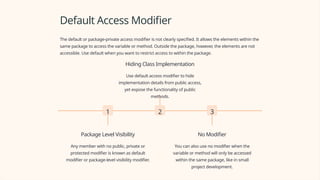
In Java, access modifiers are an essential part of coding best practices. Each modifier has a unique purpose and usage. It's essential to use them properly to ensure the security and maintainability of your code. In summary, public is the least restrictive while default is the most restrictive. Private restricts access to the same class while protected restricts access to the same package and subclass. Keep in mind that proper encapsulation means hiding implementation details and exposing functionality through public methods.