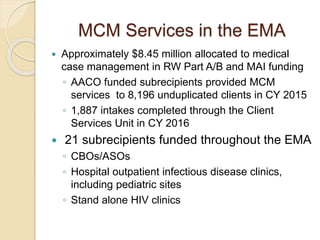
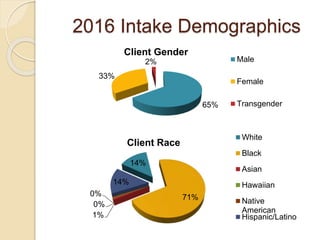
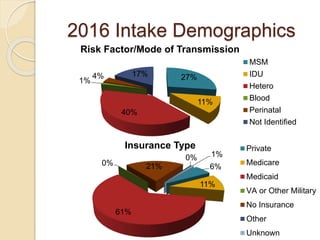
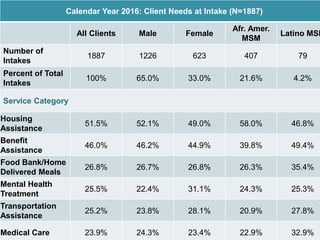
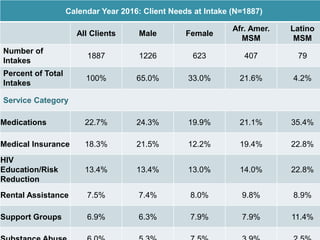
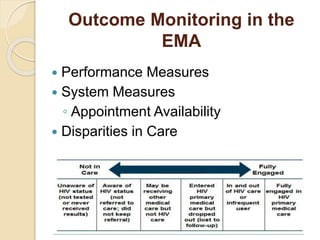
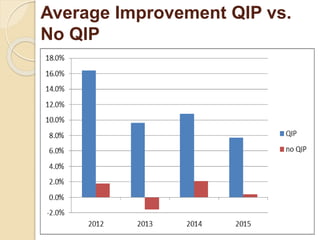
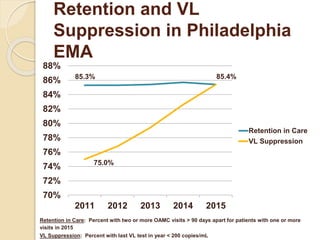
The document records the March 9, 2017 meeting of the Philadelphia Department of Public Health's Ryan White Planning Council, emphasizing the Client Services Unit's mission to assist HIV-infected individuals through medical case management and various support services. It provides detailed statistics on client demographics, needs at intake, and outlines funding sources for different programs, including housing assistance. The document also highlights the Quality Improvement process focusing on enhancing service delivery and outcomes within the HIV care continuum.