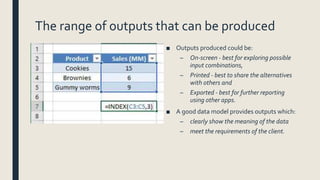
This document discusses using data modeling to consider alternatives. It begins by identifying the key inputs required for a model and the range of outputs that can be produced. It then discusses the benefits and limitations of alternative solutions and the impact and consequences of each alternative. Finally, it addresses identifying the alternative solutions that produce the best decision or compromise, noting that the best solution may require compromising between alternatives.