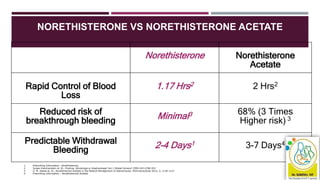
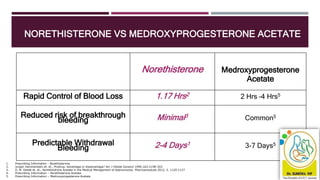
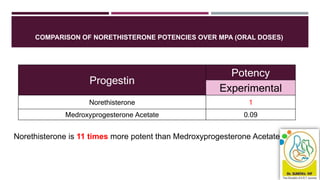
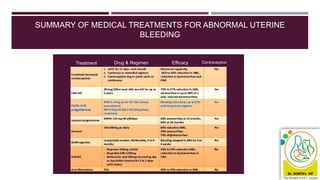
This document discusses abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB), including definitions, prevalence, assessment, causes, and management. Some key points:
- AUB is irregular bleeding that affects 10-30% of reproductive-aged women. It has many potential causes and can seriously impact quality of life.
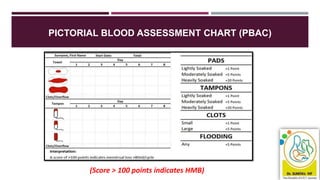
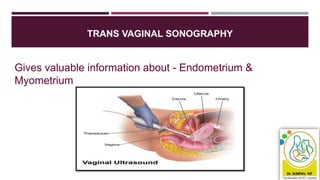
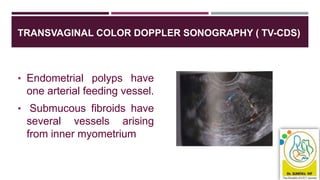
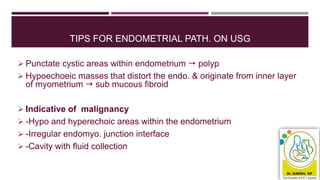
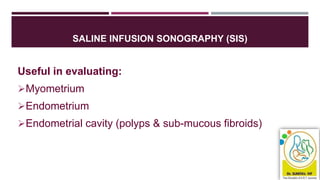
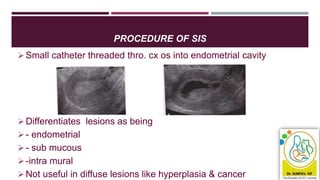
- Assessment involves history, physical exam, blood tests, imaging like ultrasound and potentially biopsy. The Pictorial Blood Assessment Chart scores bleeding to indicate if it is heavy.
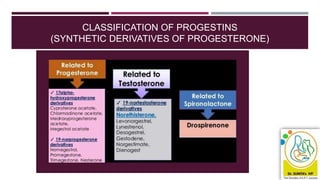
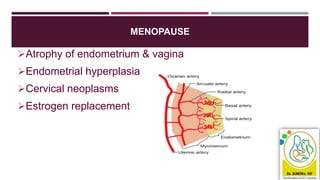
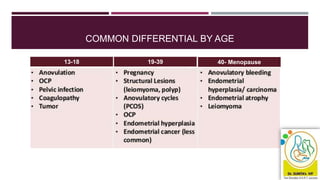
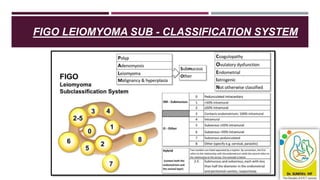
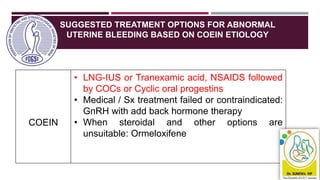
- Causes vary by age but include issues like fibroids, polyps, hormonal imbalances, and cancer. The 2018 FIGO classification system standardized terminology.
- Initial treatment is usually medical like hormones, NSAIDs, or tran





























![TREATMENTS FOR WOMEN WITH NO IDENTIFIED PATHOLOGY,
FIBROIDS LESS THAN 3 CM IN DIAMETER, OR SUSPECTED OR
DIAGNOSED ADENOMYOSIS
41
Consider an LNG-IUS as the first treatment for AUB in women [2018]
If a woman with HMB declines an LNG-IUS or it is not suitable, consider the
following pharmacological treatments:
Non-hormonal: Tranexamic acid NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
Hormonal: combined hormonal contraception OR cyclical oral
progestogens. [2018]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cmeslidesaub-201220012027/85/ABNORMAL-UTERINE-BLEEDING-WHAT-IS-NEW-41-320.jpg)