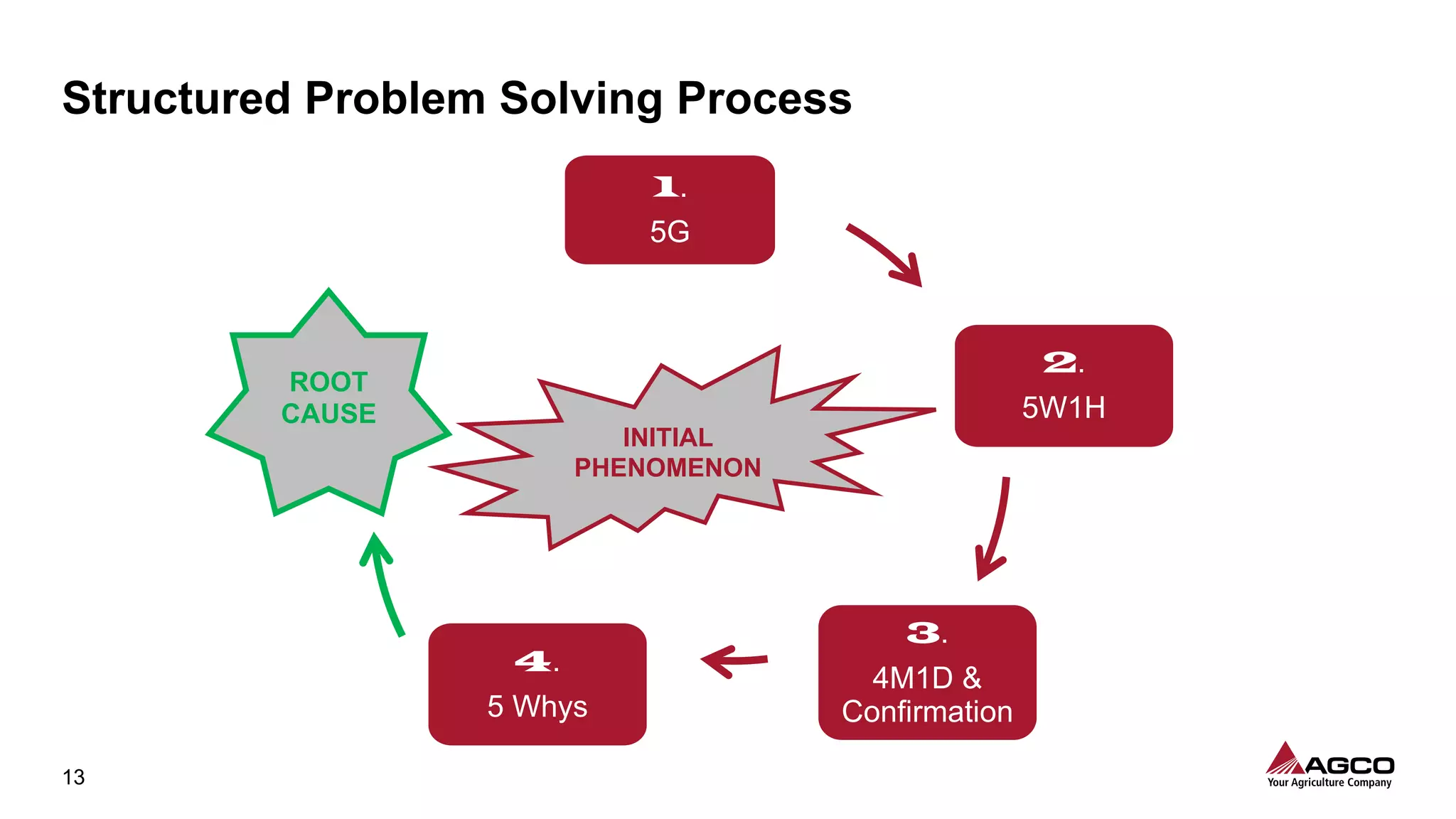
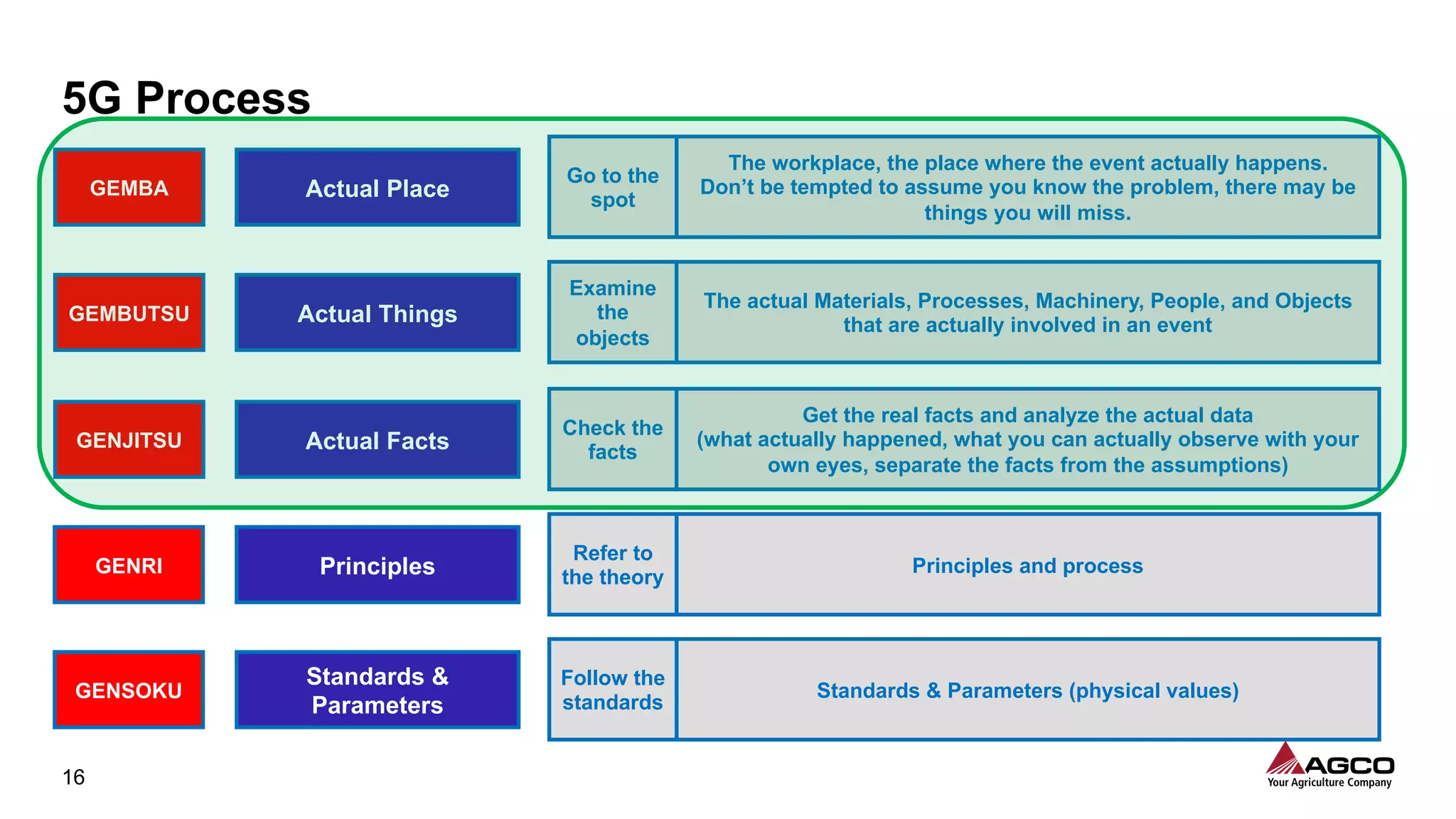
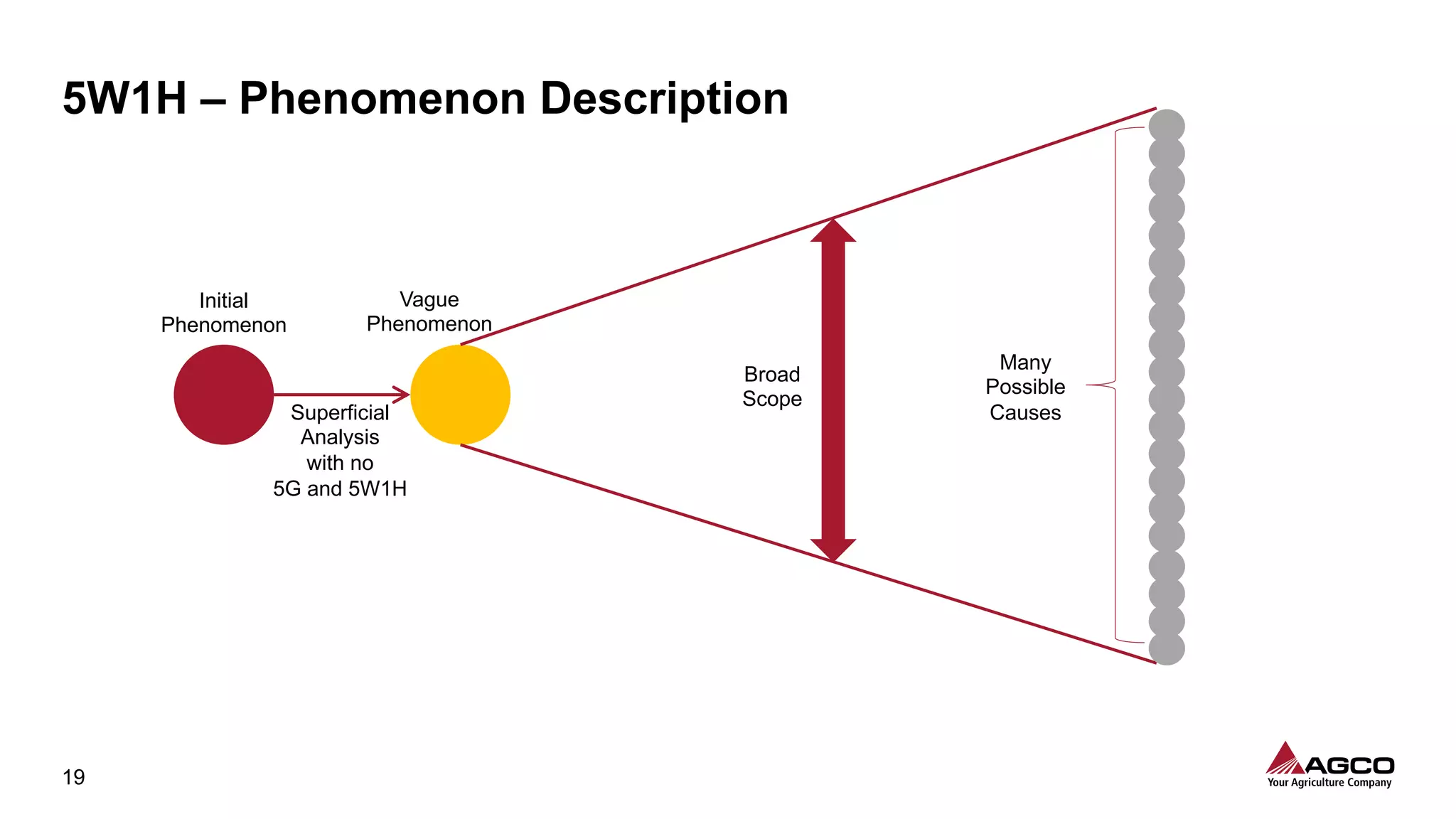
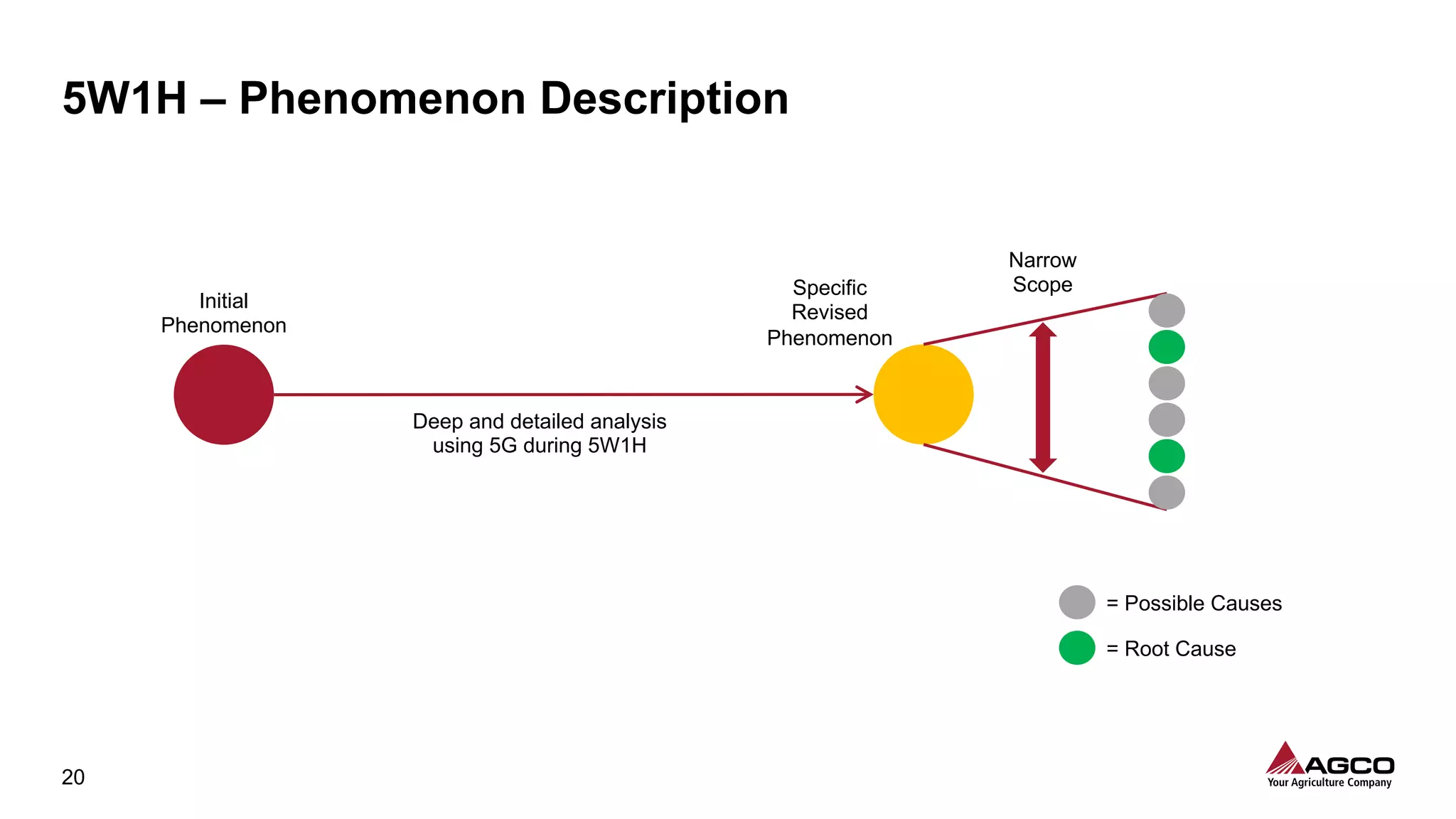
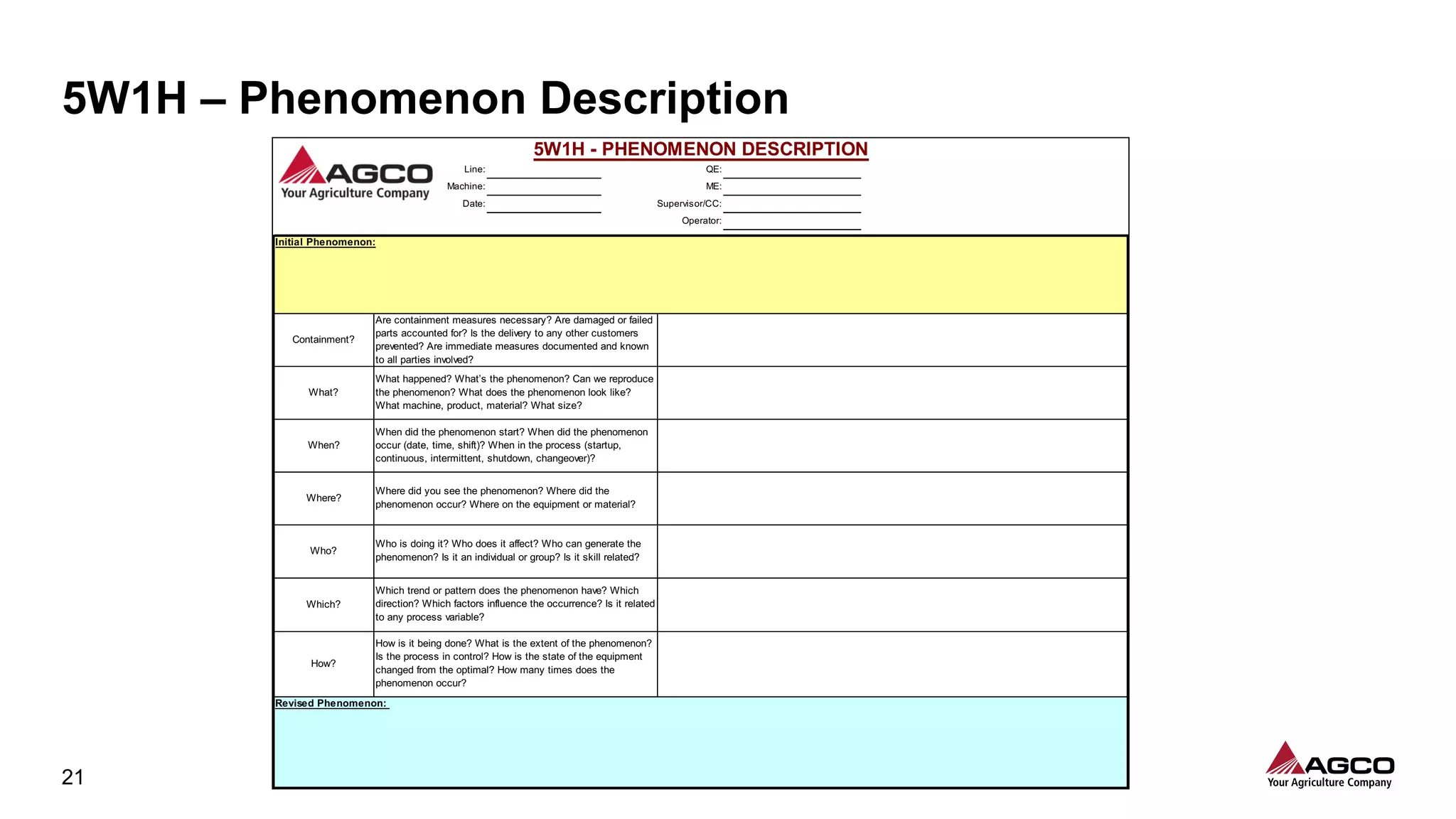
