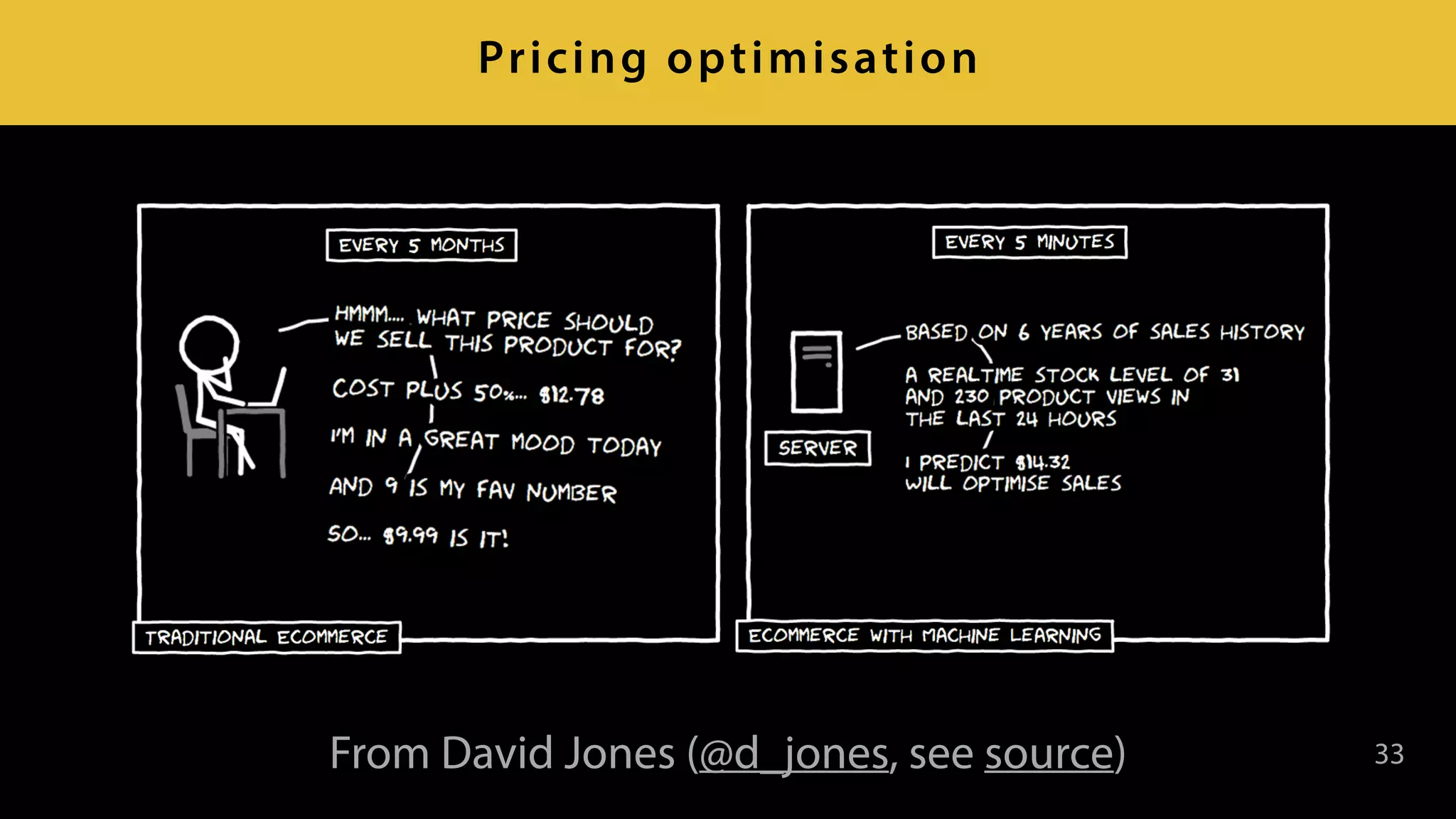
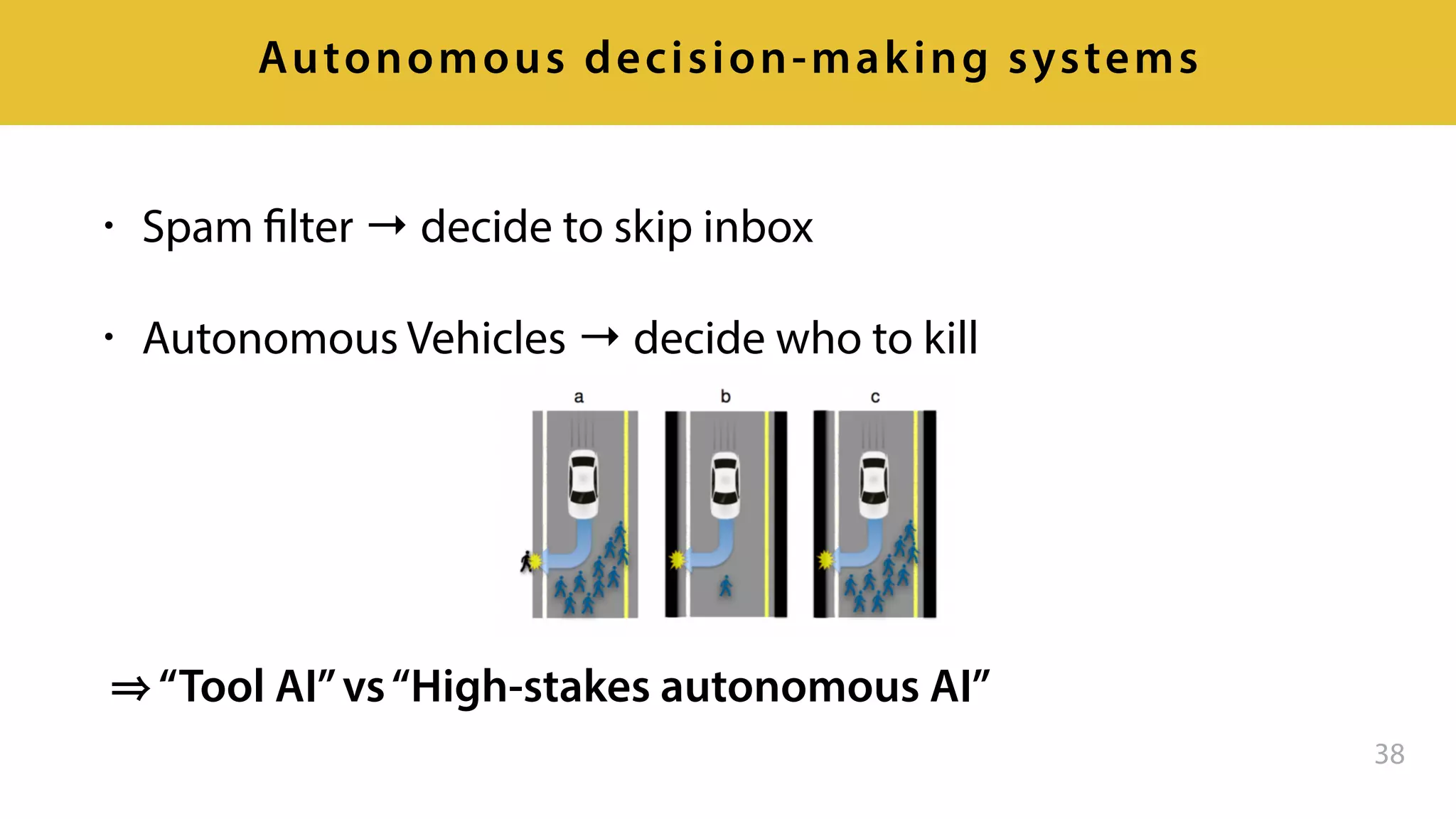
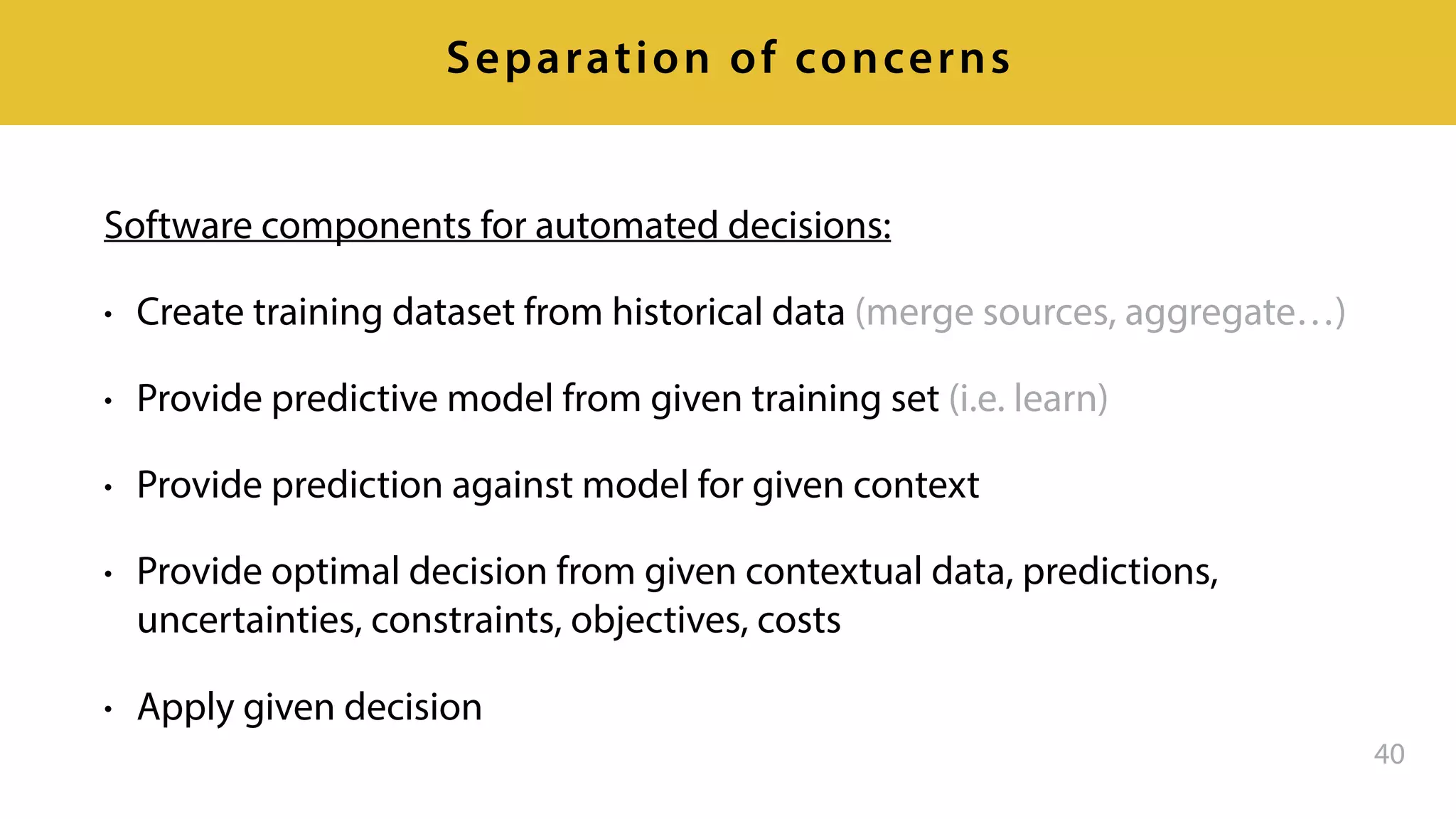
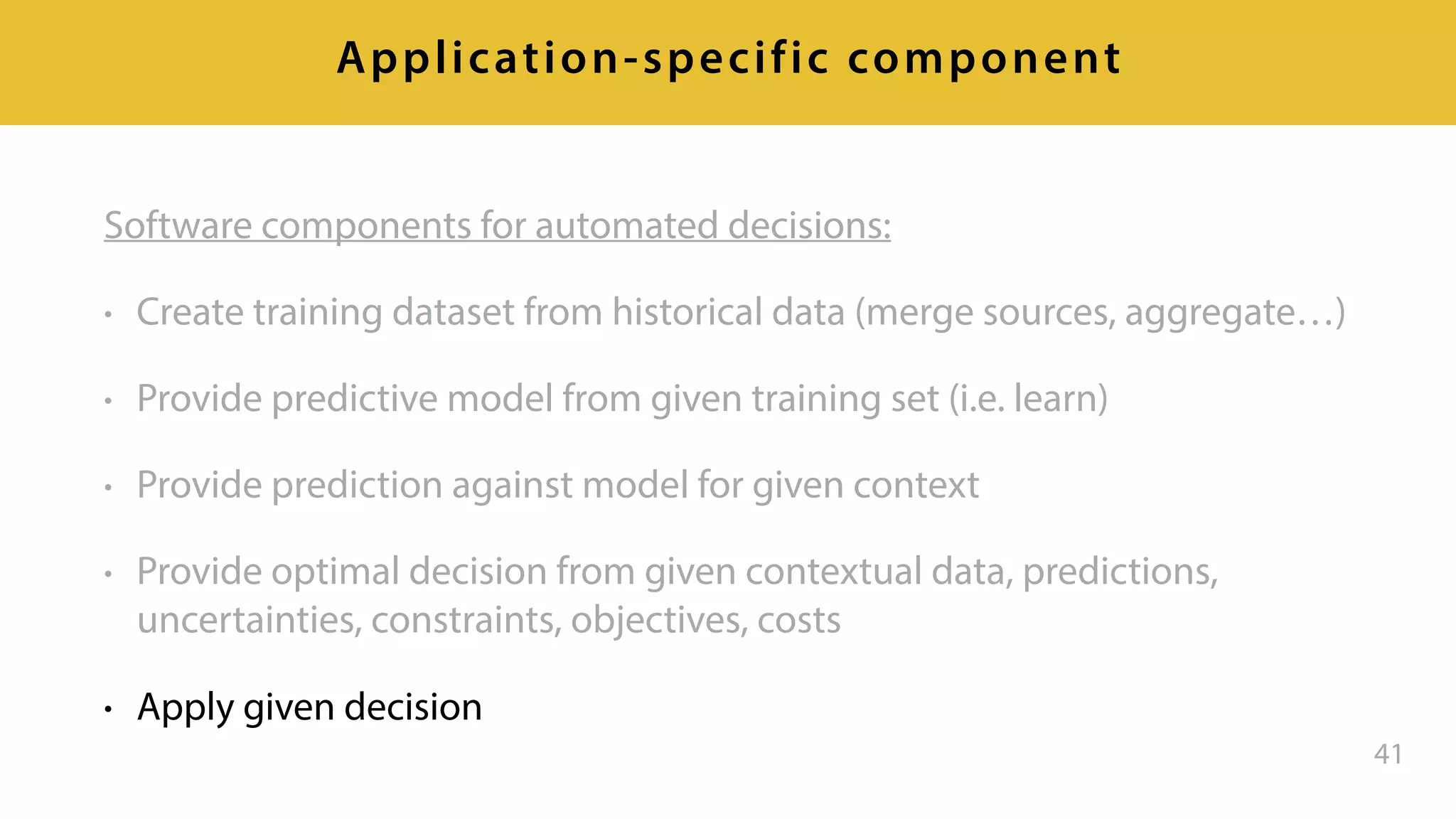
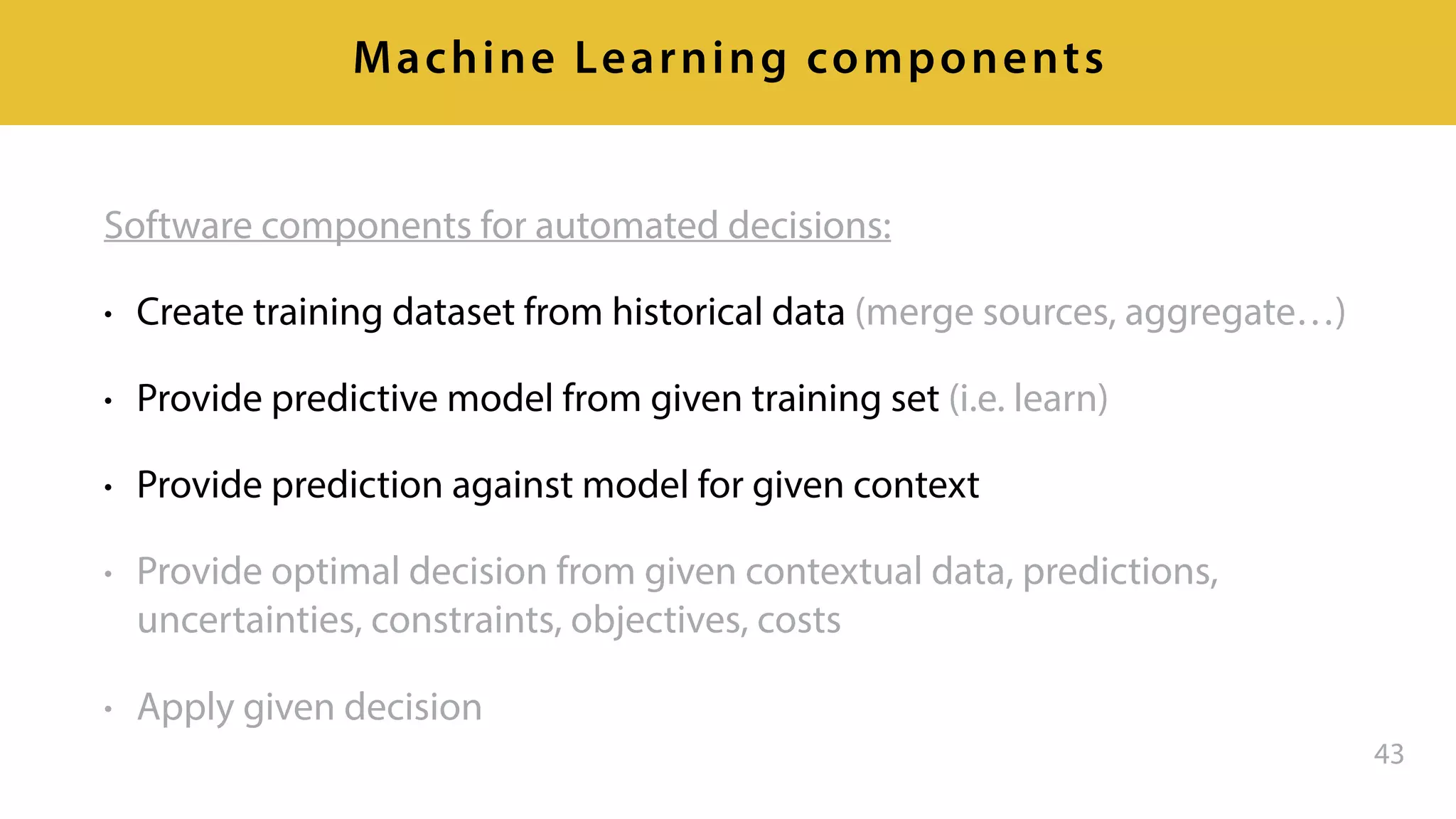
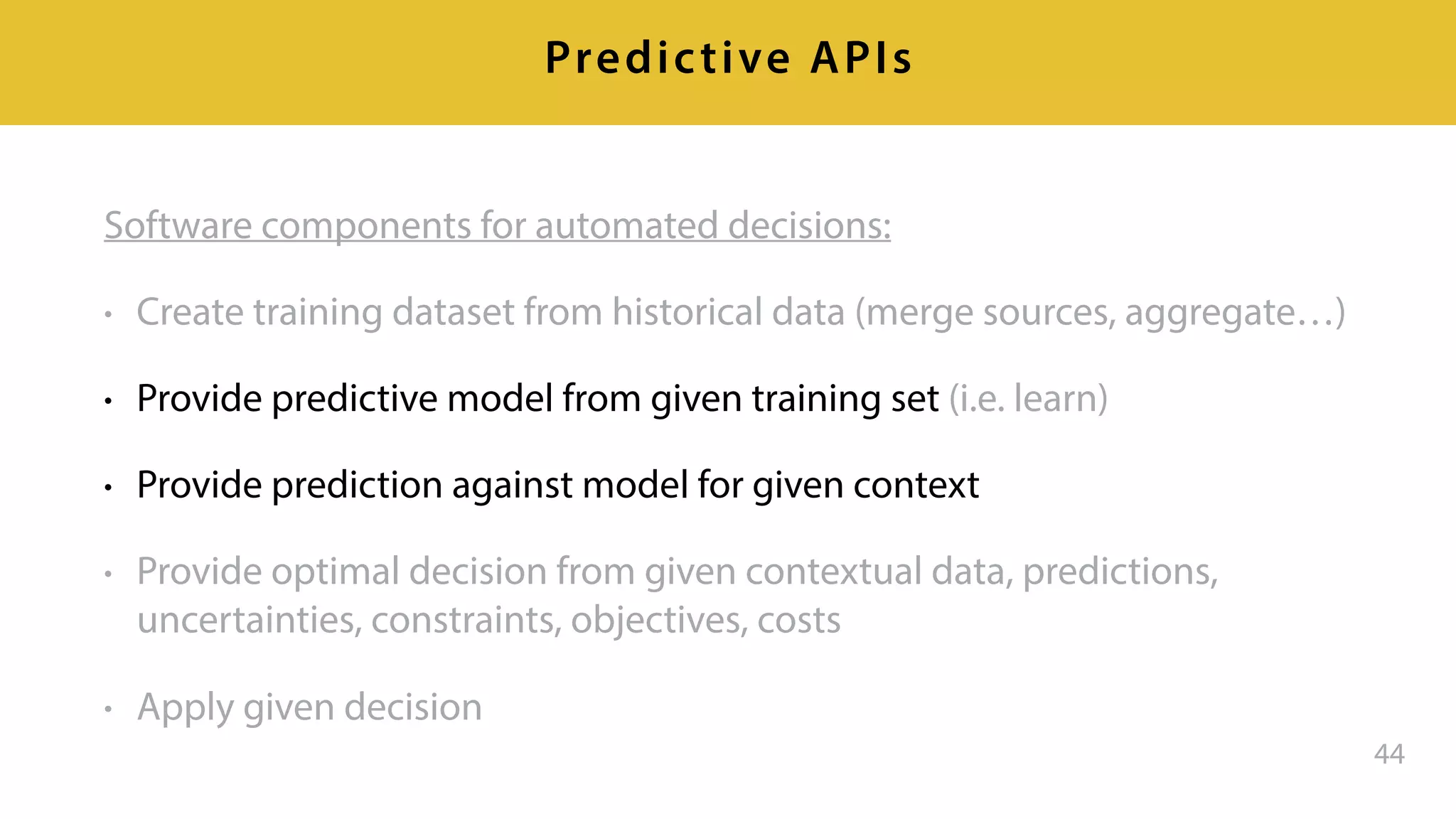
