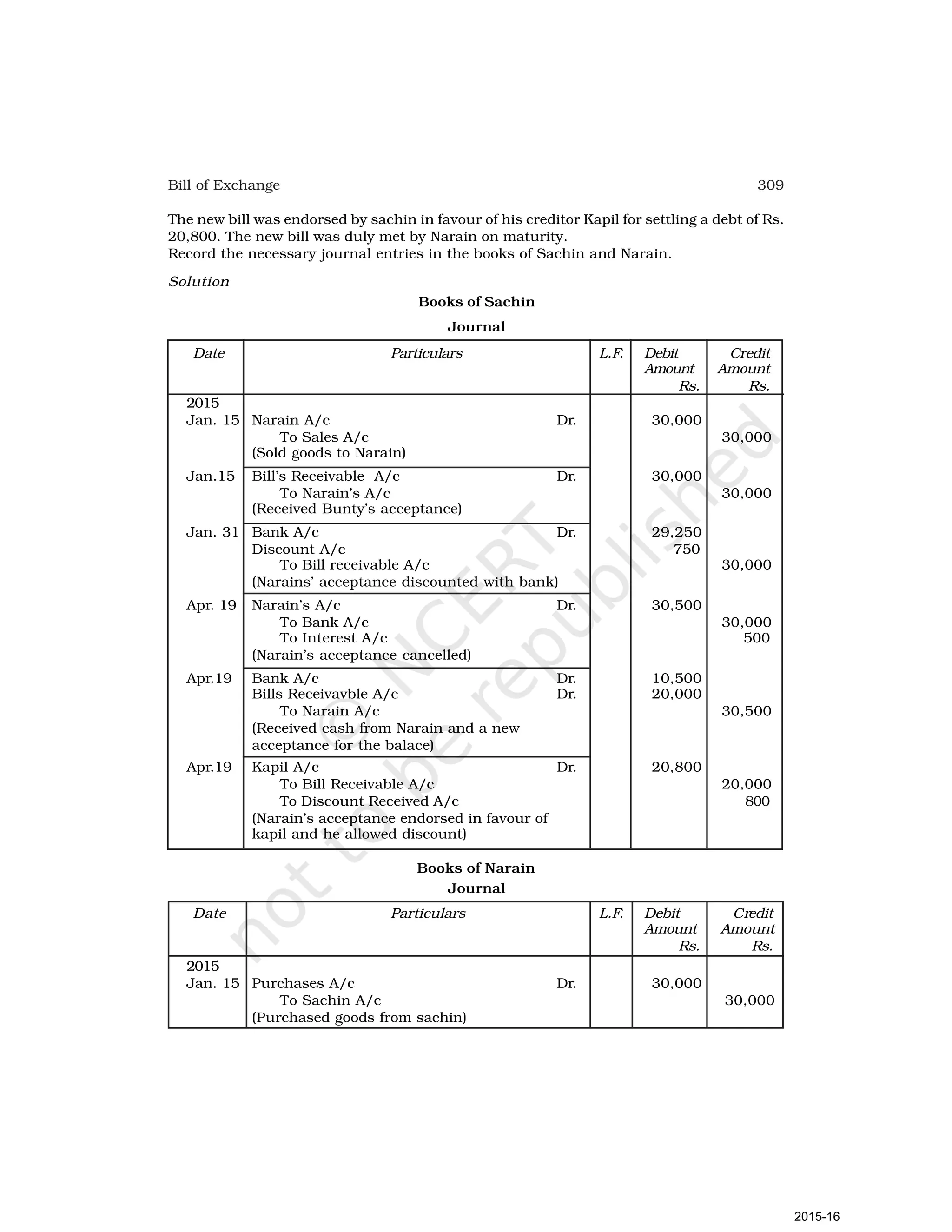
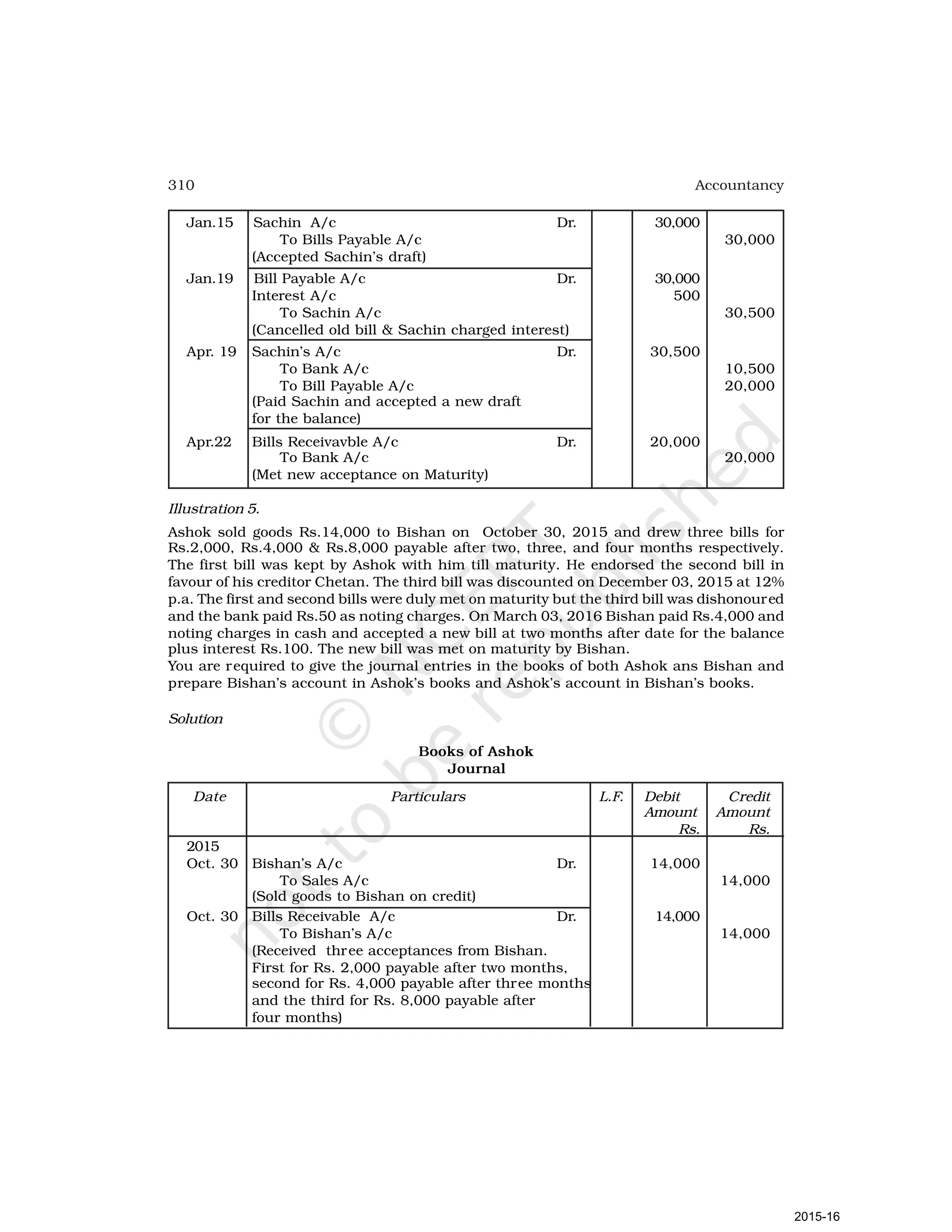
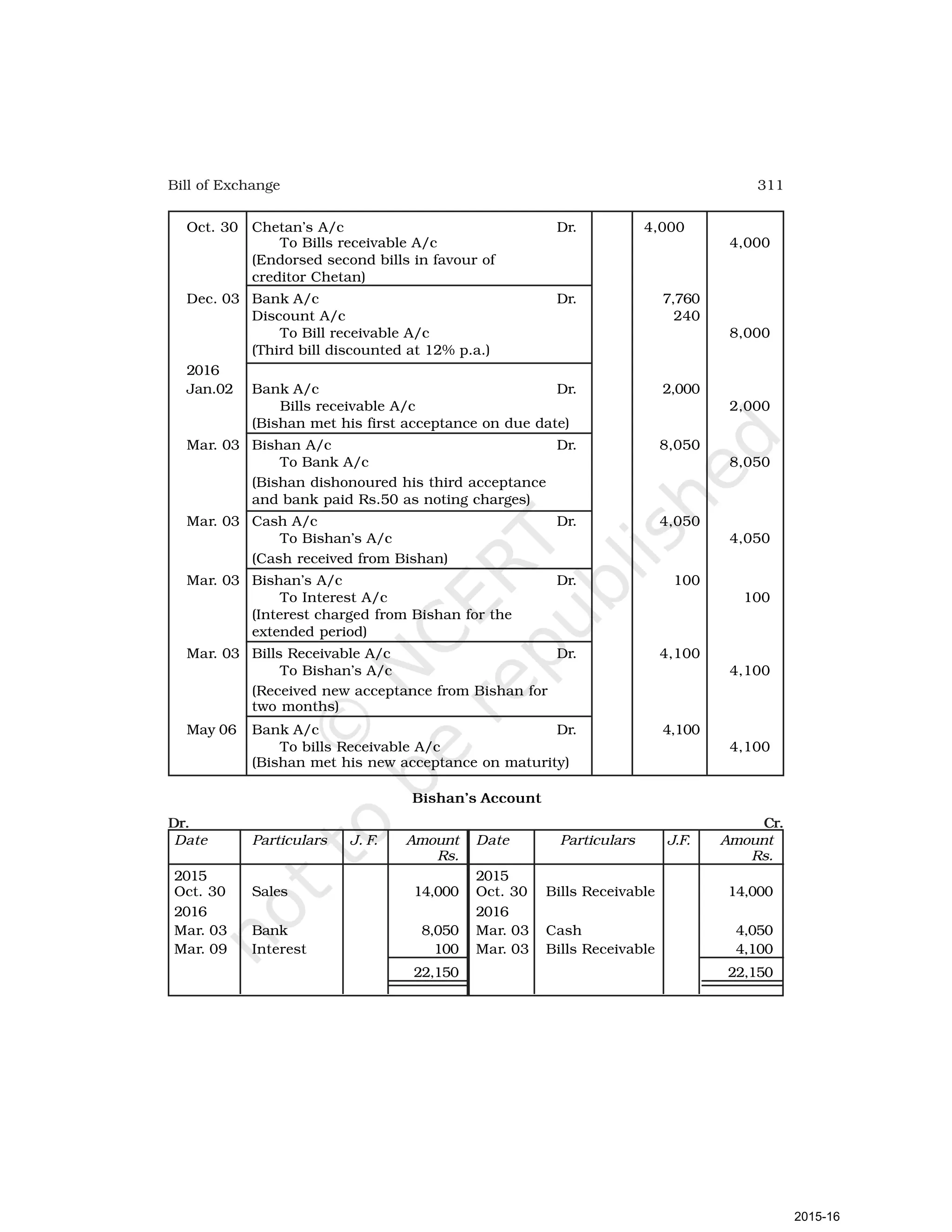
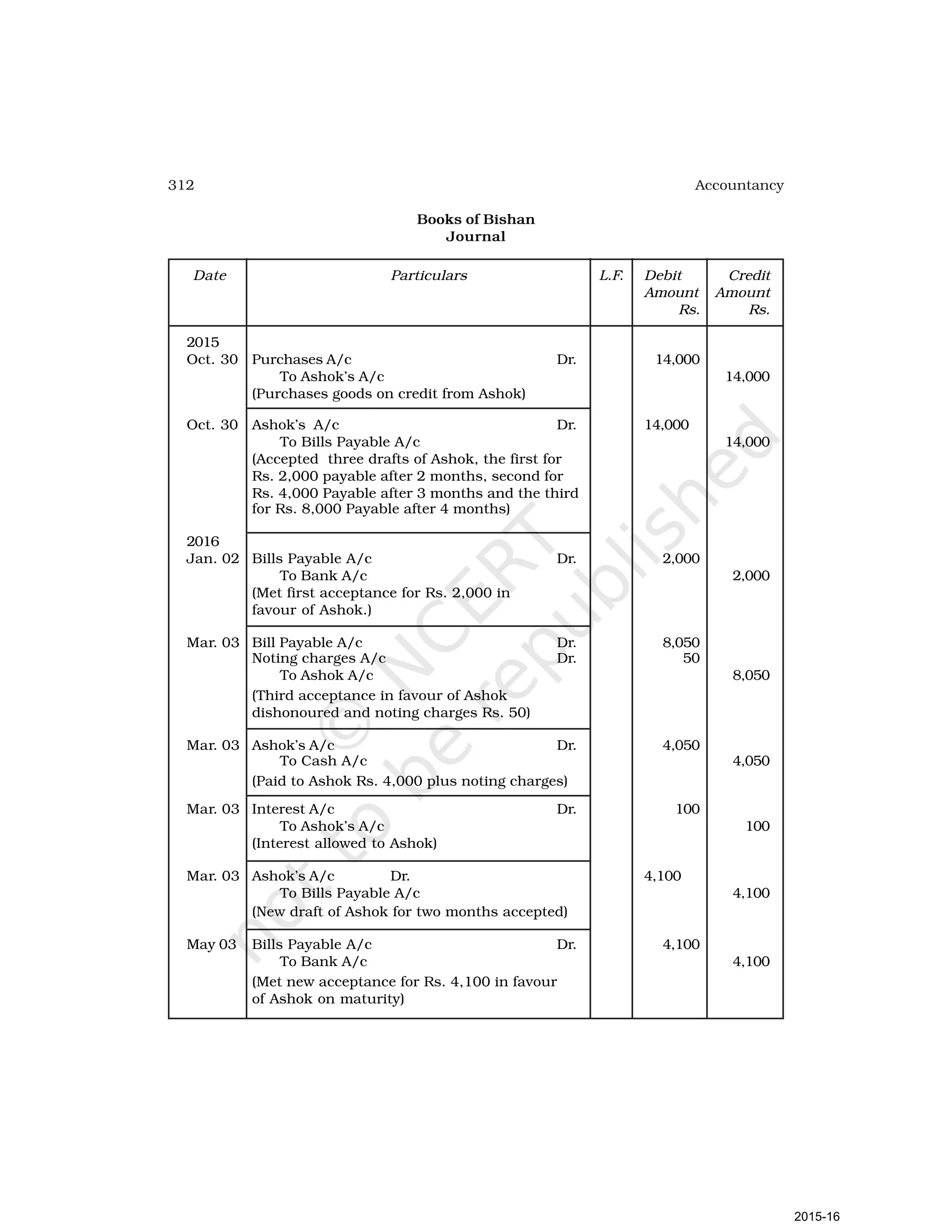
