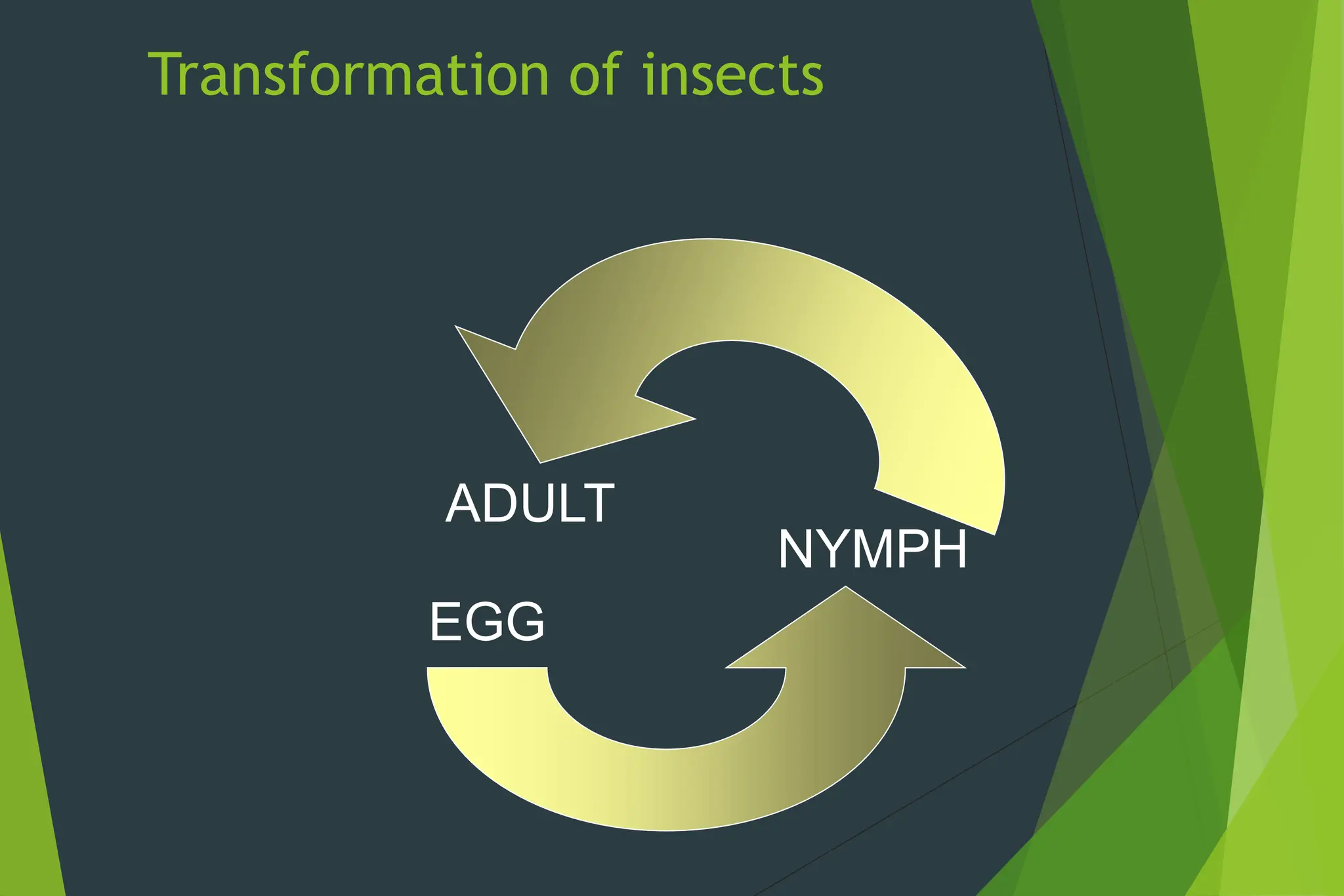
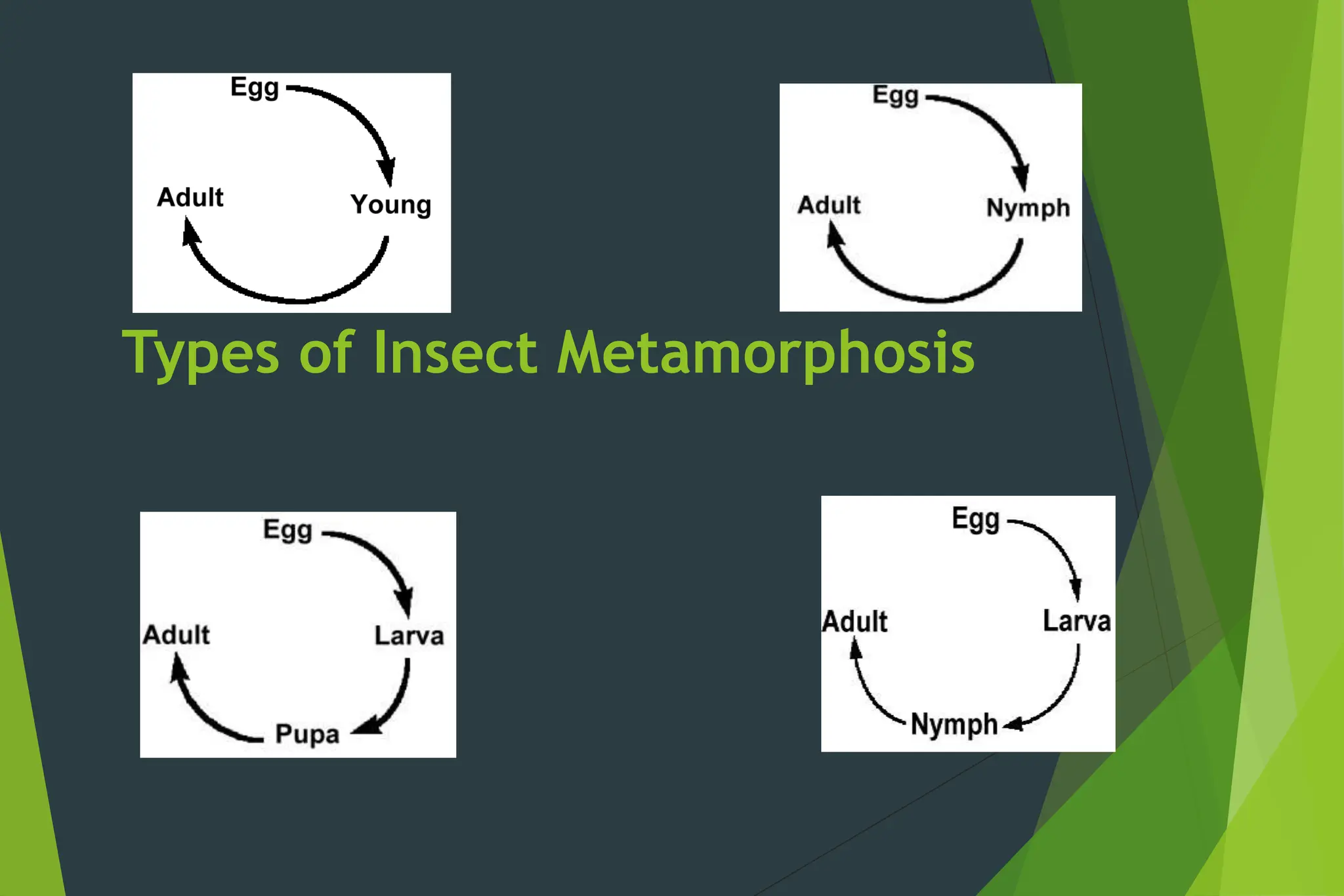
This document discusses the growth and metamorphosis of insects. It begins by explaining that all insects develop from eggs and provides examples of different types of eggs. It then describes the process of insect growth, which involves molting and is regulated by hormones like ecdysone and juvenile hormone. The document outlines the main life stages of insects as egg, immature (nymph or larva), and adult. It defines the different types of insect metamorphosis, including no metamorphosis, gradual metamorphosis, and complete metamorphosis. Complete metamorphosis involves distinct life stages of egg, larva, pupa, and adult. The summary provides an overview of the key topics and stages discussed in