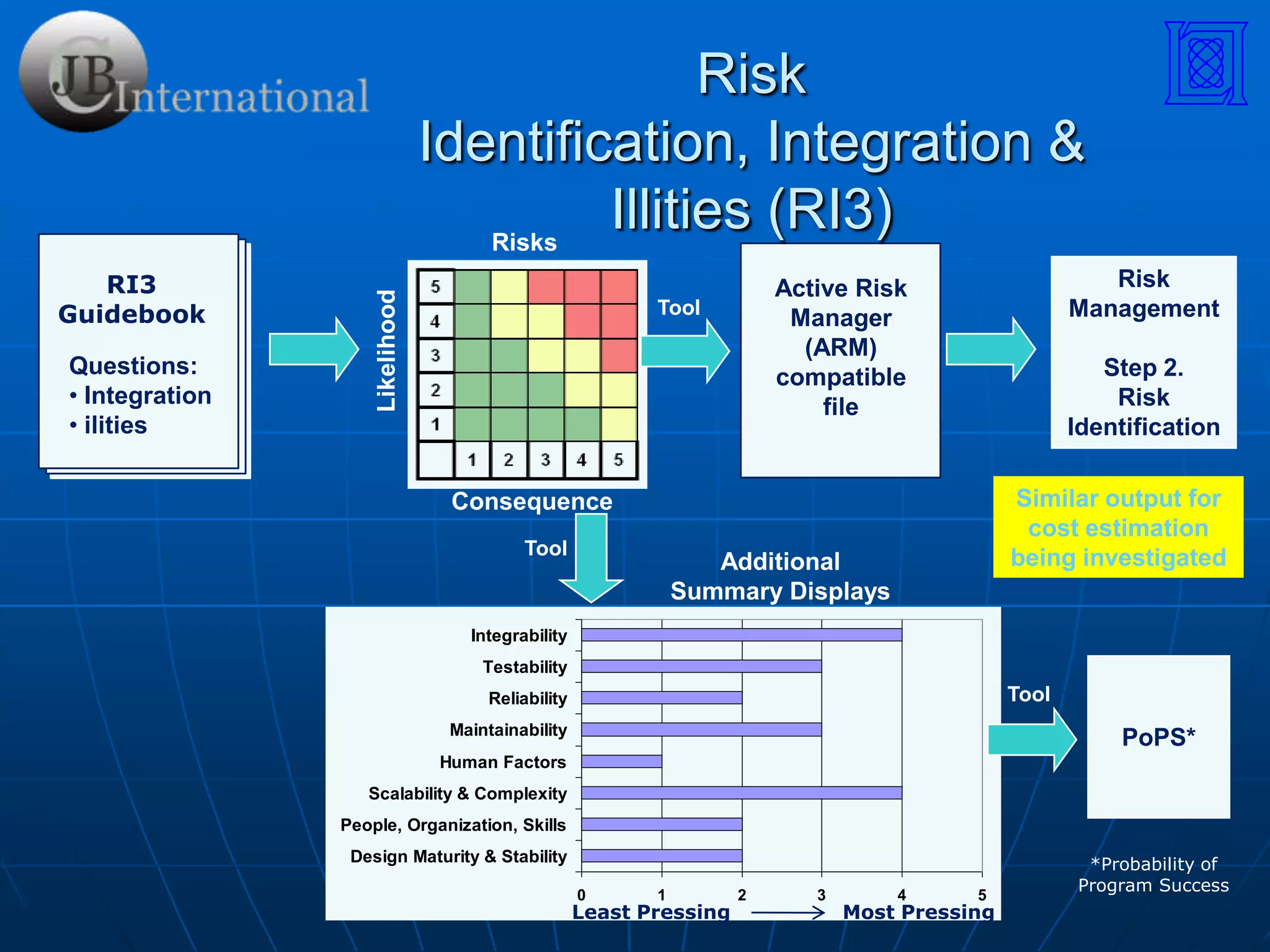
This document discusses several techniques for measuring system readiness, including Technology Readiness Levels (TRL), Risk Identification, Integration, and Illities (RI3), Advancement Degree of Difficulty (AD2), and various System Readiness Level (SRL) approaches. It provides an overview of each technique, how they are used, and what aspects of readiness they aim to evaluate, such as design maturity, integration complexity, and manufacturing readiness. The document also lists several tools that have been developed to help conduct assessments using these techniques.