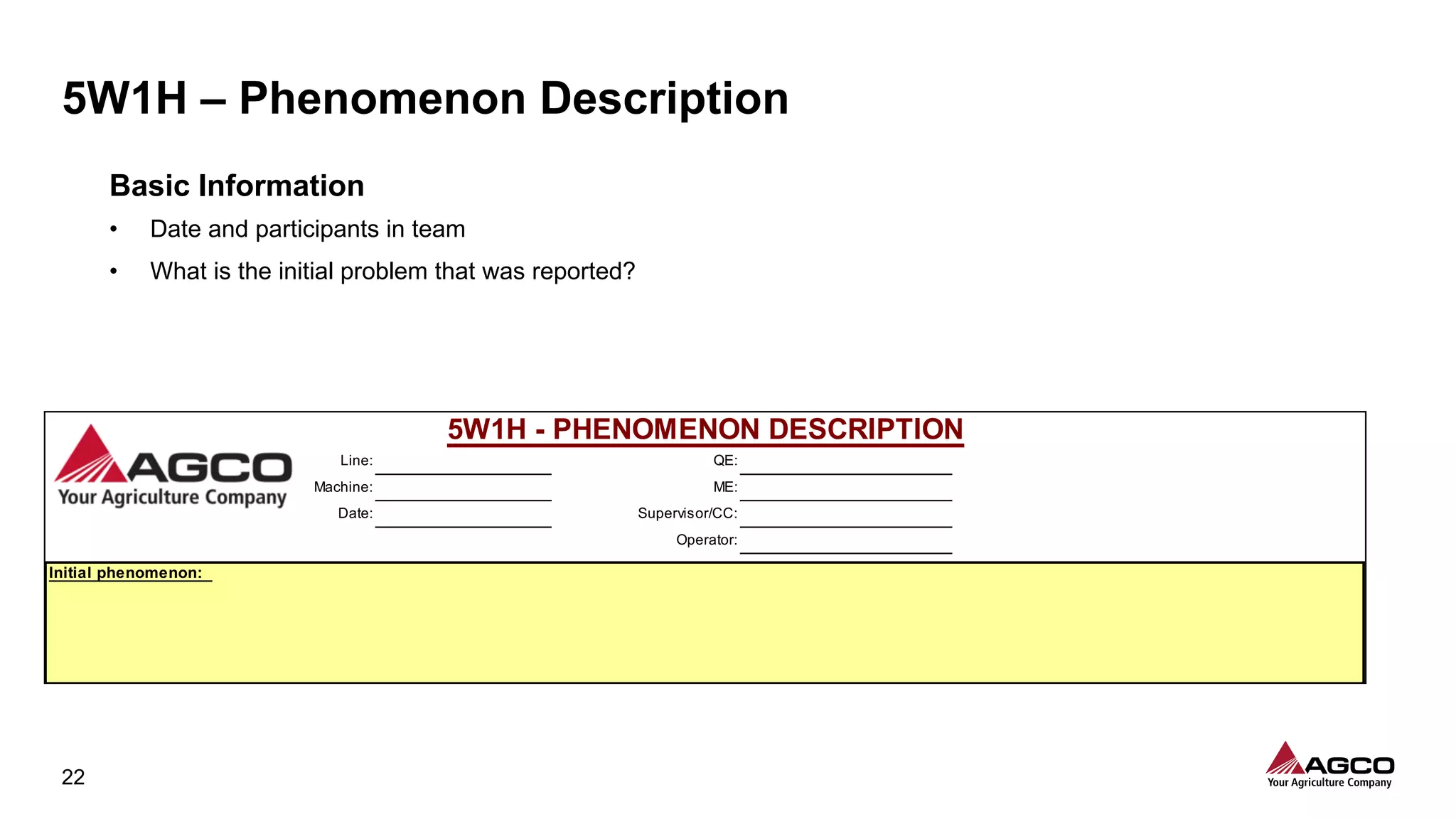
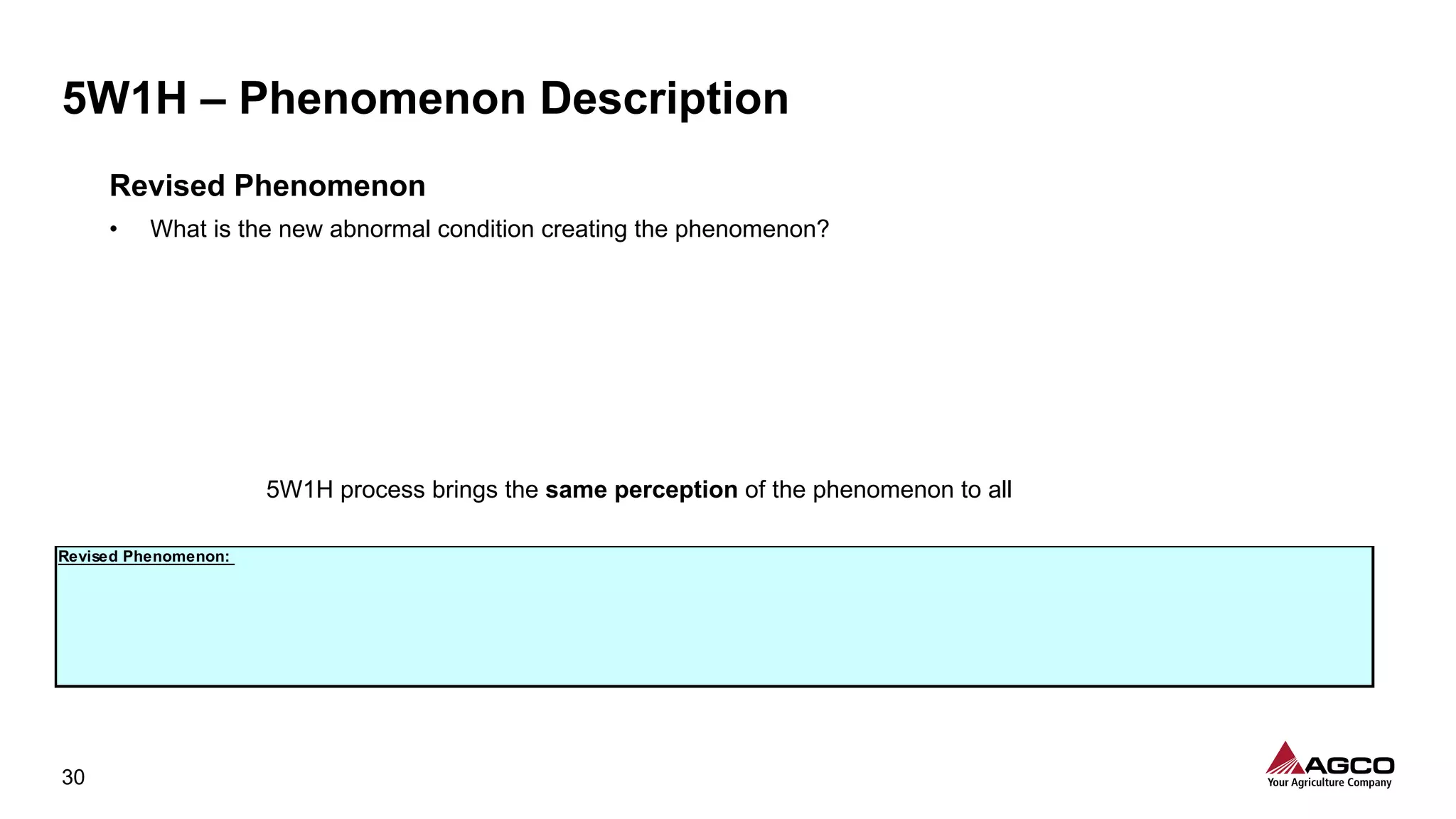
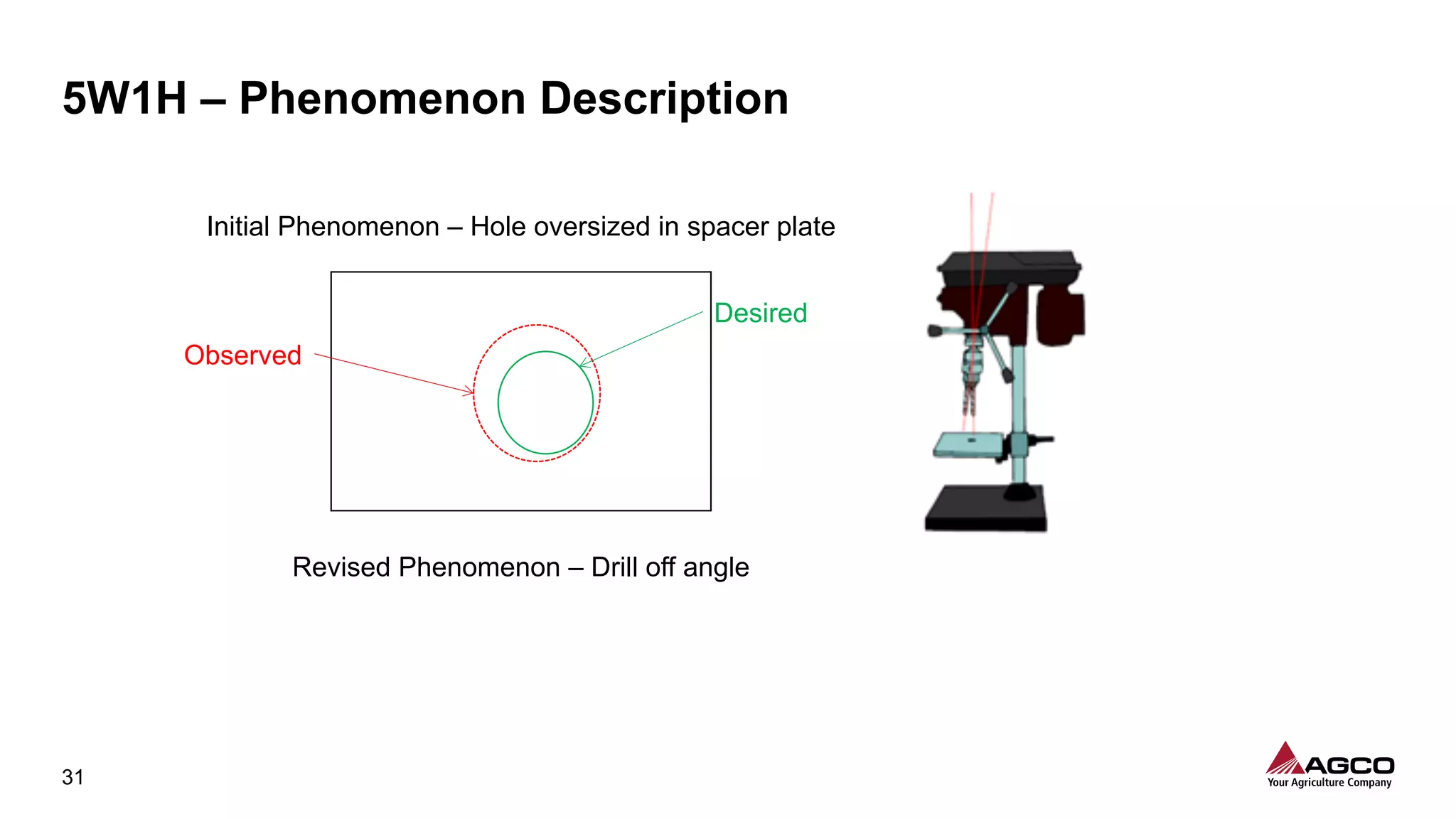
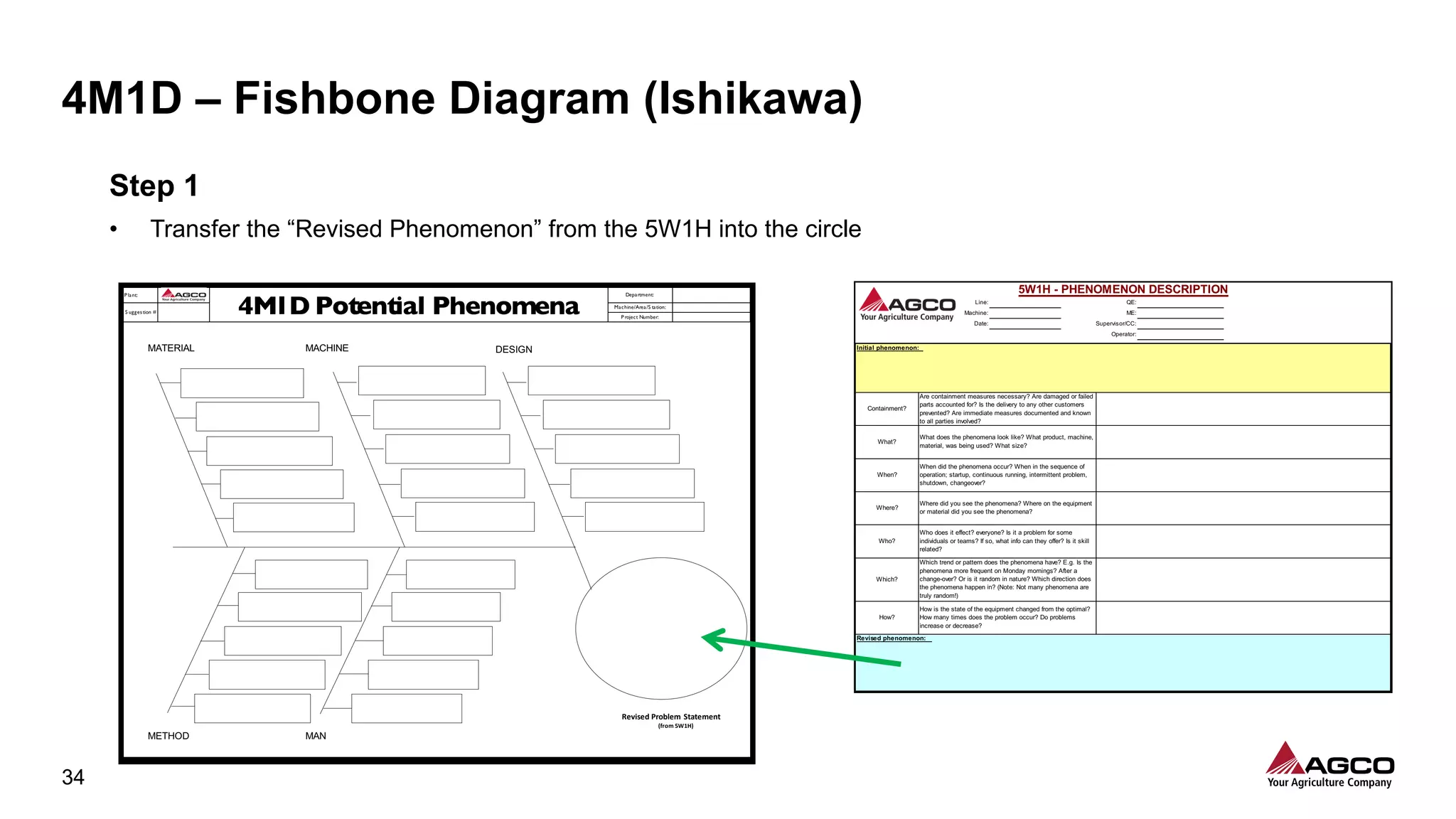
