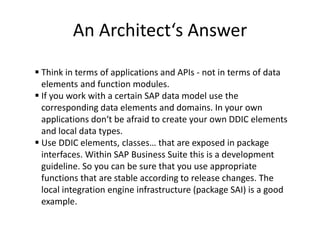
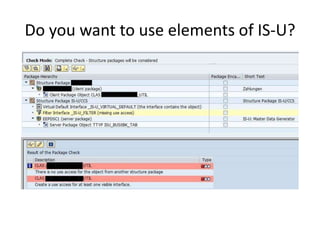
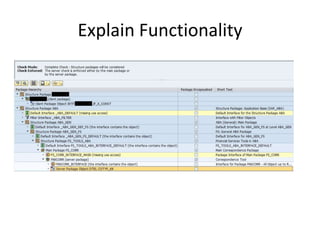
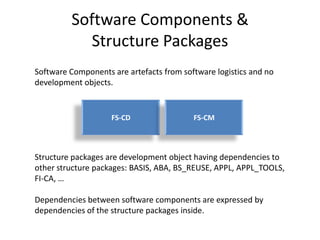
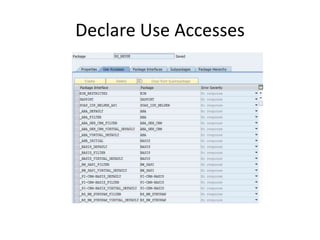
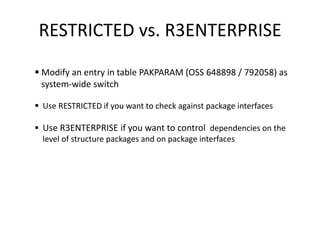
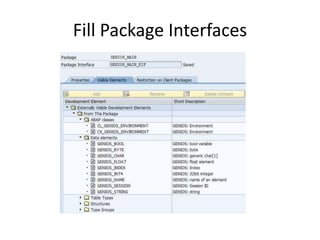
This document discusses the ABAP package concept, use cases, and best practices. It describes how packages can help structure applications, define dependencies, and control reuse through stable APIs. Packages allow dividing large systems into independently evolvable components. The document outlines how to implement the package concept including defining package properties, hierarchies, interfaces, and performing package checks. Migrating legacy systems and changes in SAP NetWeaver 7.30 are also addressed.