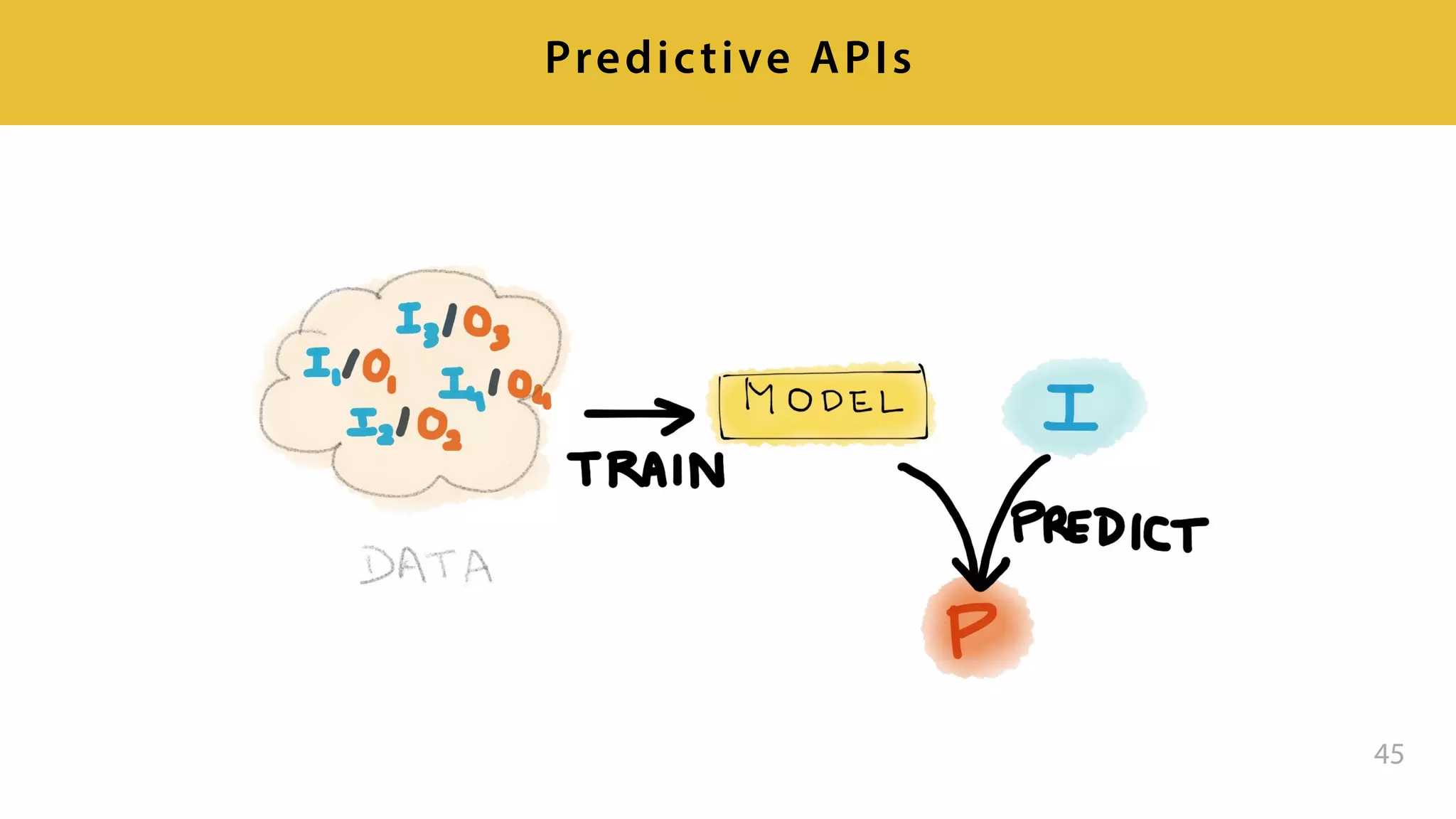
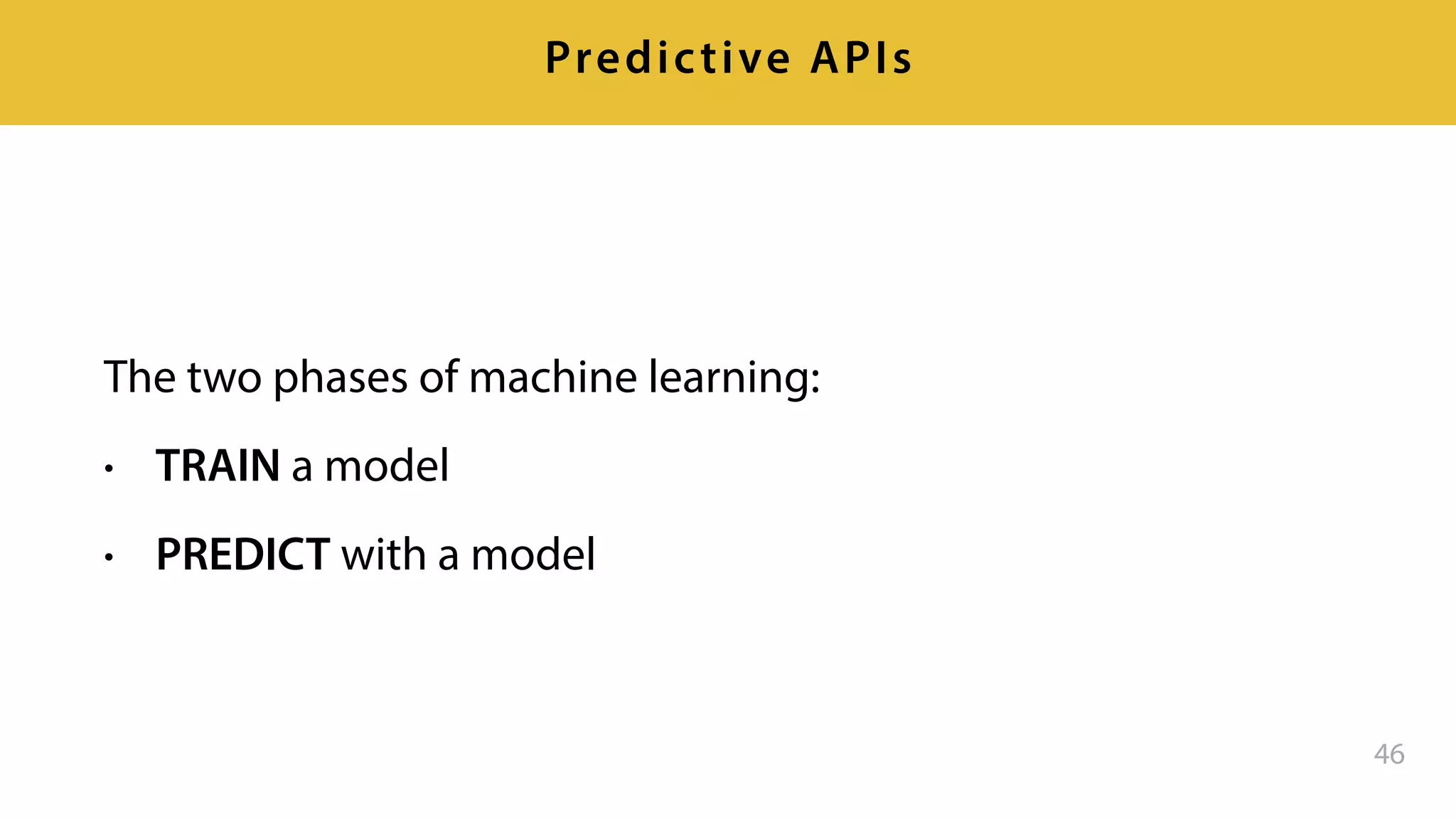
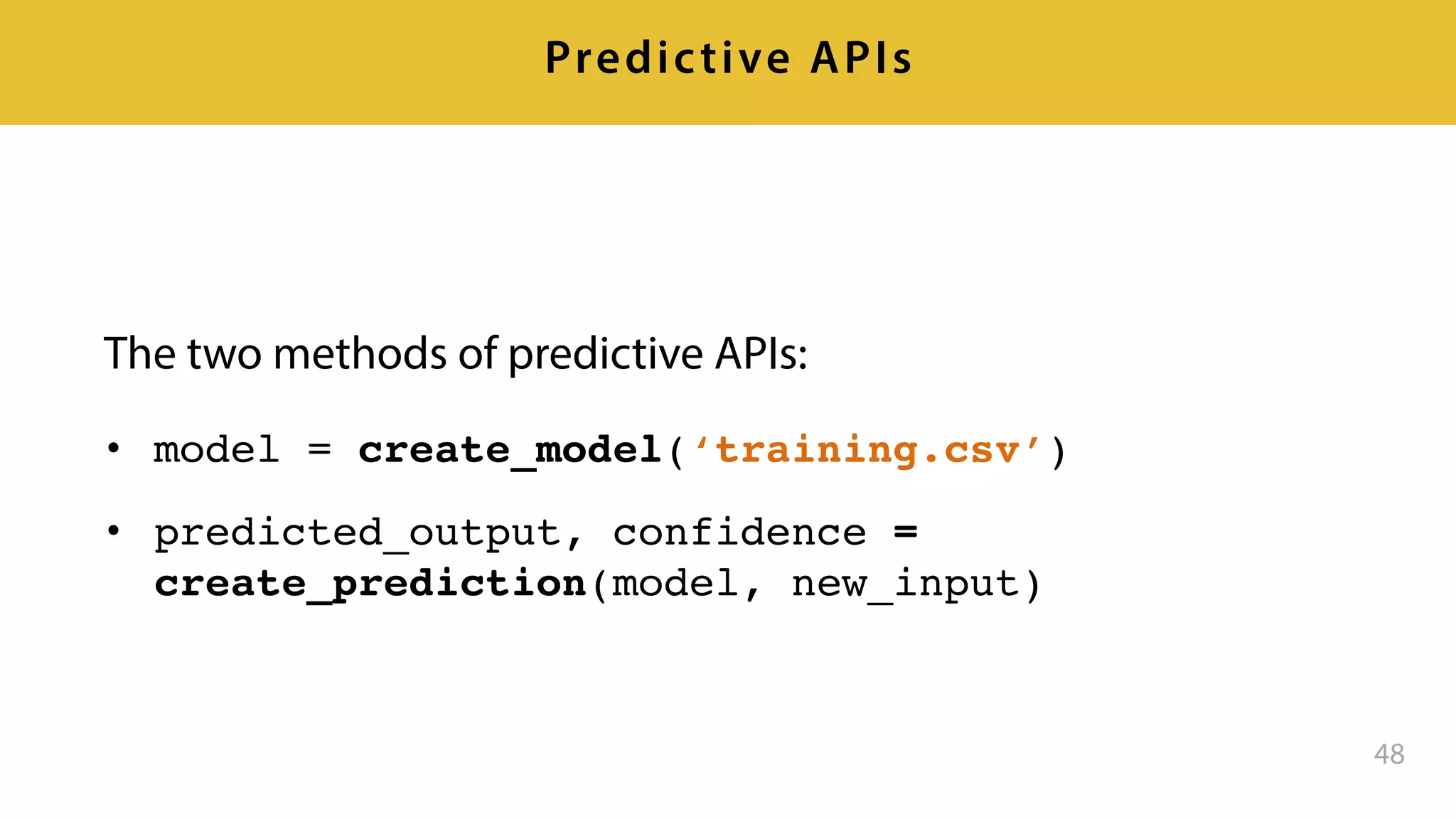
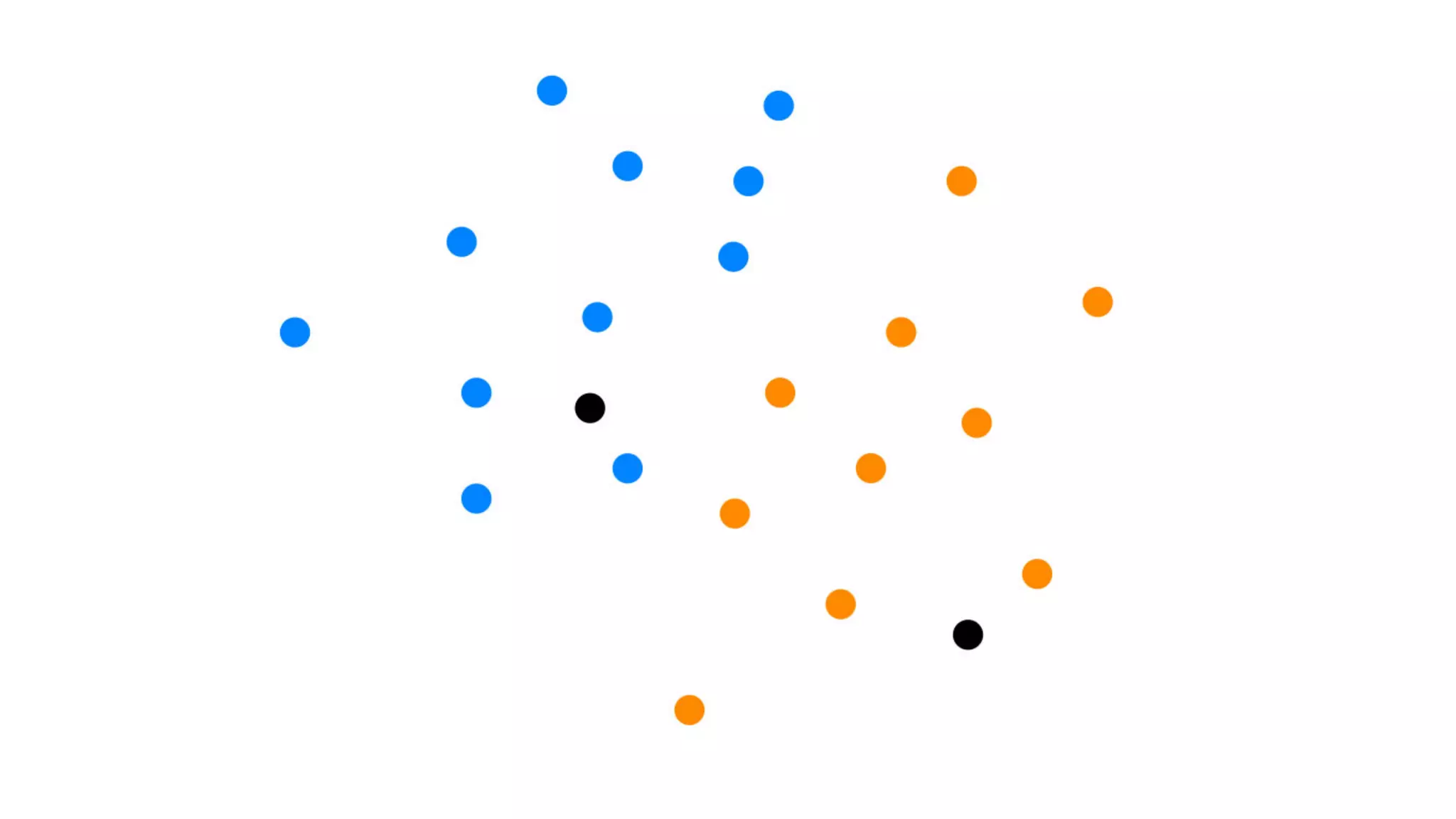
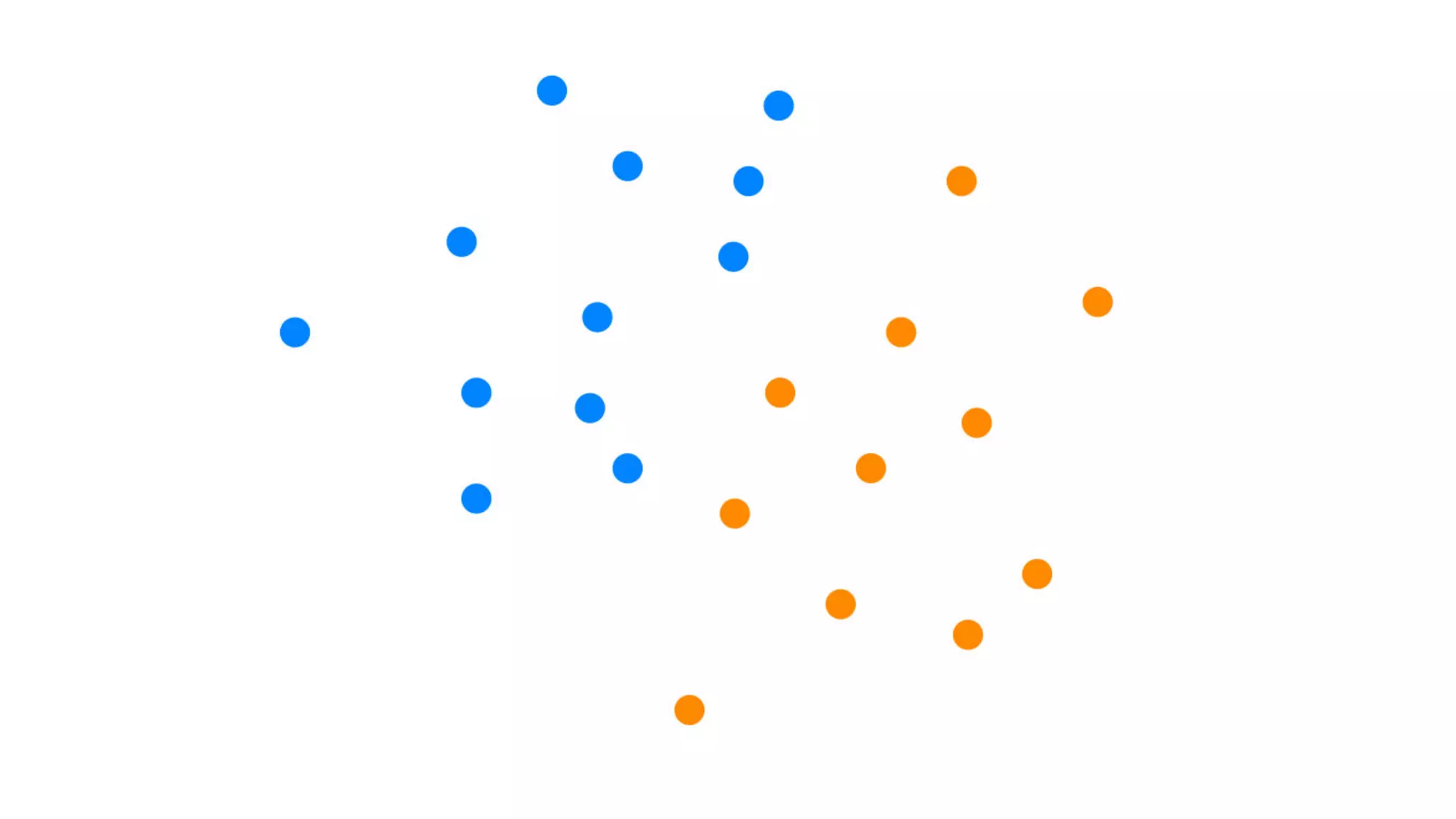
