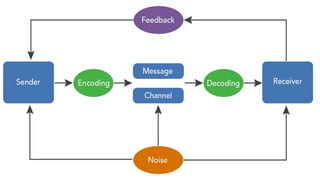
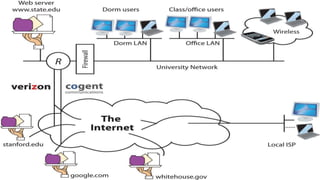
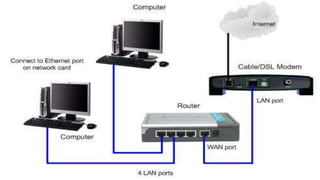
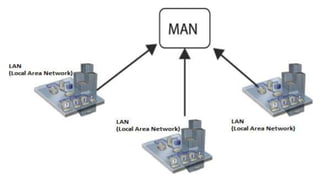
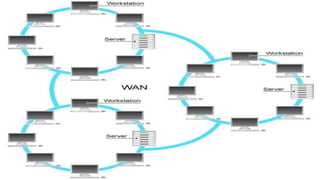
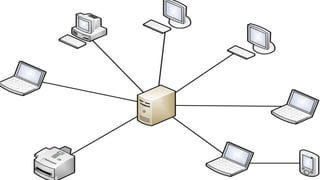
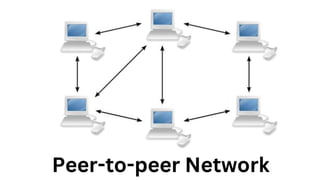
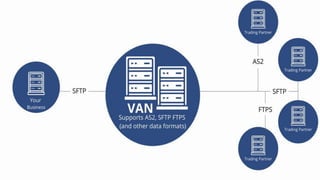
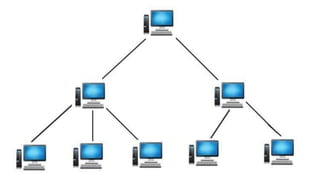
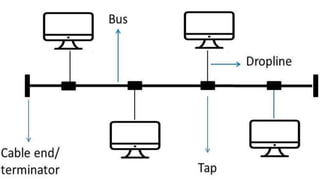
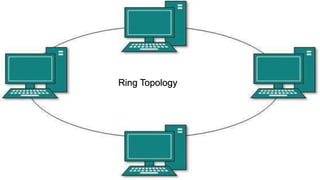
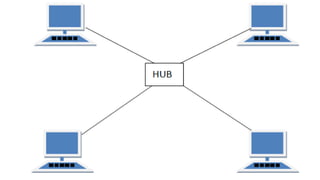
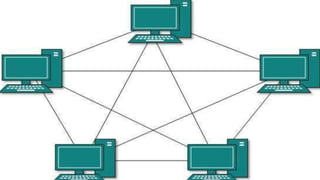
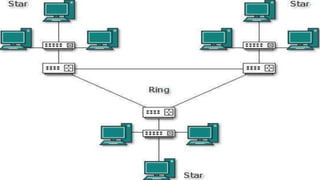
The document provides an overview of communication systems and computer networks, detailing their components, types, advantages, and disadvantages. It covers specific network types such as LAN, MAN, and WAN, and their respective characteristics and uses. Additionally, the document discusses various network topologies including hierarchical, bus, ring, star, mesh, and hybrid topologies, highlighting their benefits and drawbacks.