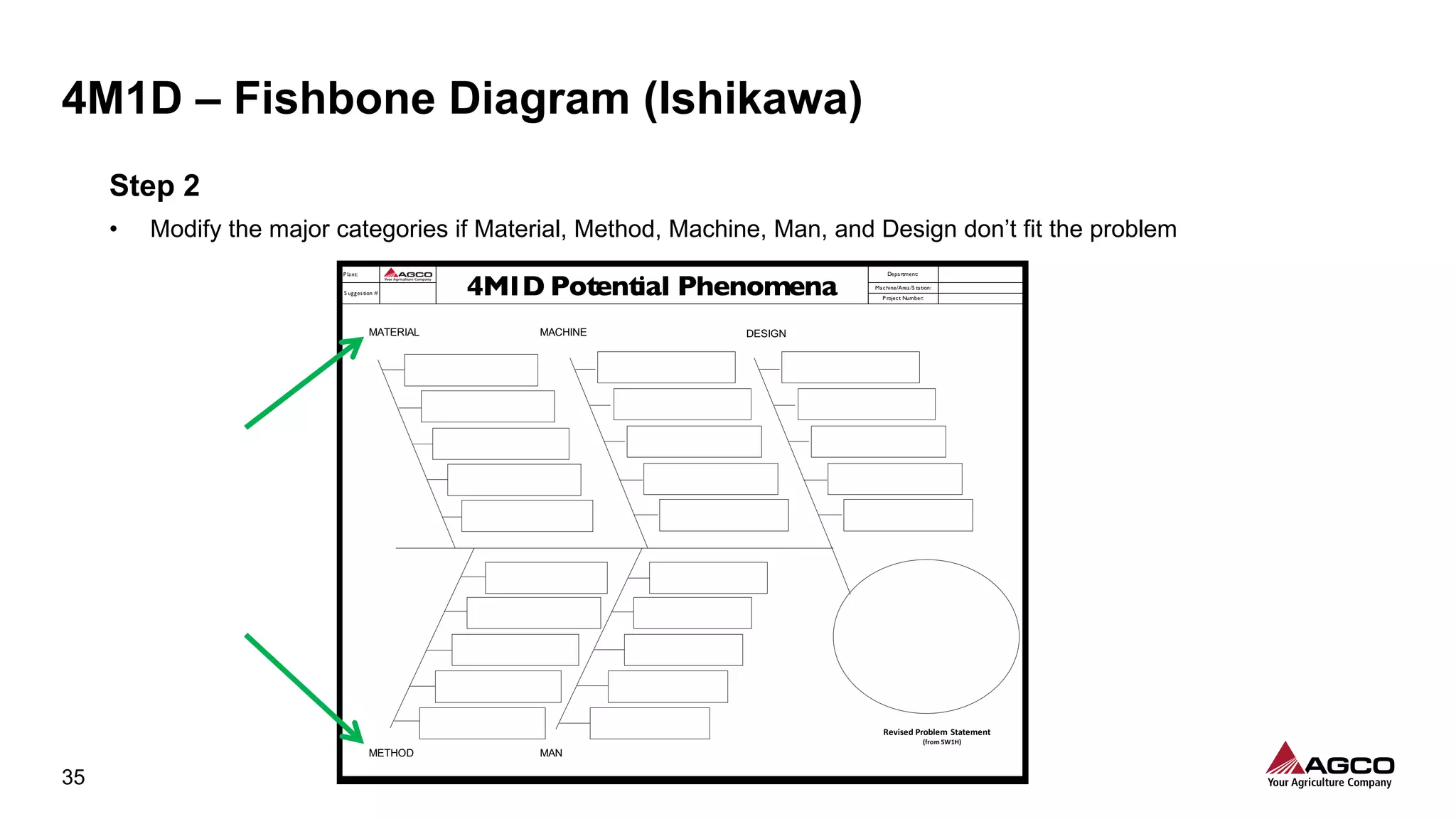
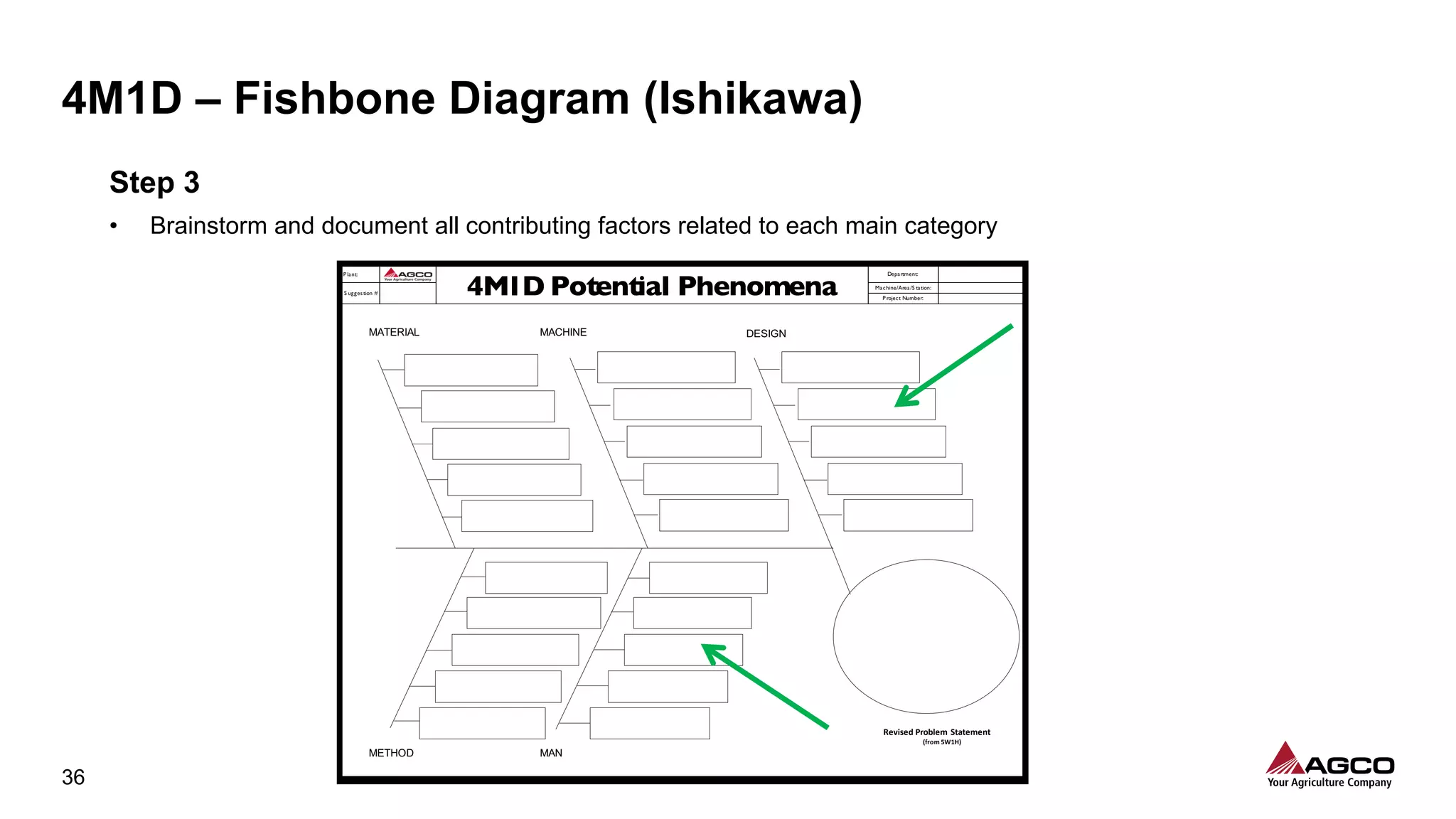
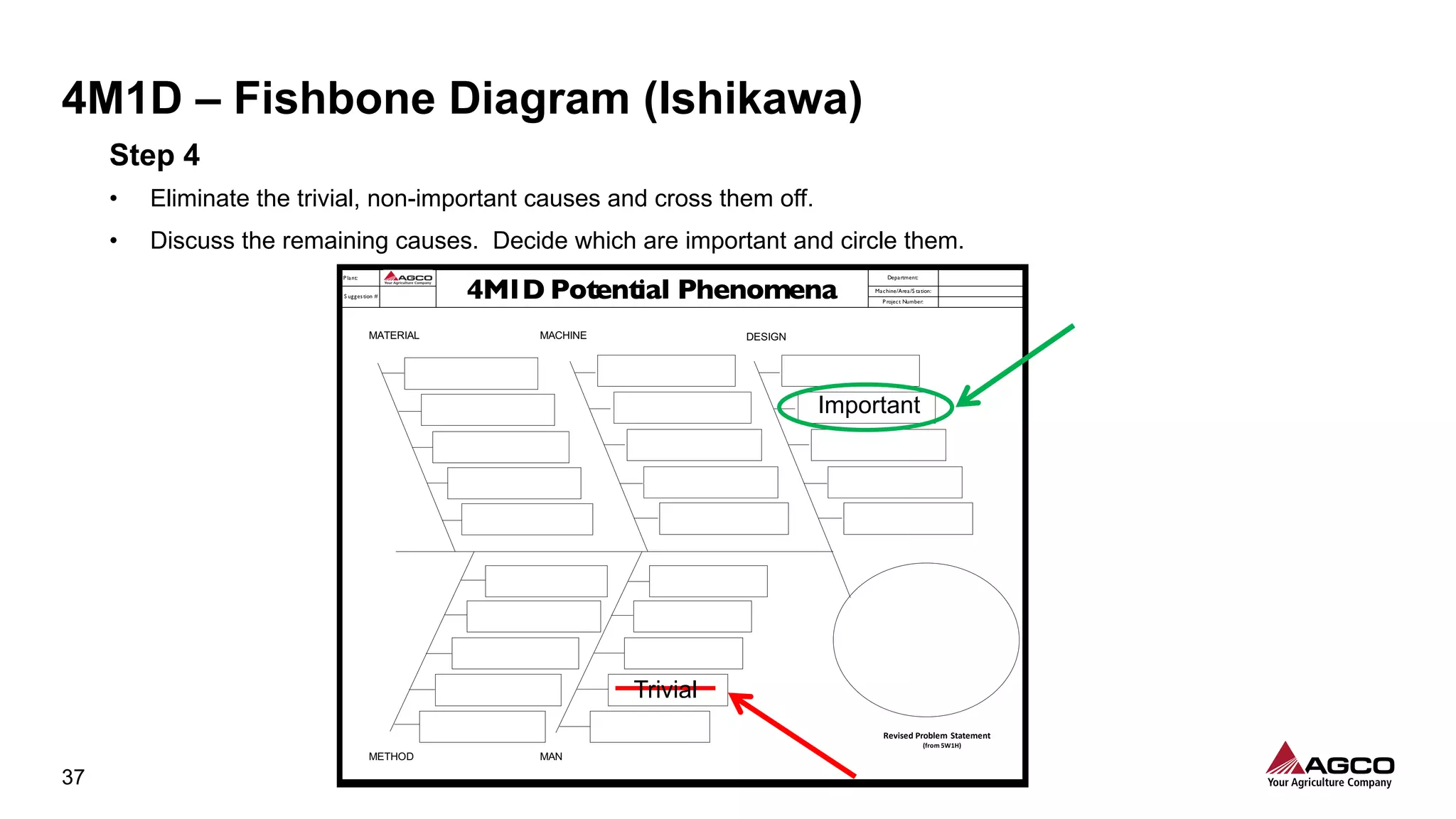
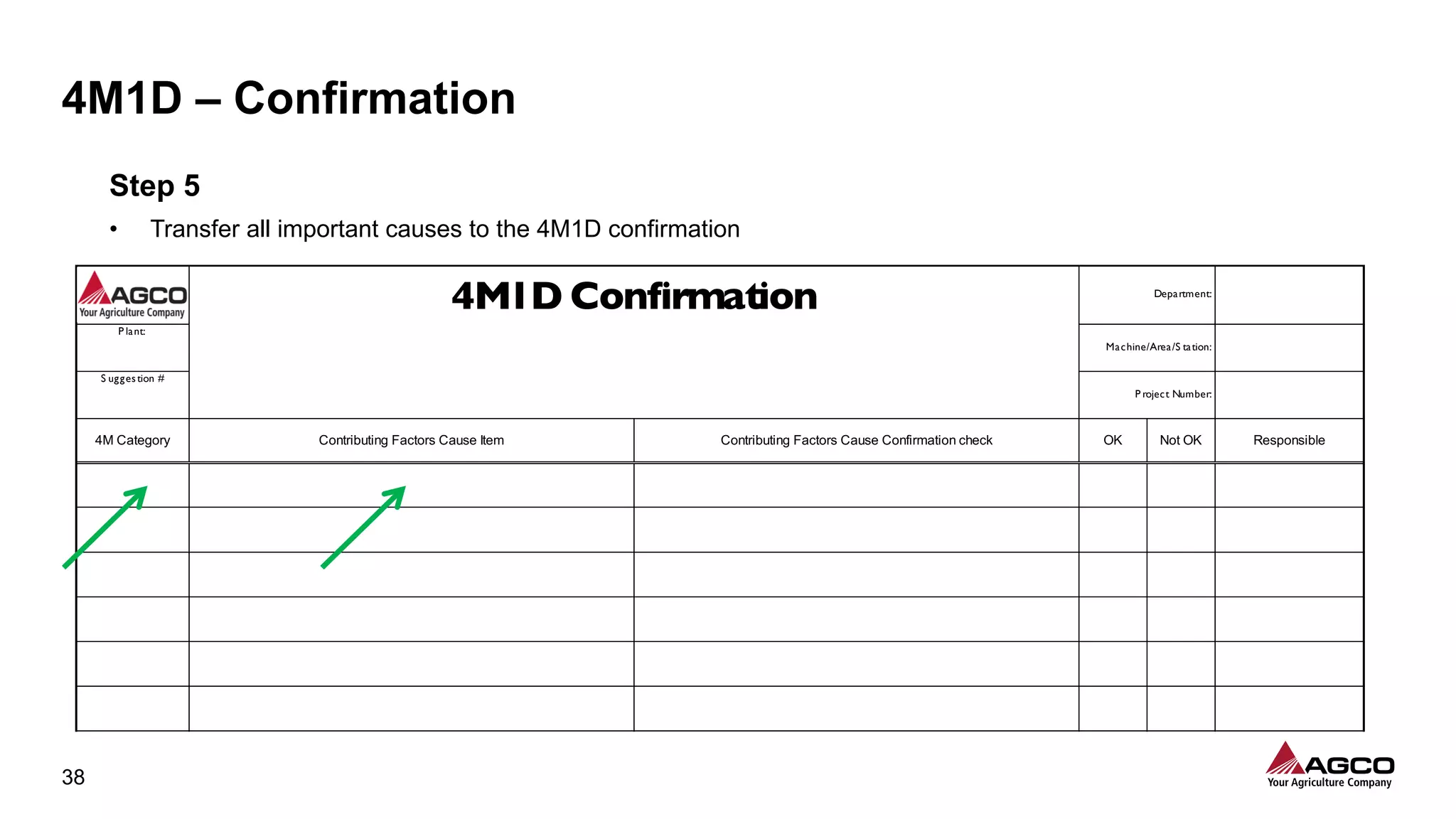
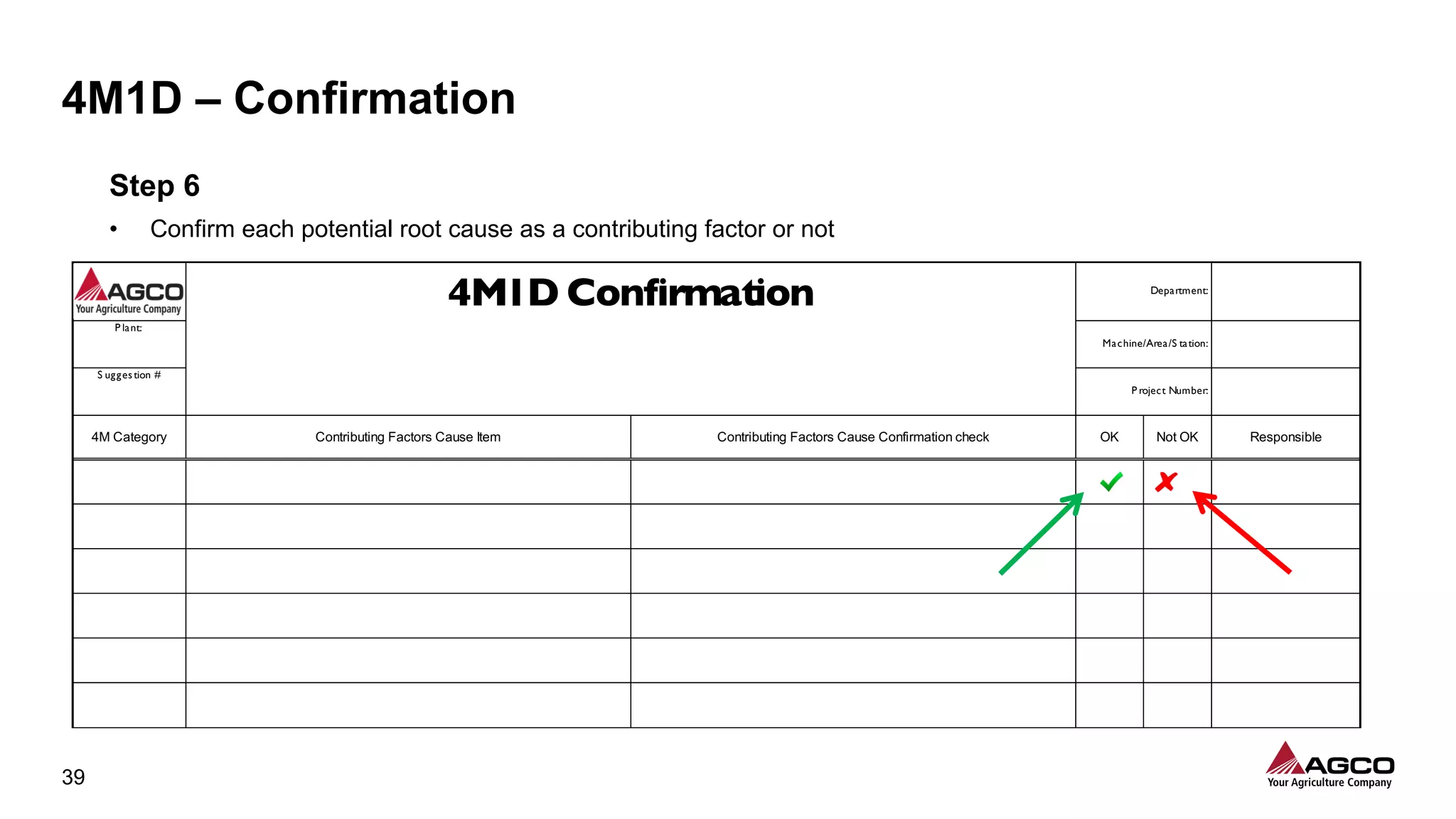