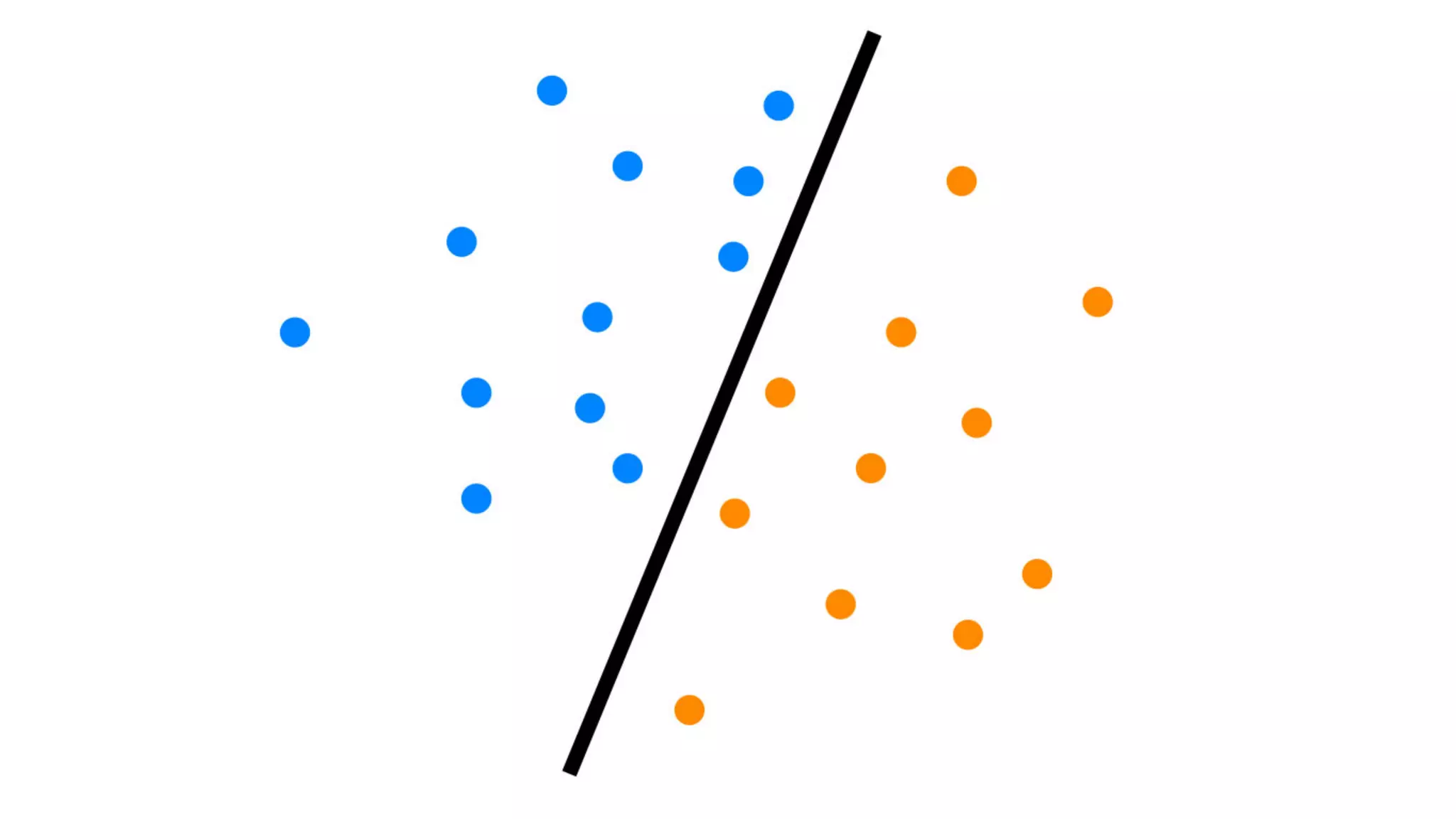
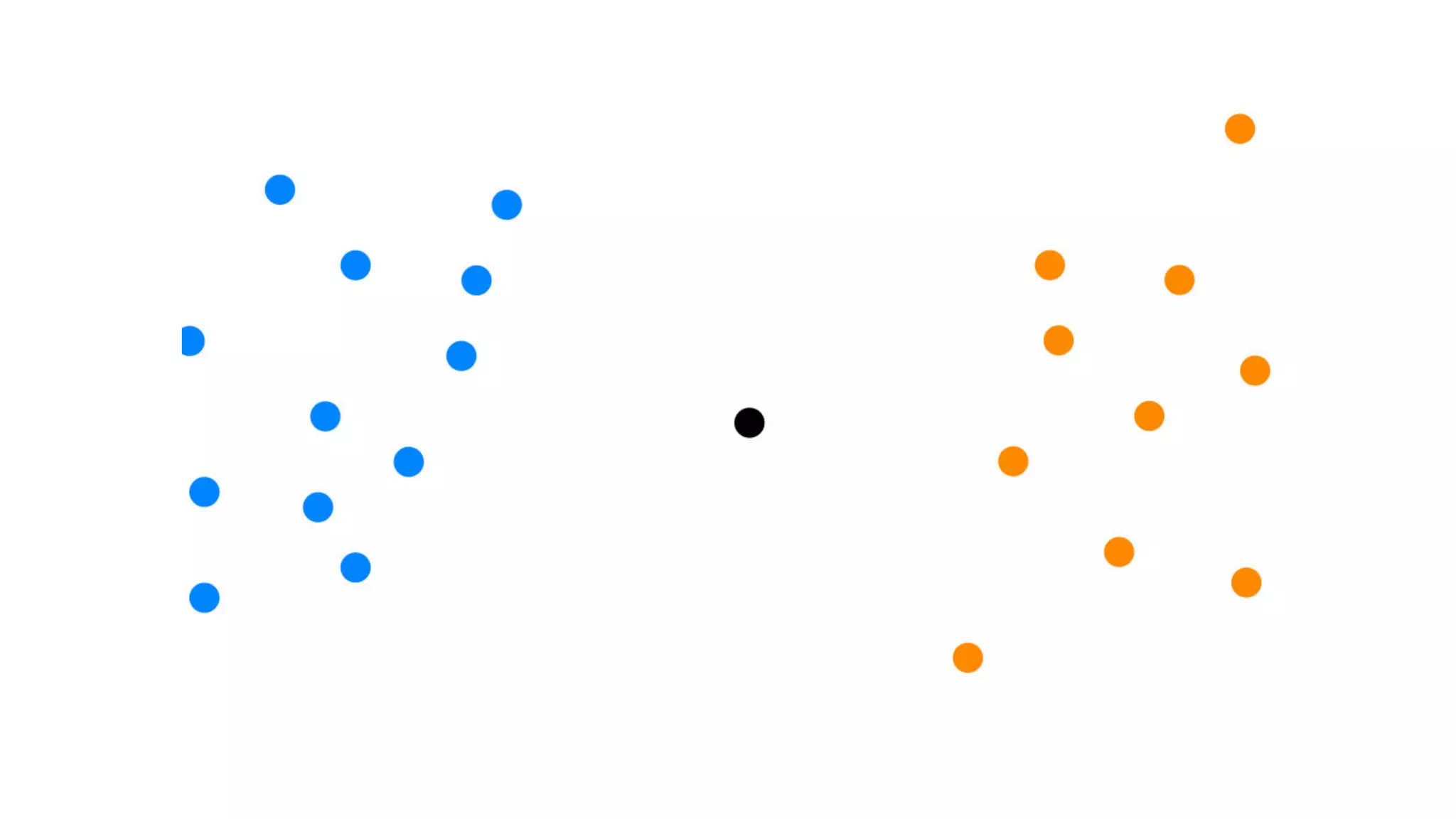
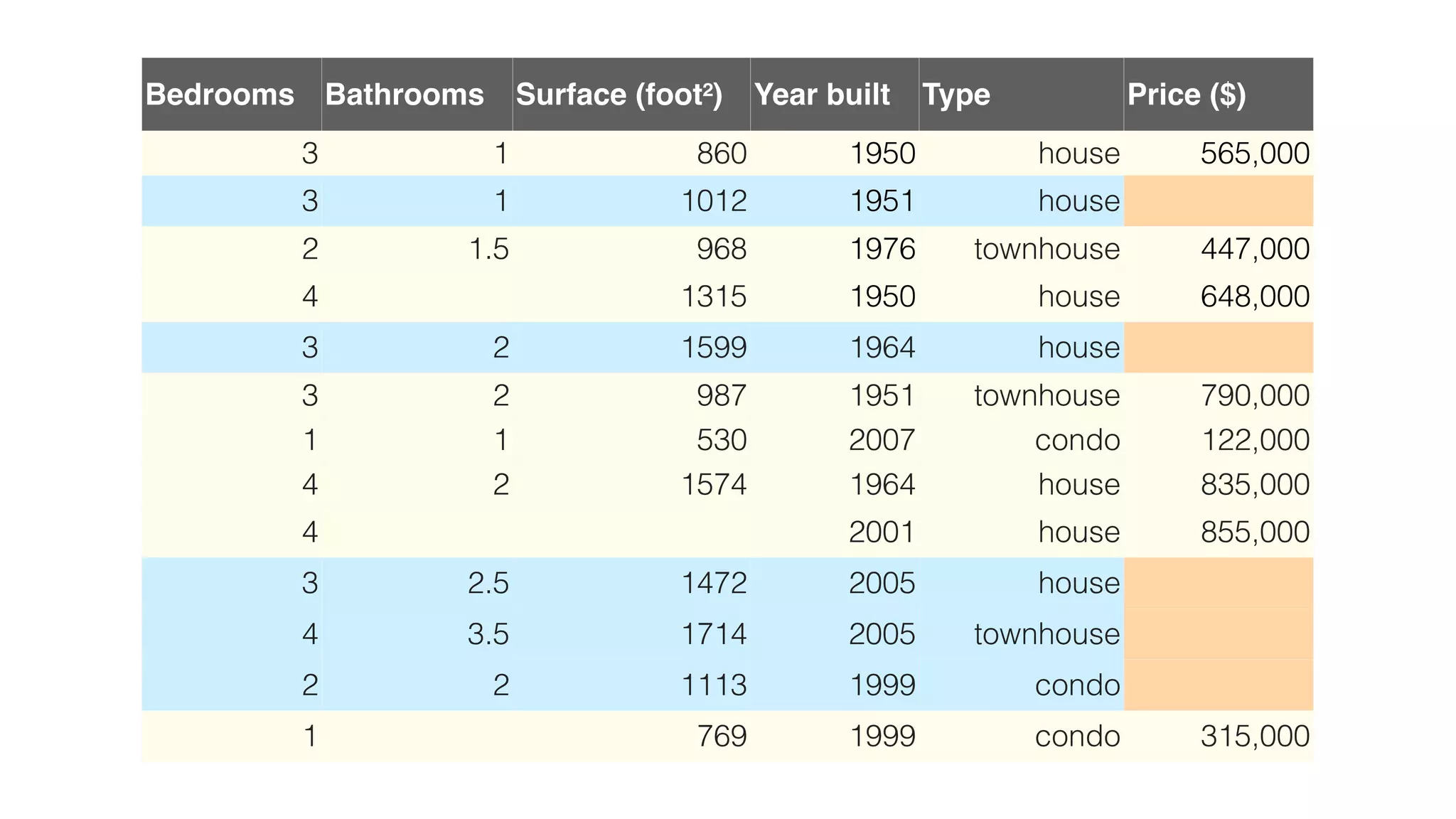
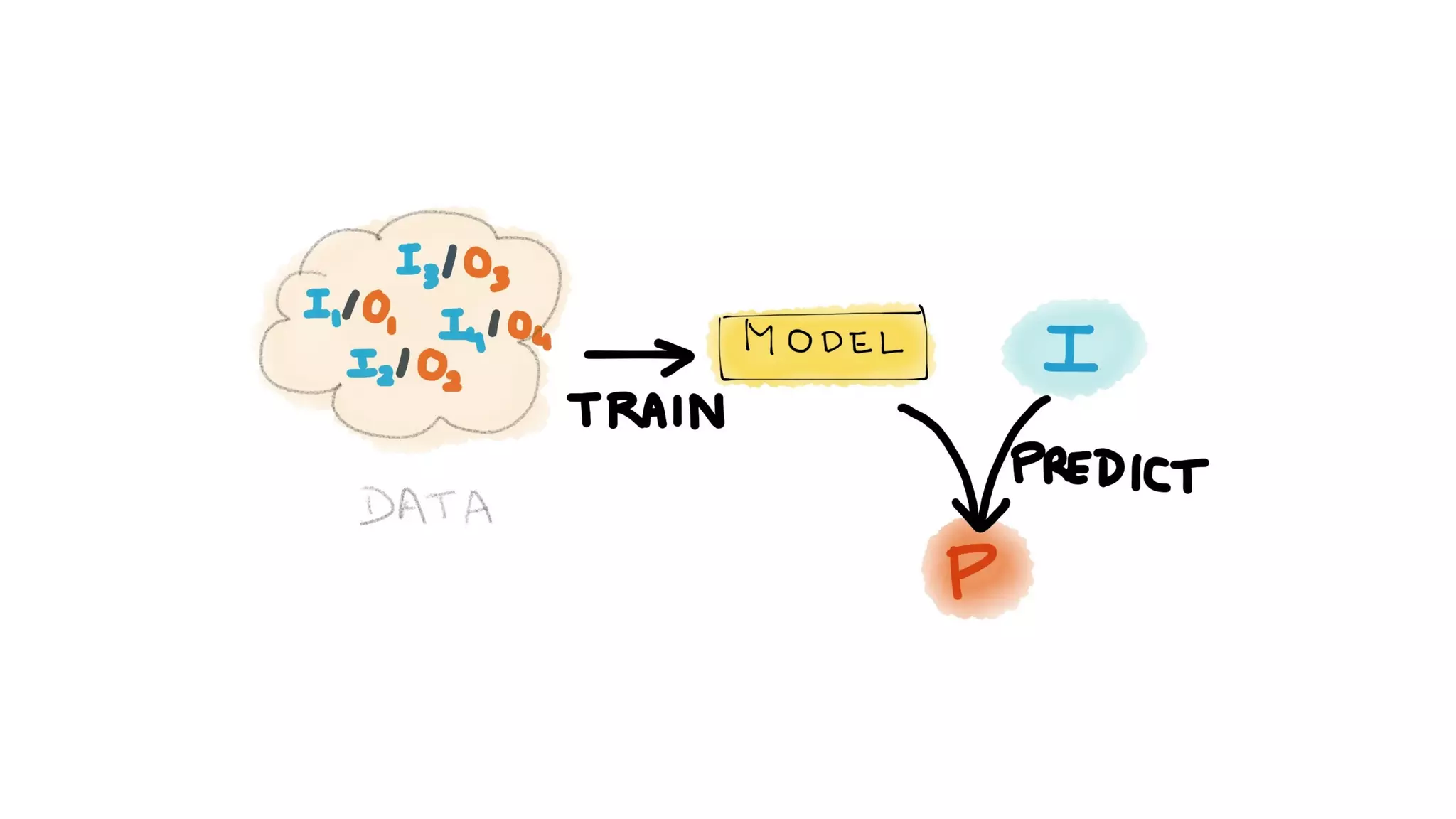
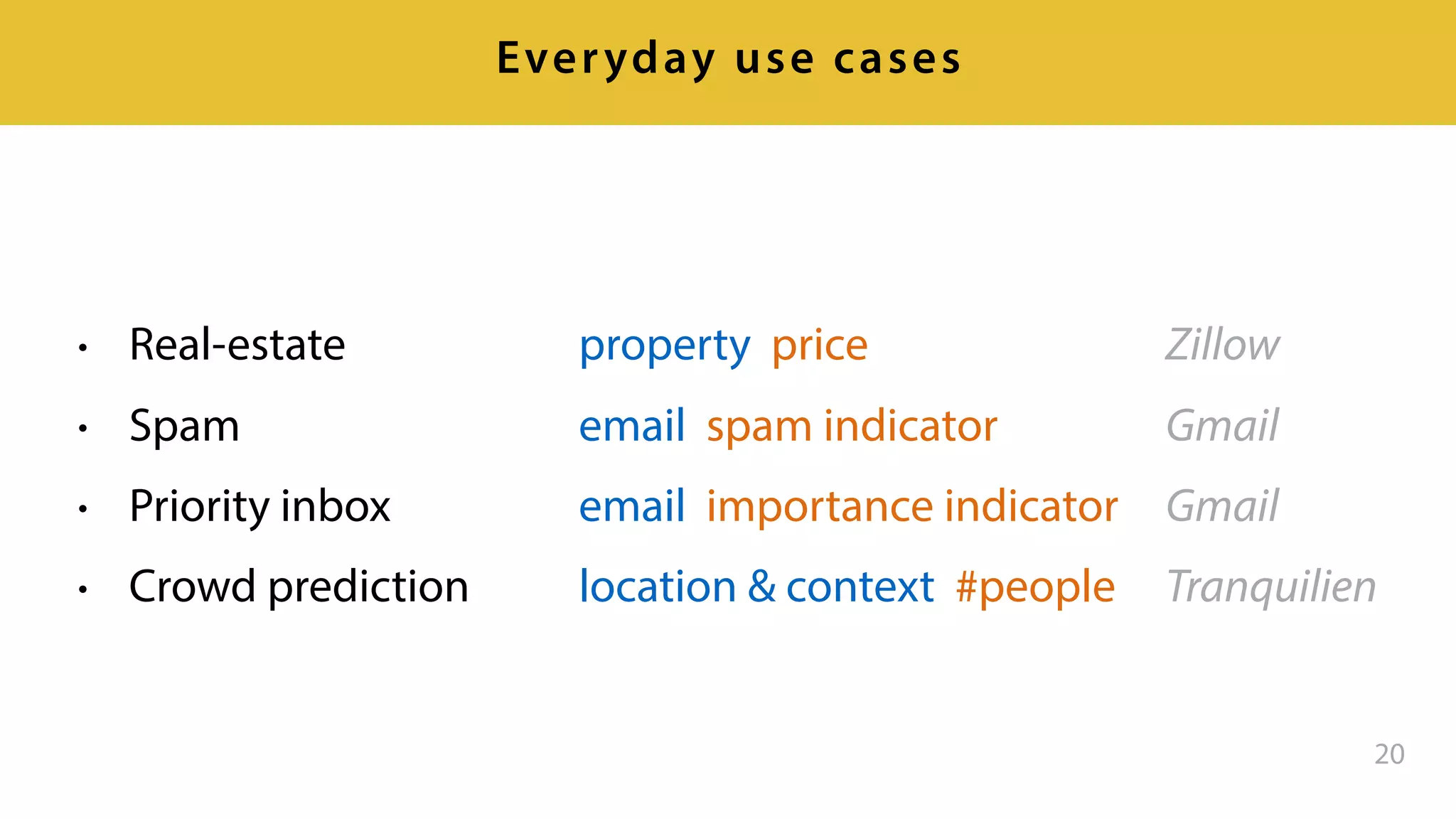
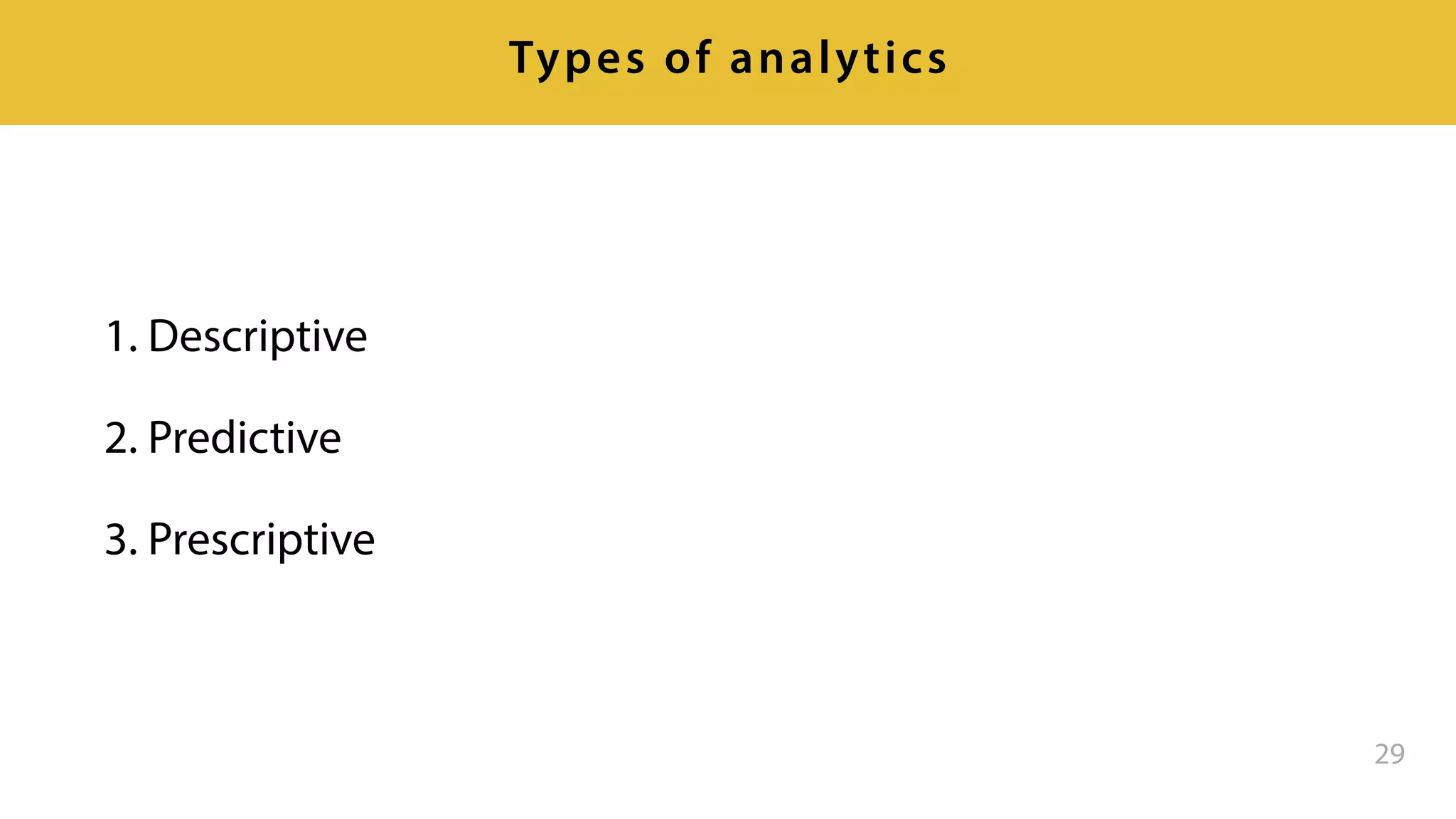
