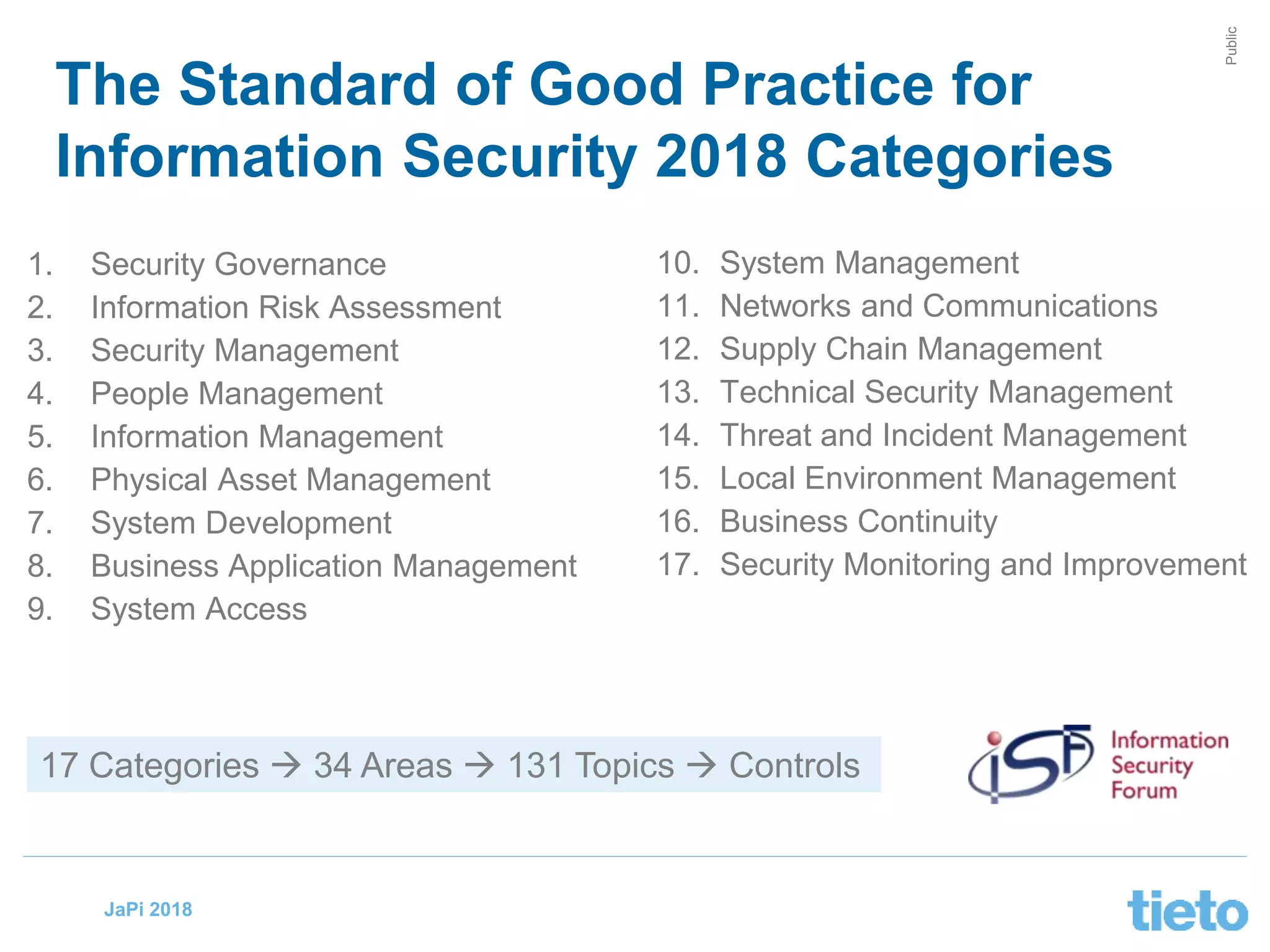
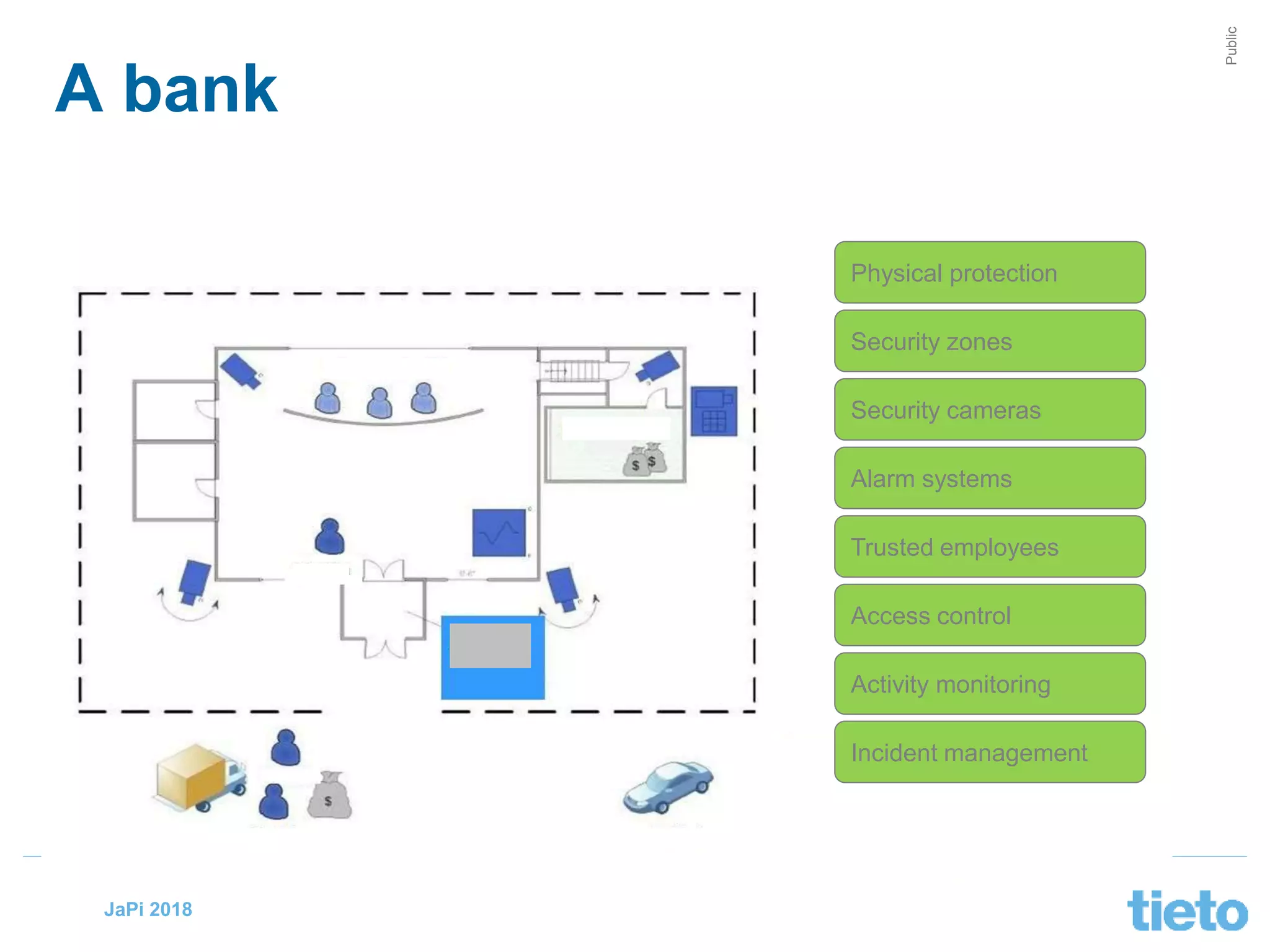
This document discusses digital security and the challenges of securing systems in a changing technological landscape. It notes that terminology around information, cyber, and digital security can be confusing, and that security requirements need to be defined on a case-by-case basis. It emphasizes that security risks will continue to increase as digitalization accelerates, and that security professionals must adapt to embrace changes like cloud computing, IoT, and new technologies. The document concludes that data and trust are key currencies, that security enables digitalization when done well, and that effective security requires balancing risks with opportunities through good design principles and lifelong learning.