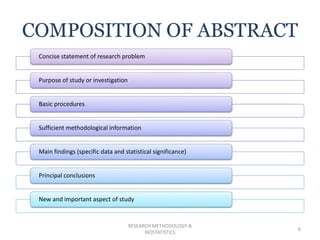
The document discusses the importance of abstracts in research papers, defining them as concise summaries that allow readers to quickly understand the essence of the studies. It outlines various types and forms of abstracts, along with considerations for their composition, emphasizing clarity, brevity, and self-containment. The need for an abstract is highlighted in terms of communication, evaluation, and aiding researchers in reviewing pertinent studies.