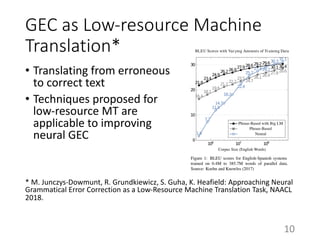
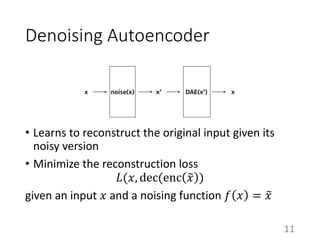
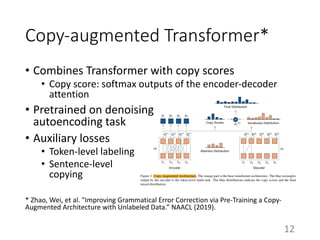
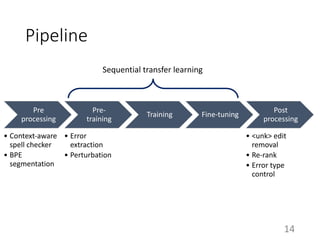
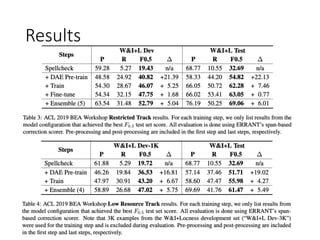
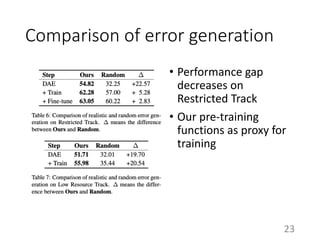
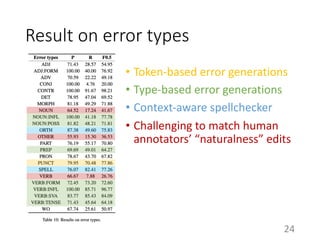
This document summarizes a neural approach to grammatical error correction that uses better pre-training and sequential transfer learning. It first discusses previous work on grammatical error correction (GEC) as a low-resource machine translation task and denoising autoencoders. It then describes the authors' approach, which includes context-aware preprocessing, pre-training a model on synthetically perturbed data to learn realistic error types, fine-tuning the model sequentially, and various postprocessing techniques. Evaluation results on the BEA 2019 shared task show that the authors' approach reduces the performance gap between the restricted and low-resource tracks, and it performs well on different error types.





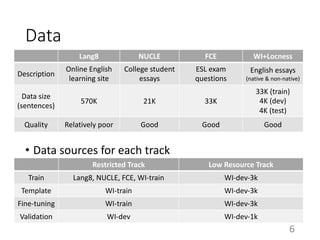

![ERRANT
Input
Travel by bus is exspensive, bored and annoying.
Output
[Travel→Travelling] by bus is [exspensive→expensive],
[bored→boring] and annoying.
8
R:SPELL
R:VERB:FORM
R:VERB:FORM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gec-slide-190830041618/85/A-Neural-Grammatical-Error-Correction-built-on-Better-Pre-training-and-Sequential-Transfer-Learning-8-320.jpg)