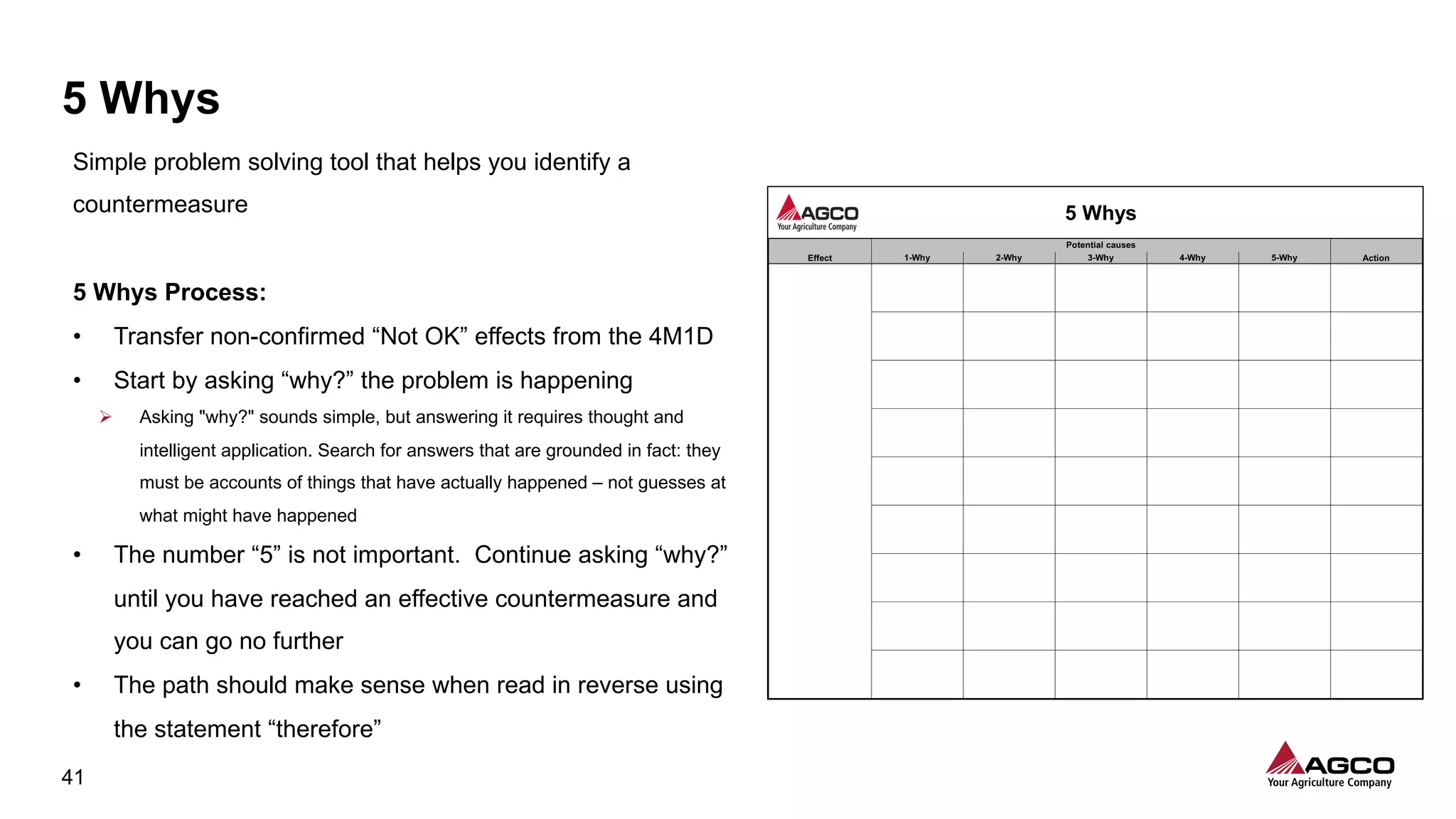
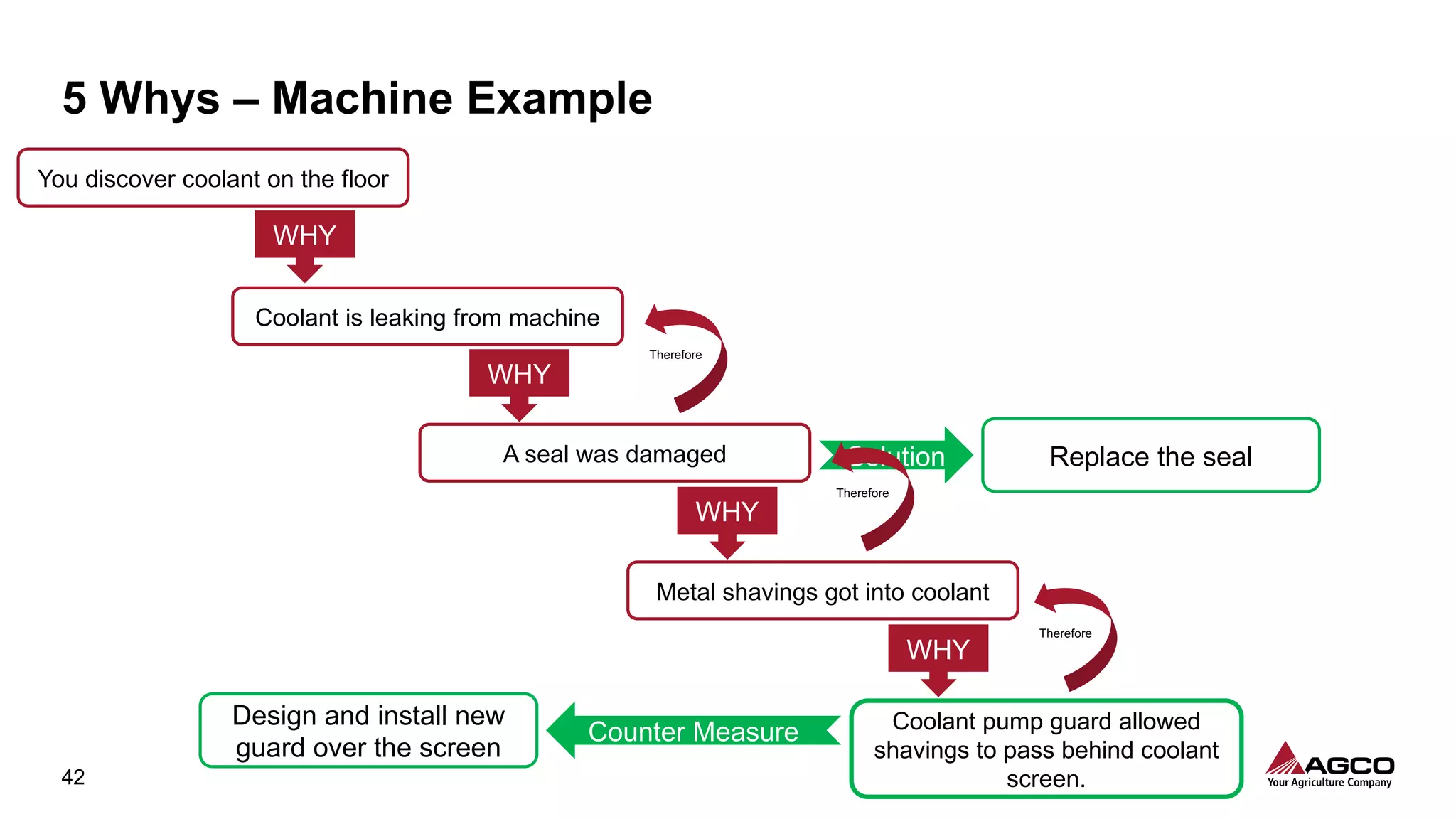
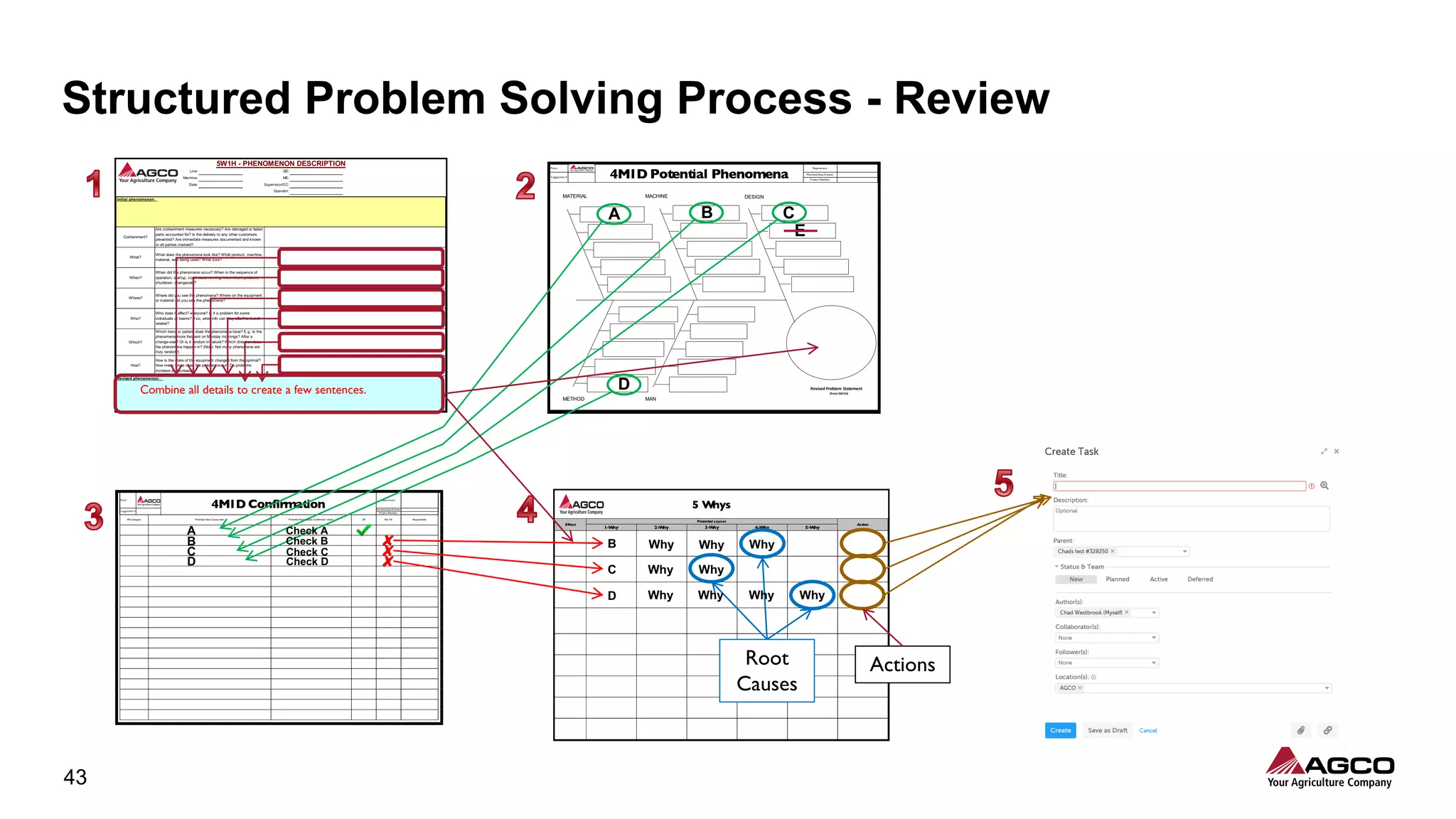
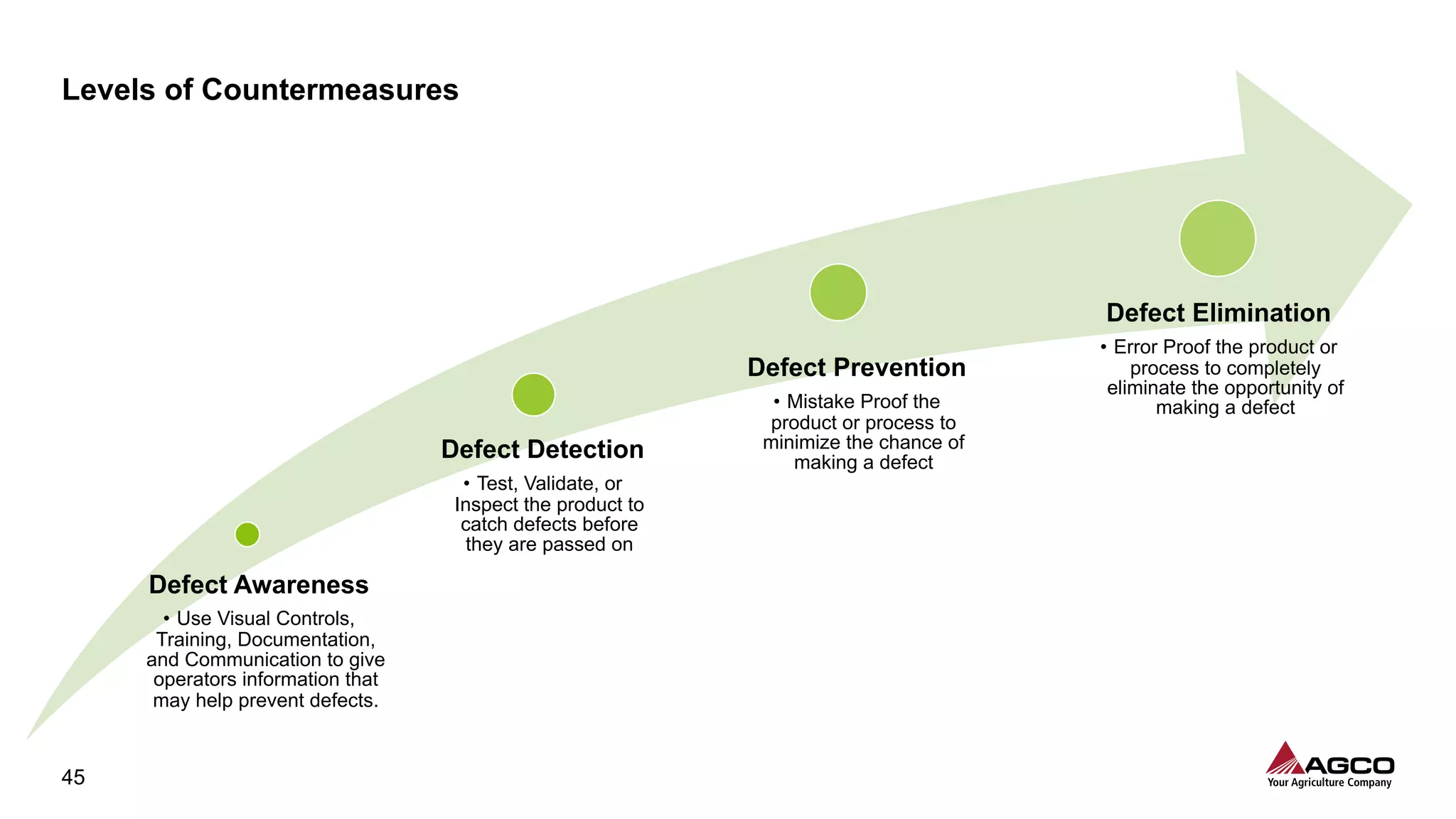
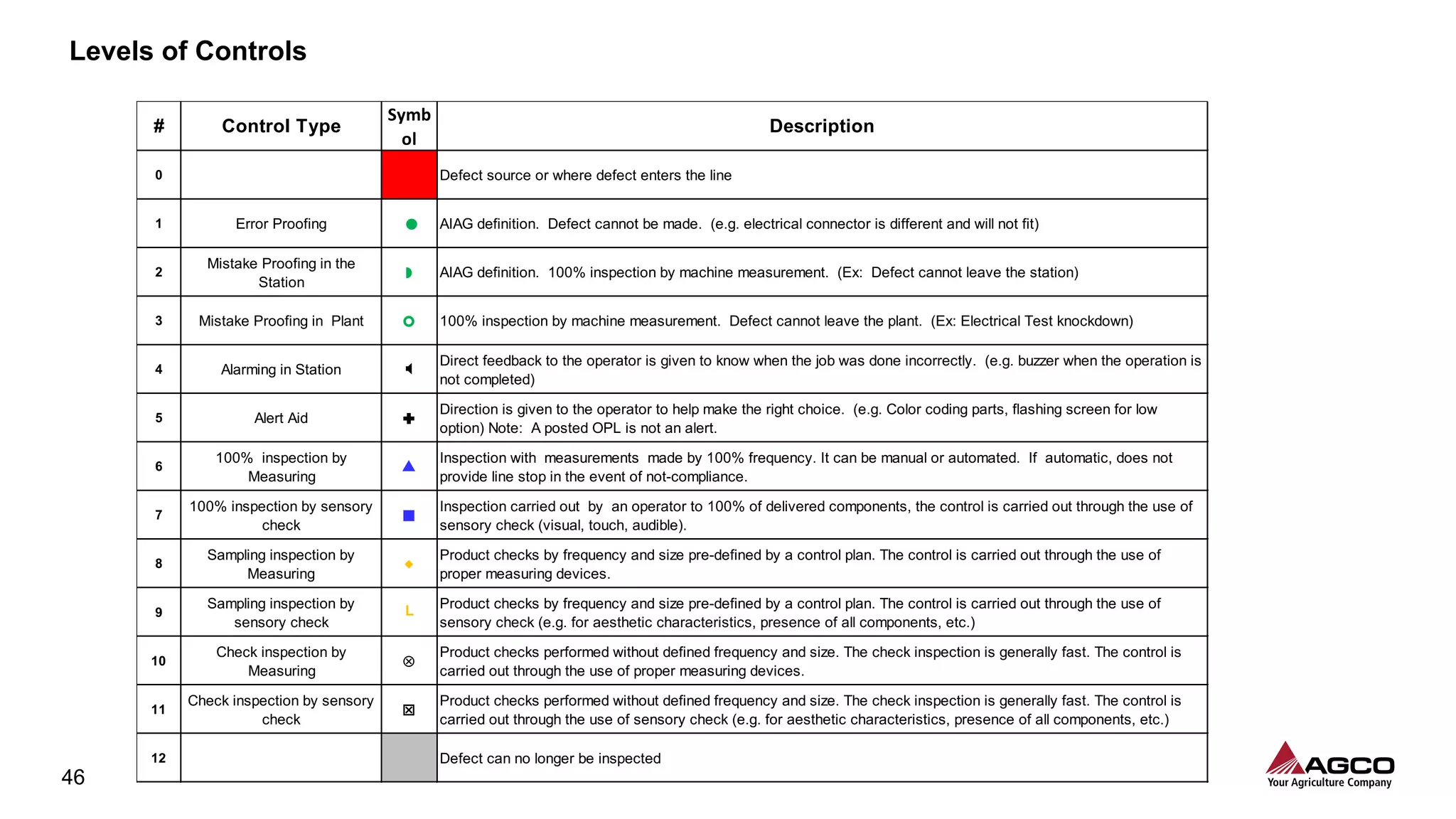
