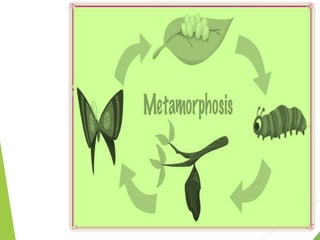
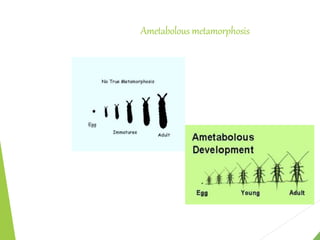
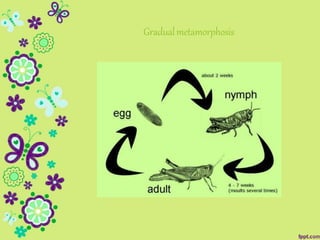
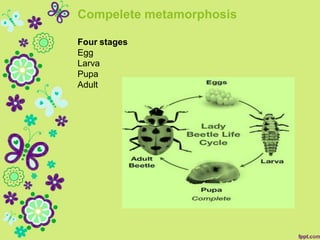
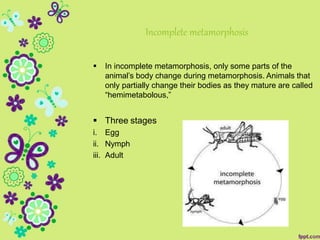
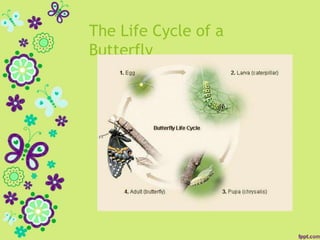
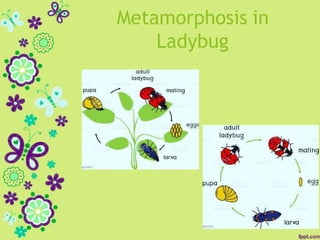
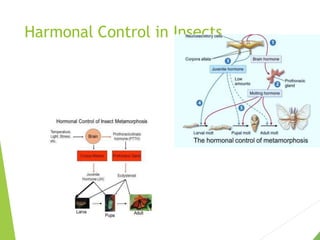
This document discusses metamorphosis in insects. It describes four types of metamorphosis: ametabolous (little change from immature to adult), gradual (changes occur gradually through nymph stages as in grasshoppers), complete (distinct egg/larva/pupa/adult stages as in butterflies), and incomplete (three stages of egg/nymph/adult as in dragonflies). Complete metamorphosis involves a dramatic transformation controlled by the hormones juvenile hormone and ecdysone. These hormones regulate molting and development between life stages and sexual maturity in insects.