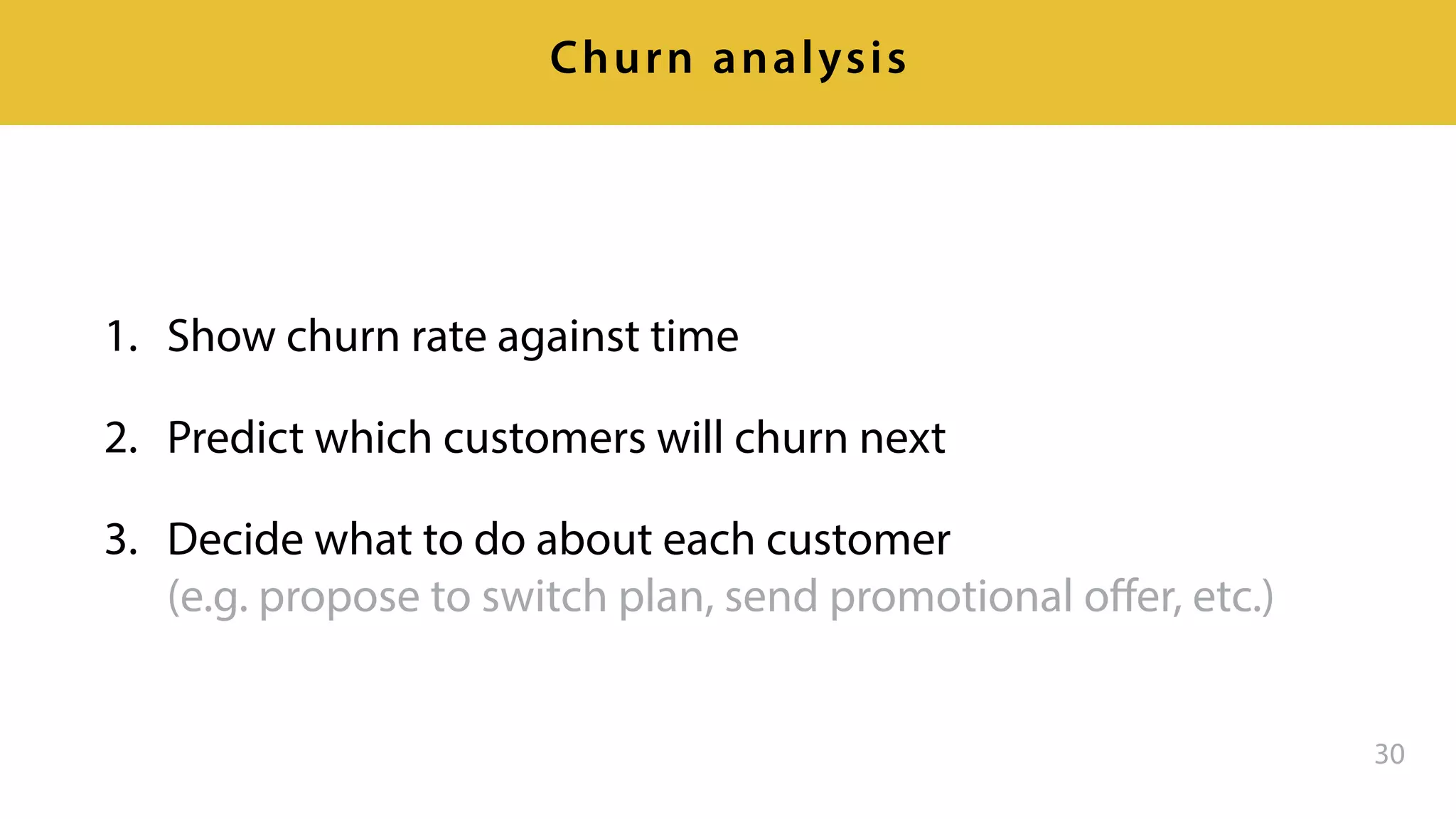
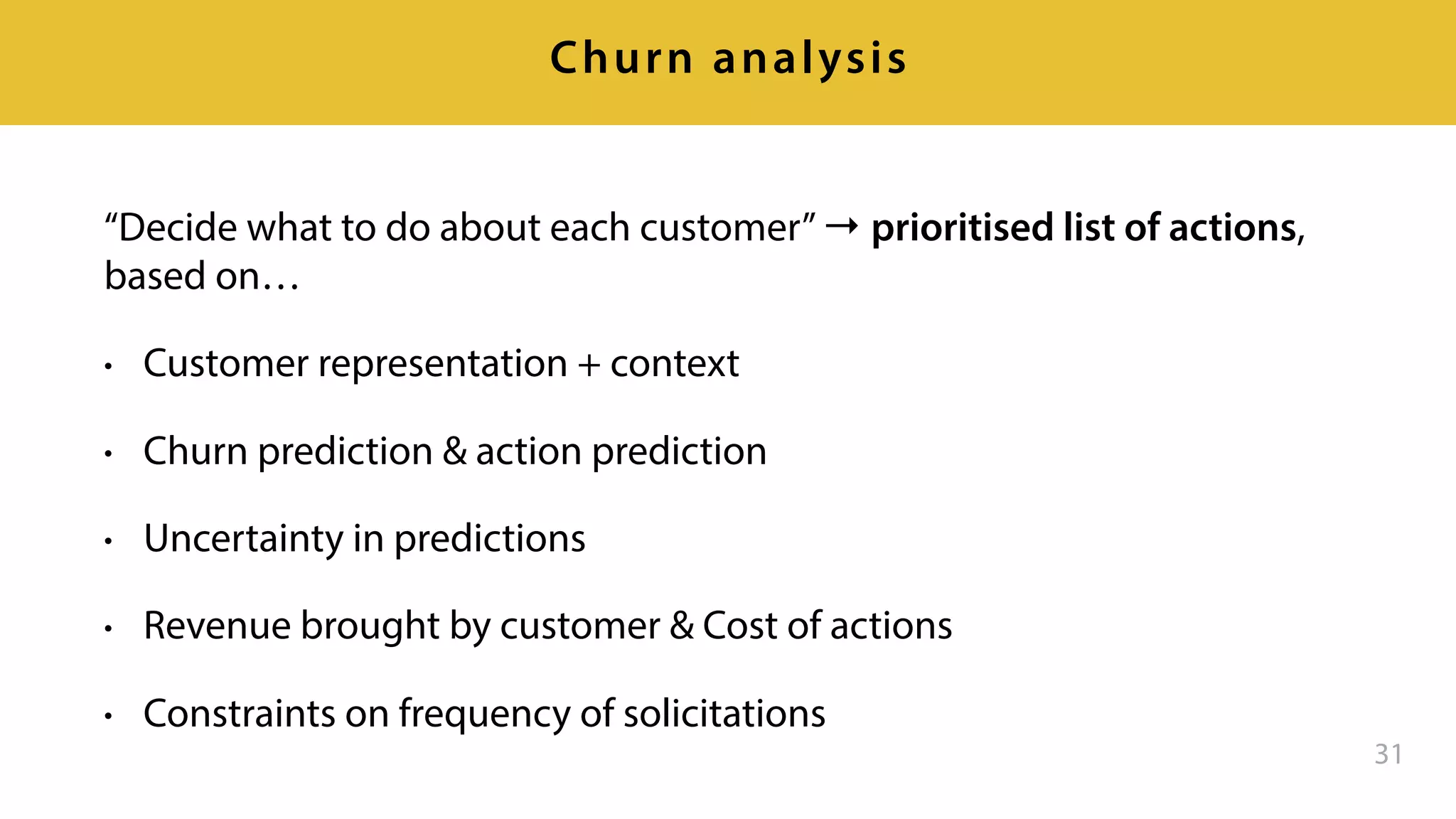
This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence and machine learning. It discusses how machine learning works using data and examples to build intelligence. Examples of everyday and business uses of machine learning are presented, such as predicting property prices, email spam detection, and demand forecasting. The document outlines the types of analytics that can be performed, from descriptive to predictive to prescriptive. It also discusses how machine learning models are developed and deployed through predictive APIs.
















![1. Show past demand against calendar
2. Predict demand for [product] at [store] in next 2 days
3. Decide how much to ship
• Trade-off: cost of storage vs risk of lost sales
• Constraints on order size, truck volume, capacity of people
putting stuff into shelves
32
Replenishment](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abusinesslevelintroductiontoai-16vlc-160314160149/75/A-business-level-introduction-to-Artificial-Intelligence-Louis-Dorard-PAPIs-Connect-32-2048.jpg)