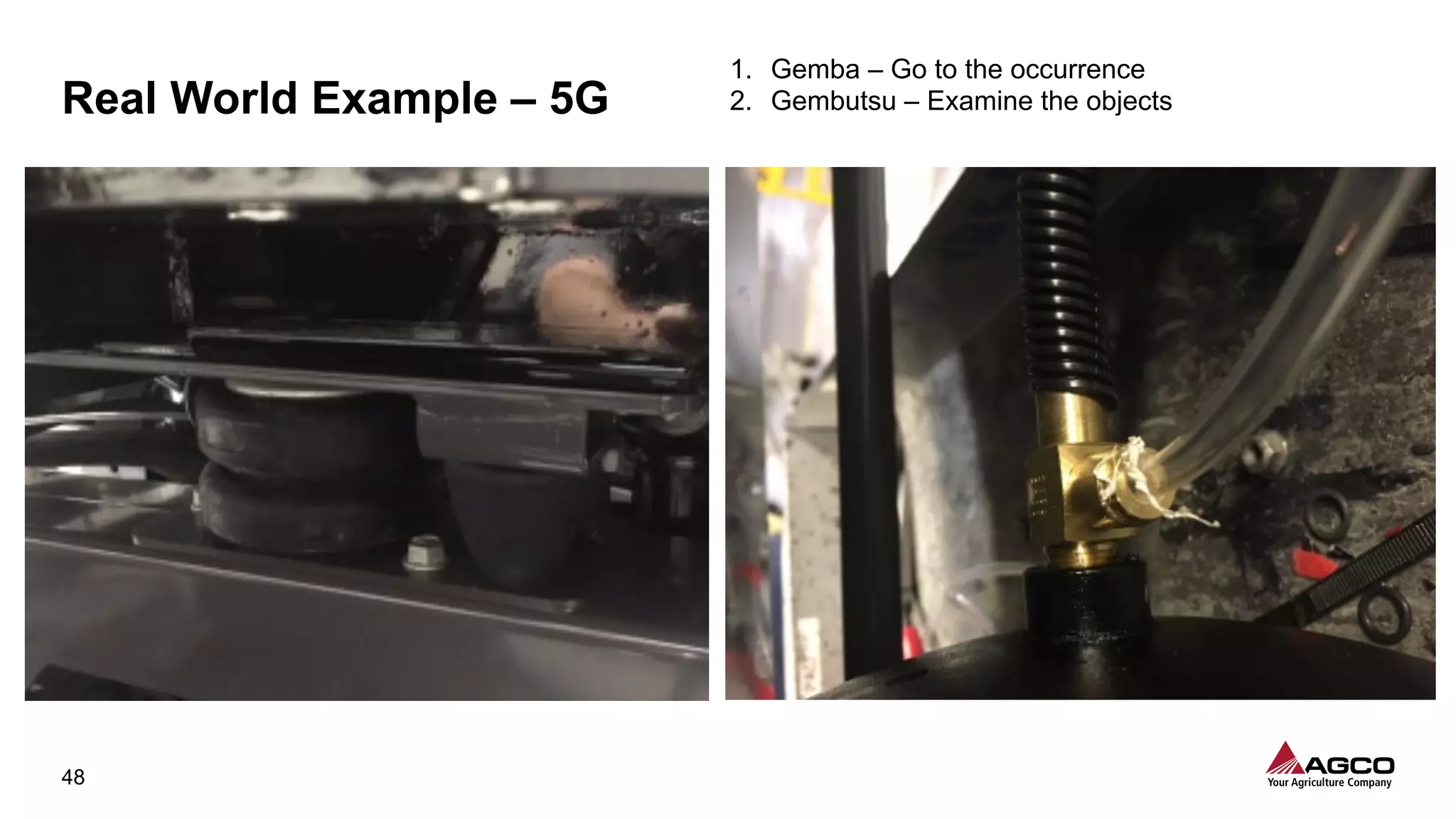
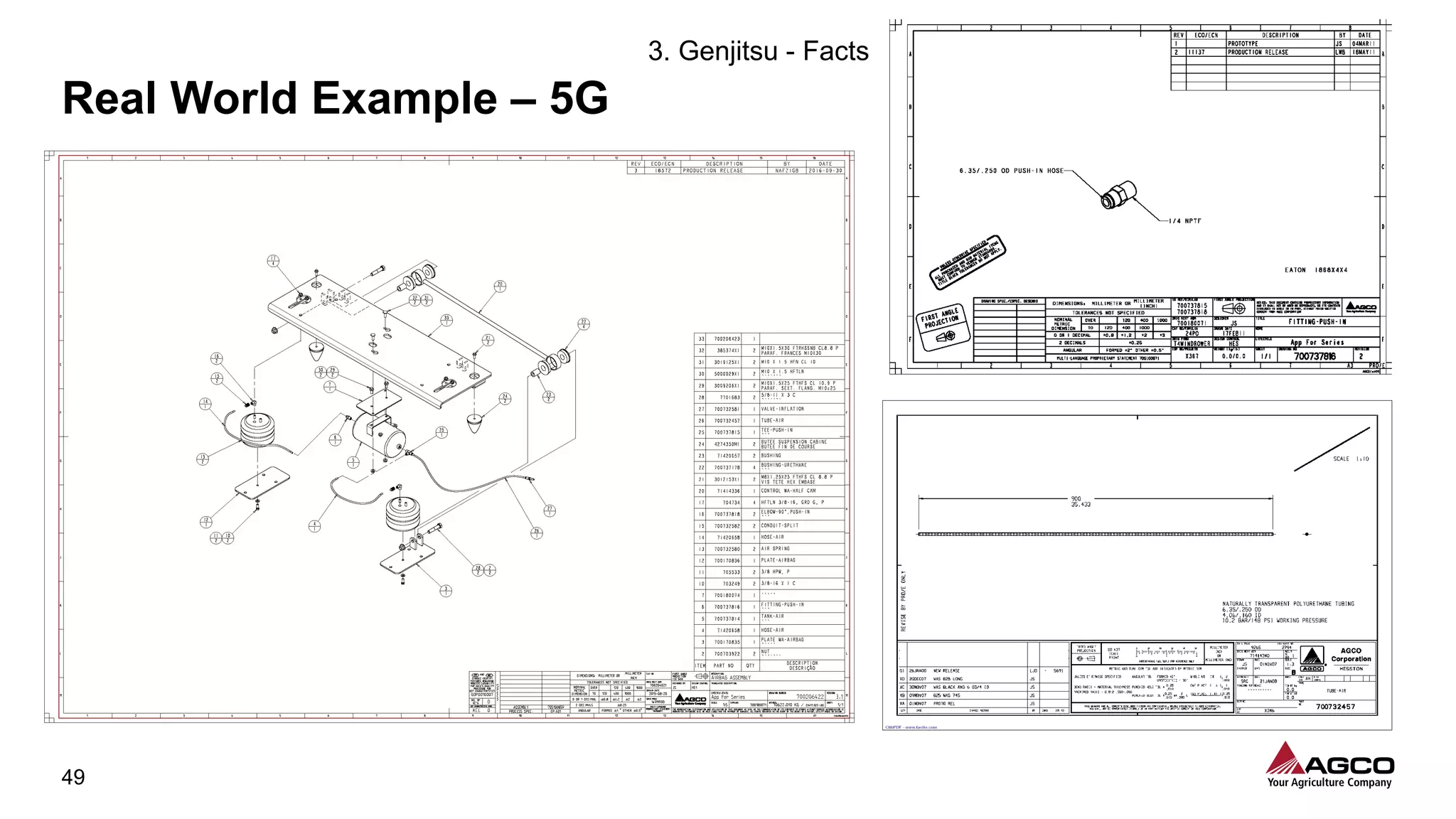
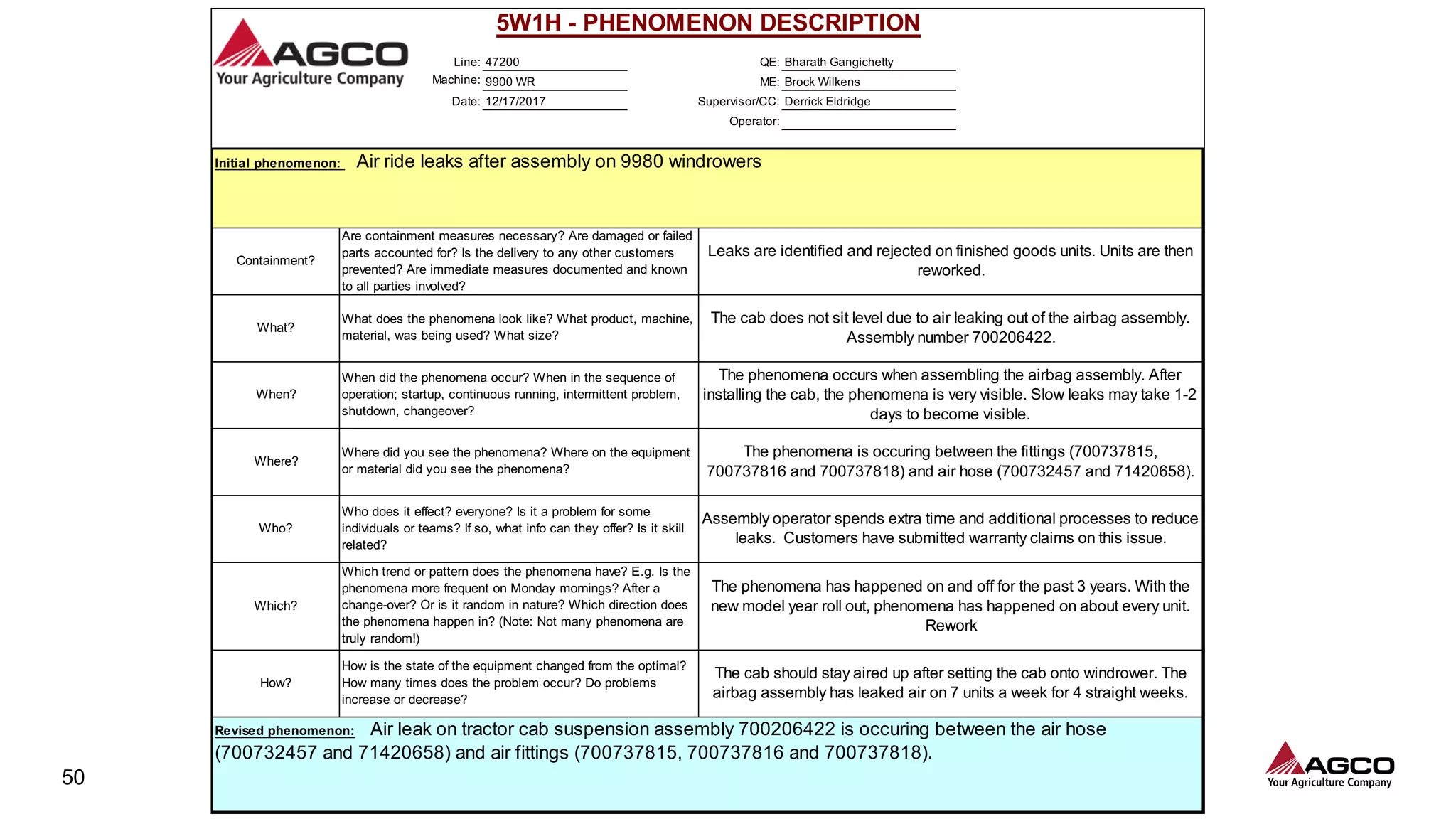
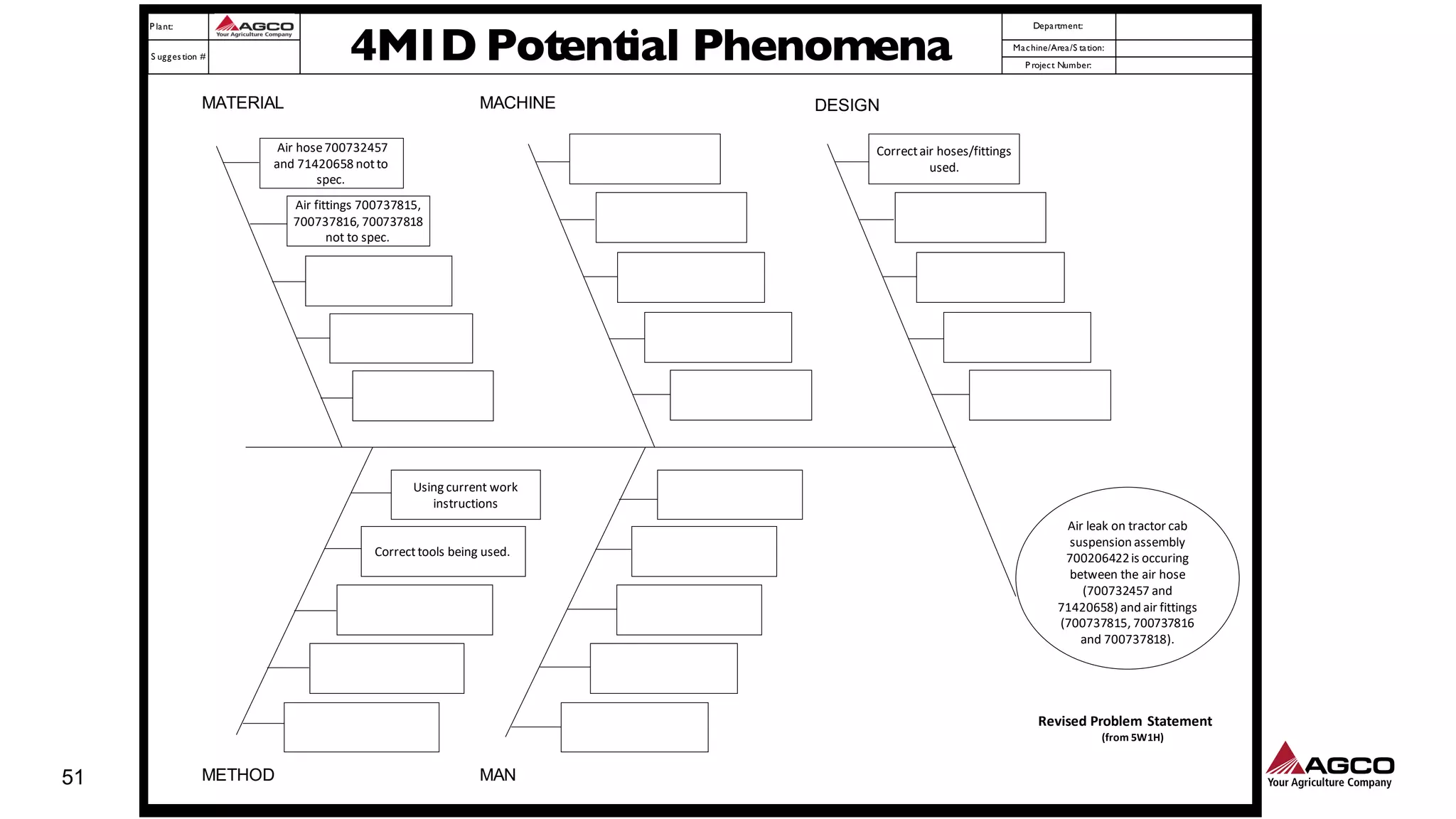
