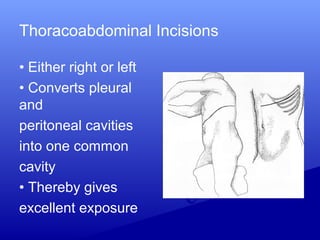
This document discusses different types of abdominal wall incisions for surgery. It provides details on:
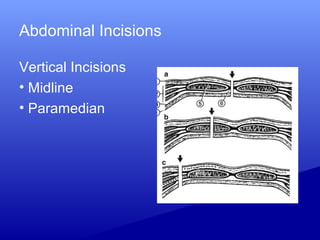
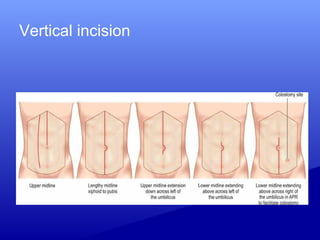
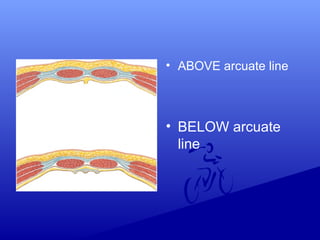
1) Various incision types including vertical, transverse, median, paramedian and their advantages and disadvantages. Transverse incisions are generally preferred as they are stronger and have a better cosmetic outcome.
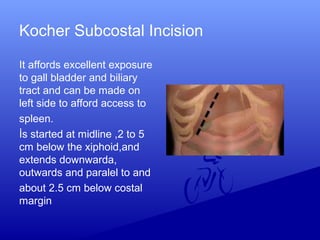
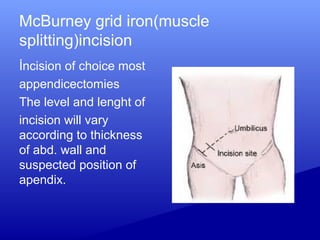
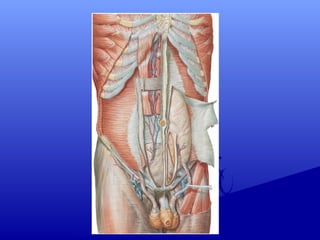
2) Specific incisions like Kocher for gallbladder access, McBurney for appendicectomies which is made at the junction of the middle and outer third of a line from the umbilicus to the ASIS.
3) Principles of abdominal incisions including adequate size for exposure, splitting rather than cutting muscles, avoiding nerves and vessels, and proper closure and drainage if needed.

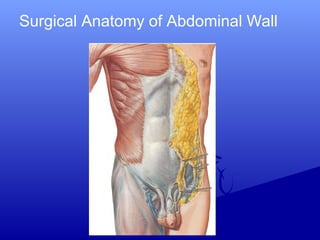
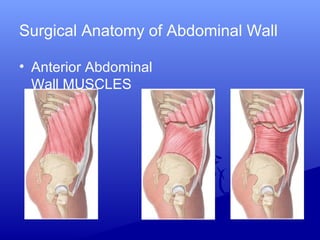


![Choice of incision
Type of surgery [elective/emergency]
Target organ
Surgeons own experience and
preference and Previous surgery.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abdominalwallincision-190803151857/85/Abdominal-wall-incision-9-320.jpg)