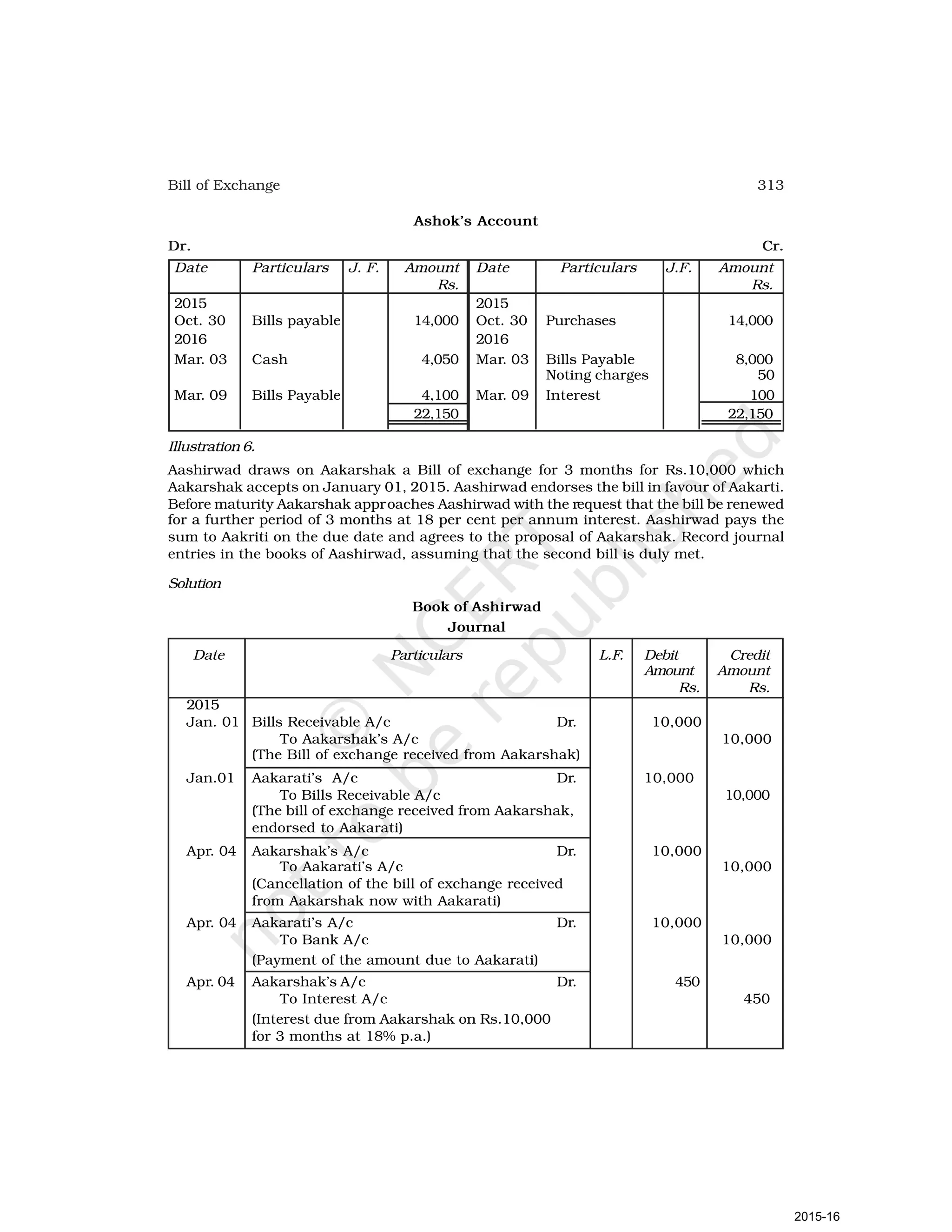
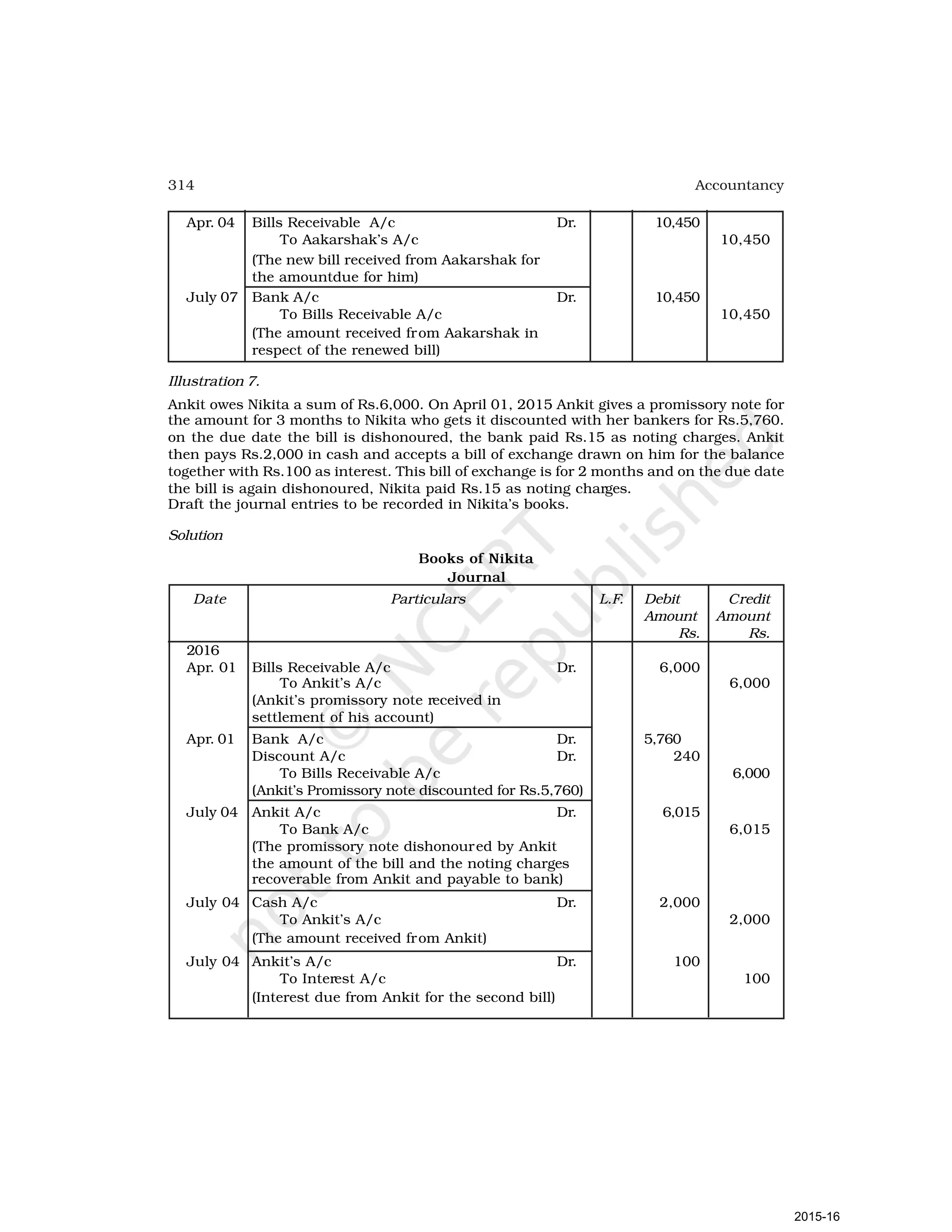
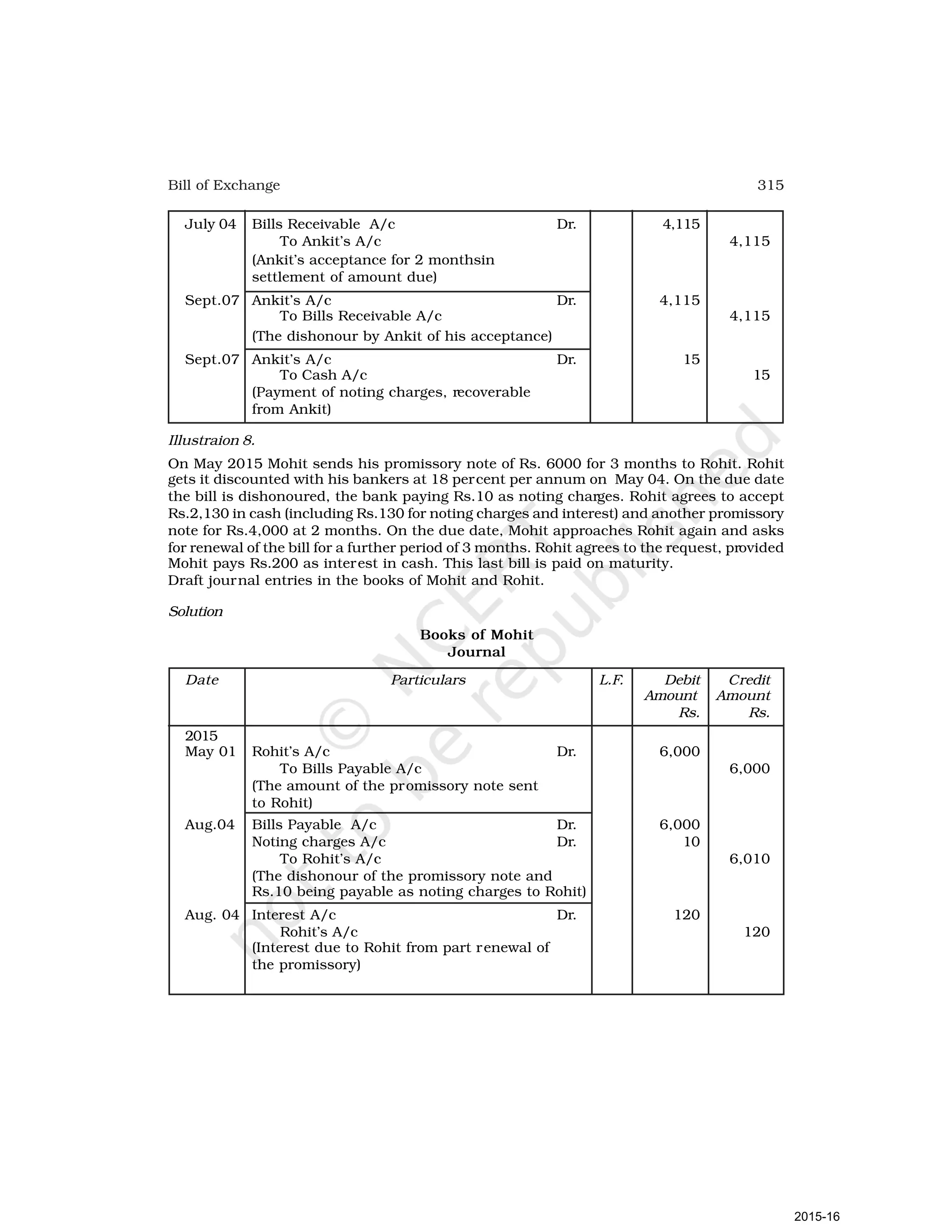
- Goods can be bought or sold for cash or credit. When sold on credit, payment is deferred to a future date and the firm relies on the party to pay on the due date. To ensure payment, instruments of credit called hundis were used in India.
- Hundis are written documents in local languages that specify payment terms. Common types include Shahjog hundi which is passed from merchant to merchant until reaching a trustworthy person, and Darshani hundi which is payable at sight, similar to a demand bill.
- Now, instruments of credit in India are called bills of exchange or promissory notes as governed by the Negotiable Instruments Act 1881. A bill