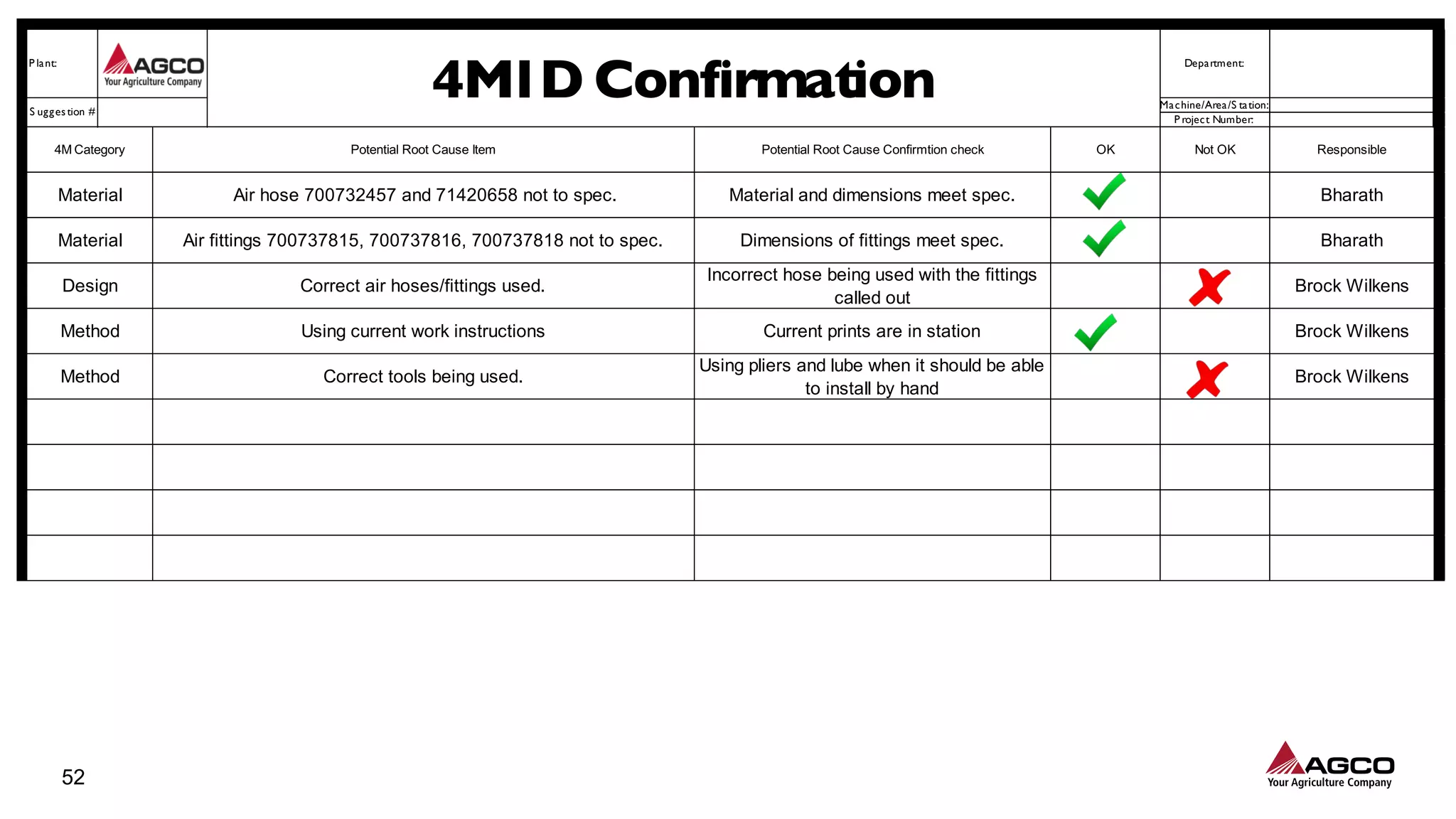
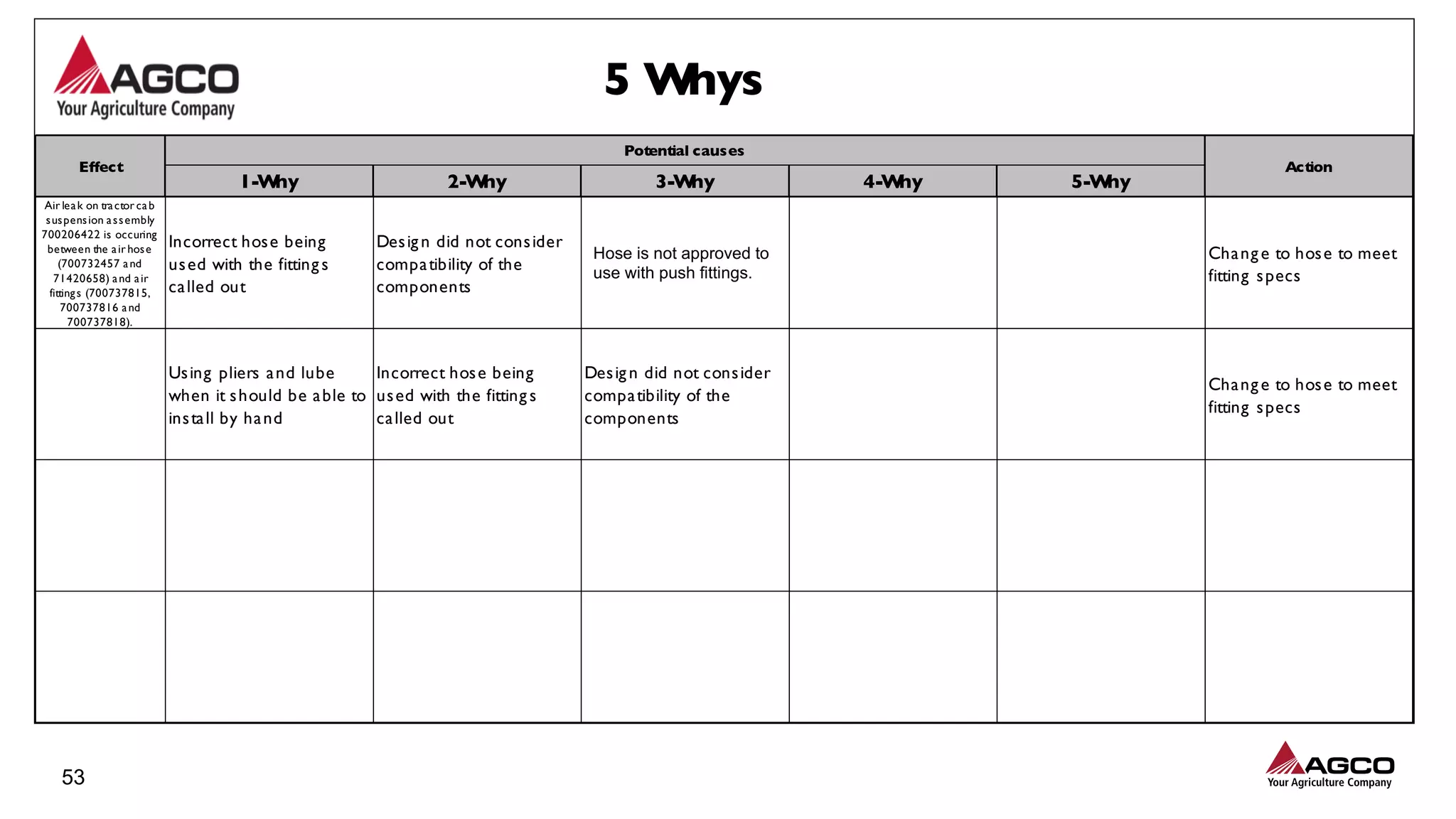
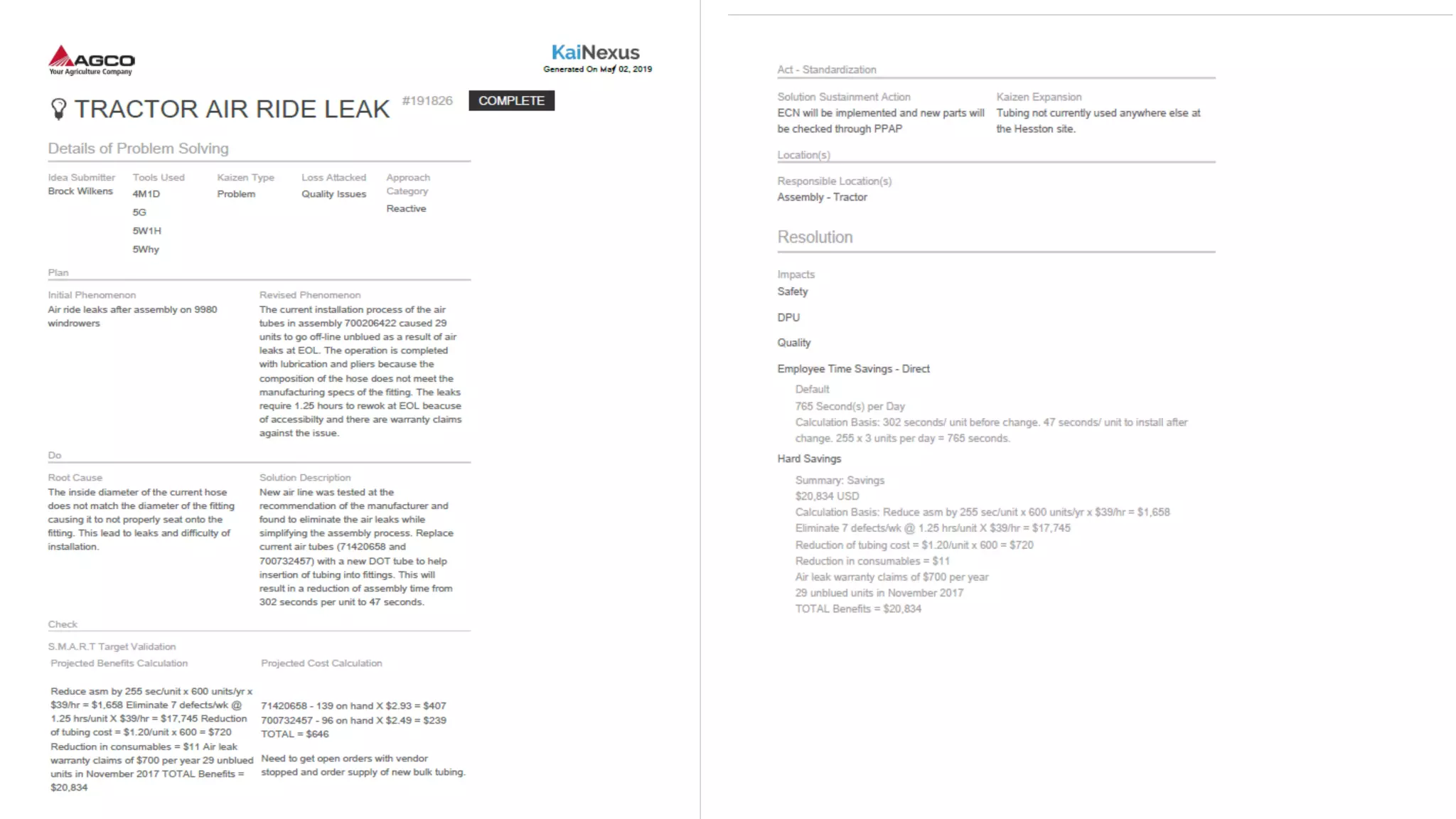
The document is a comprehensive overview of a structured problem-solving process presented during a webinar by Chad Westbrook from AGCO. It includes various problem-solving tools such as 5G, 5W1H, 4M1D, and the 5 Whys technique, aimed at identifying and addressing manufacturing issues in a systematic way. The presentation emphasizes the importance of understanding the actual conditions and carefully analyzing the phenomena to develop effective countermeasures.